Abstract
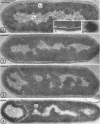
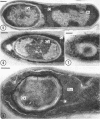
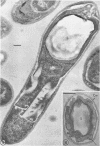
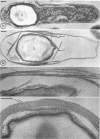
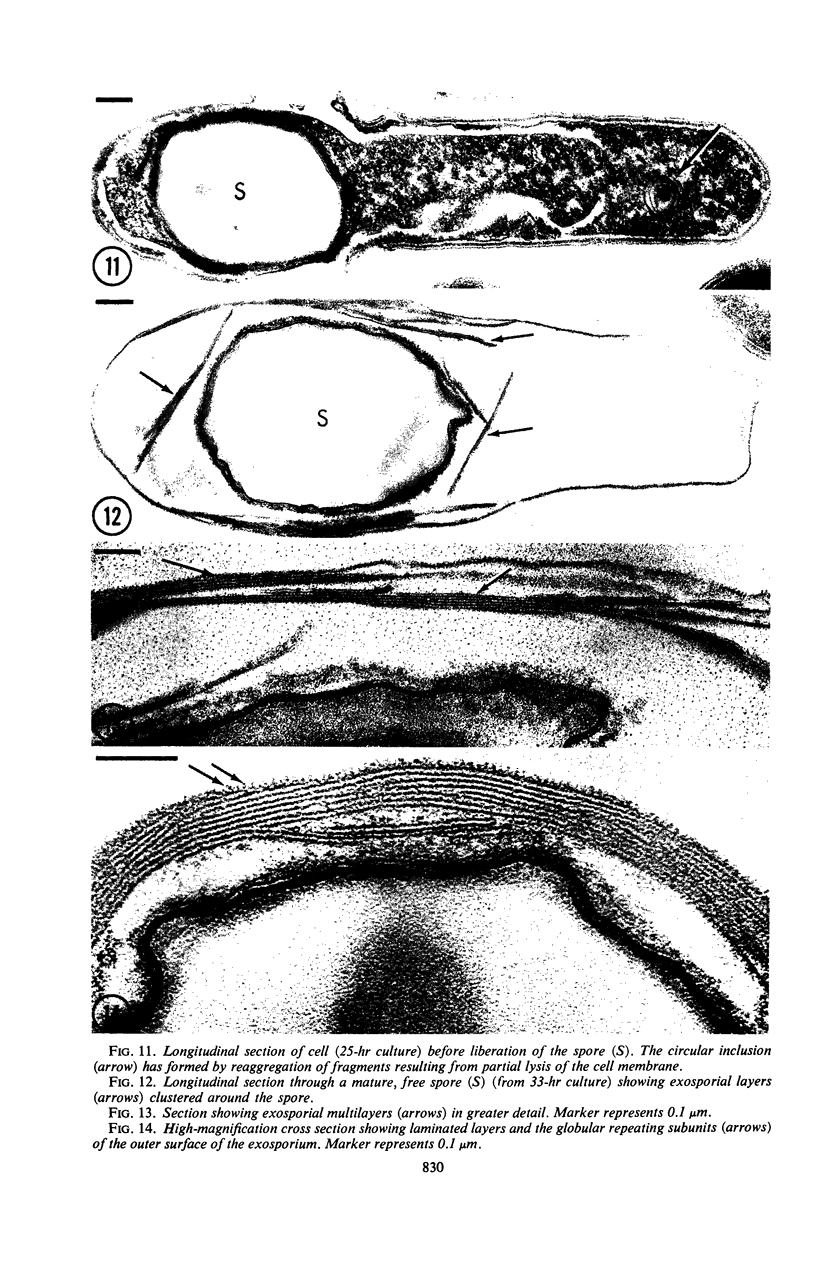
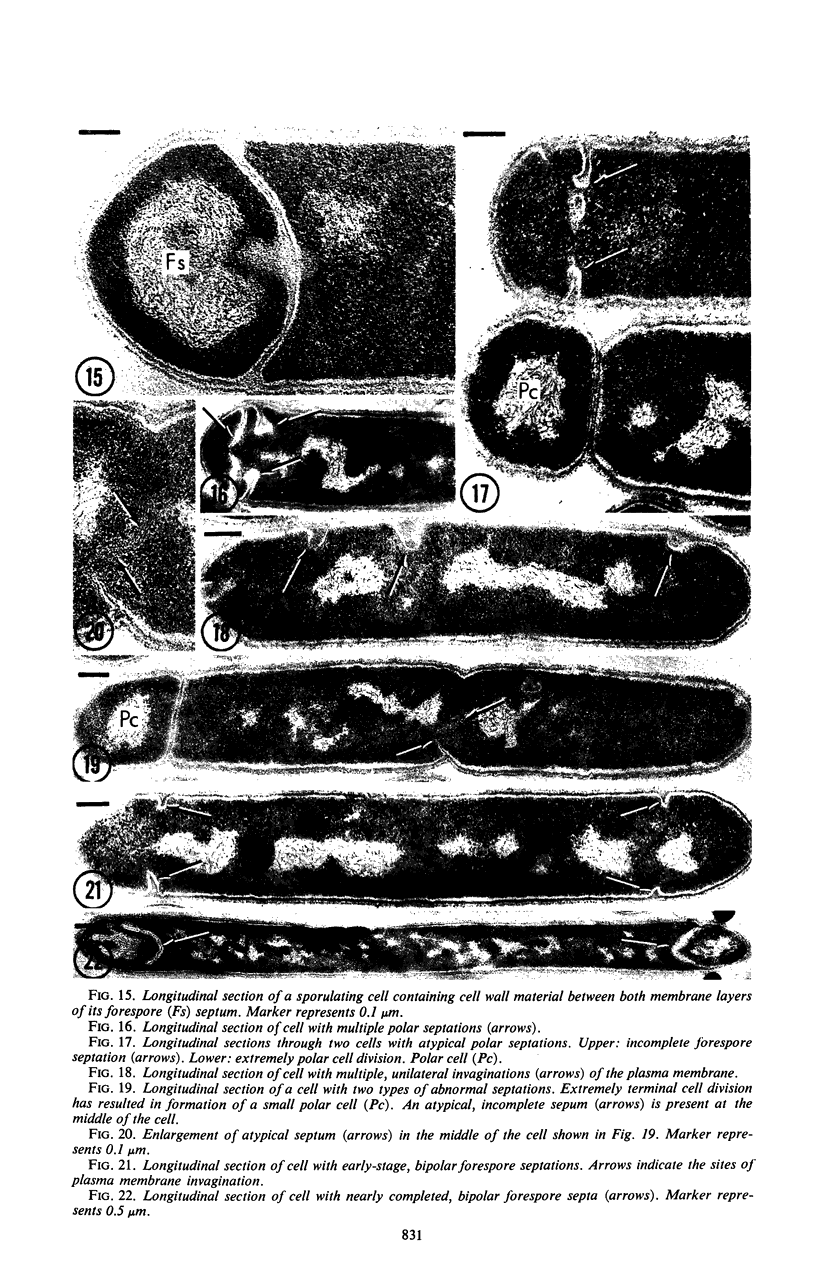
Sporulation of putrefactive anaerobe 3679h was studied by observation of ultra-thin sections in the electron microscope. The customary stages were observed during forespore formation, spore maturation, and liberation of the free spore. The exosporium was partially laminated and devoid of the hairlike surface projections observed on spores of some species. Atypical membrane configurations occurred in some cells, and, occasionally, cells with bipolar forespores were found.
Full text
PDF

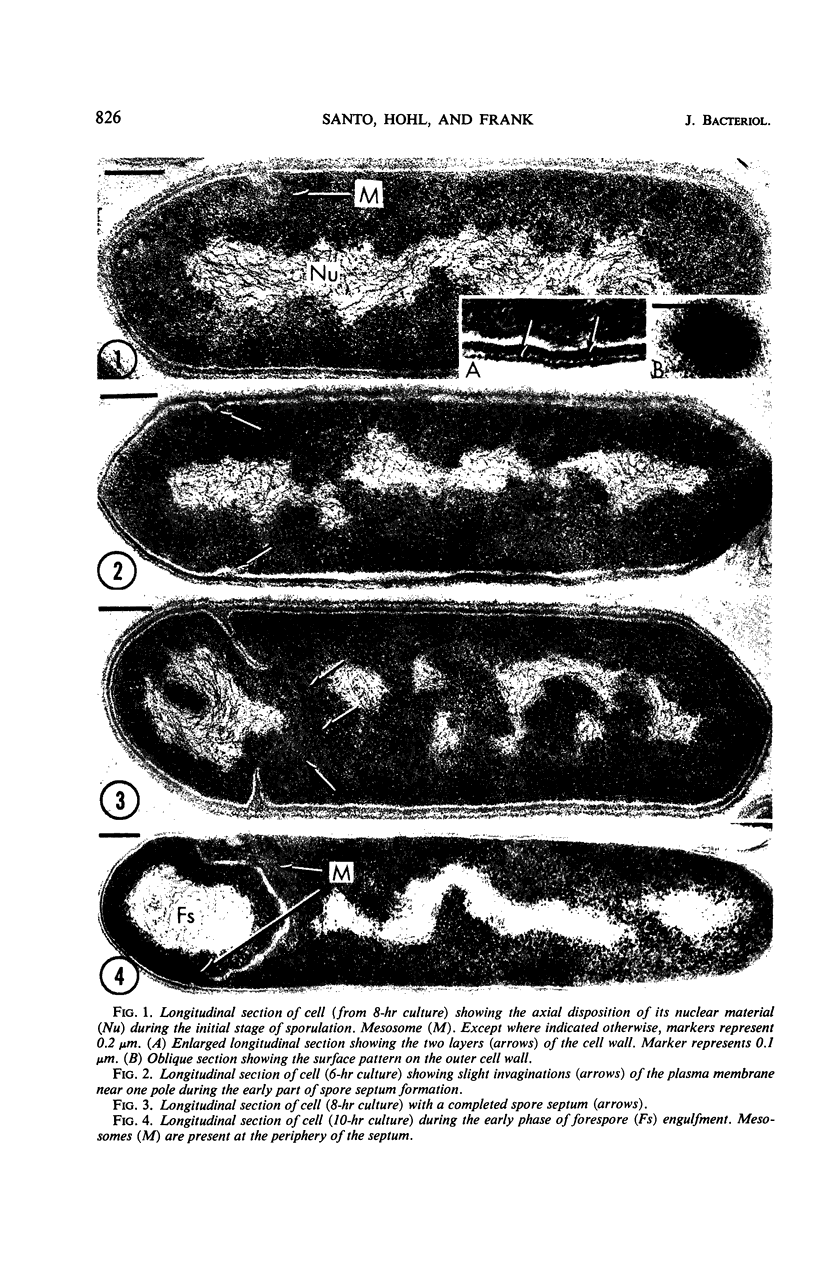
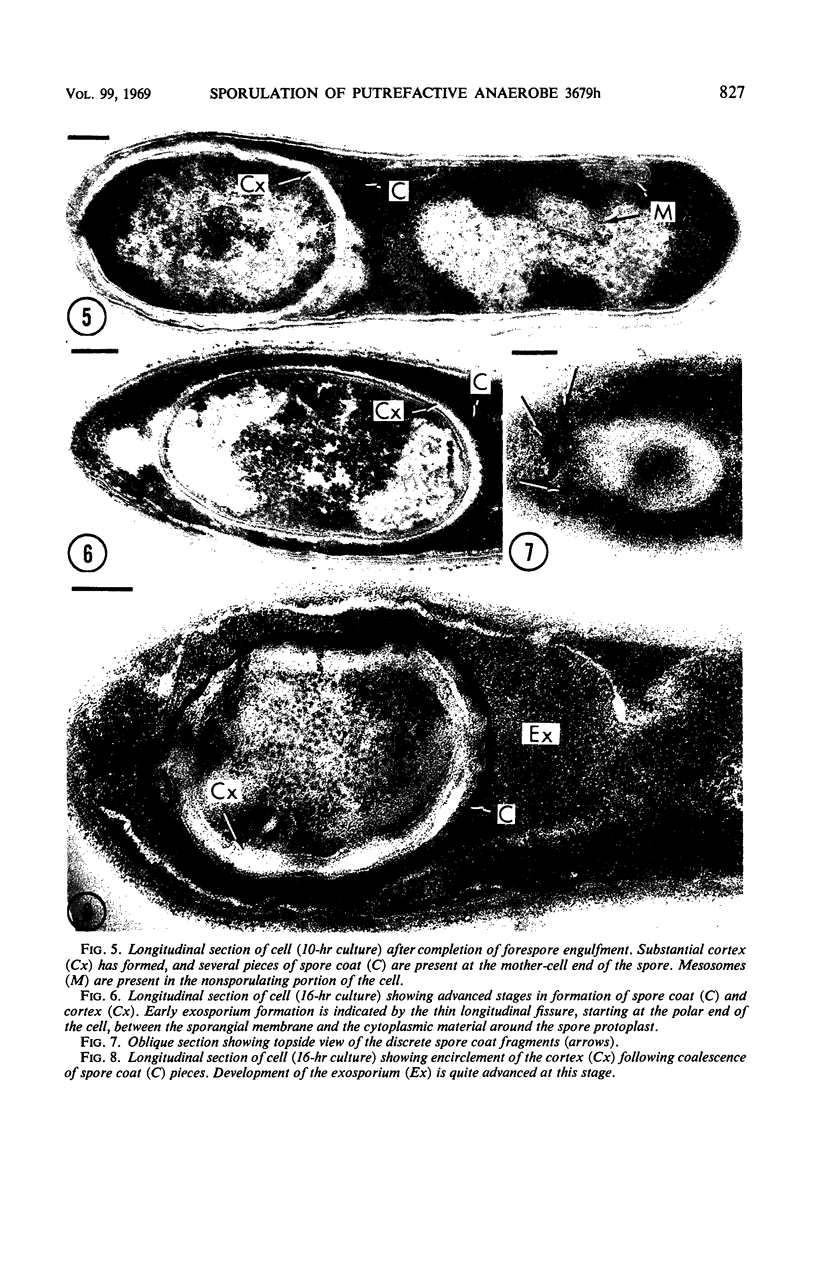
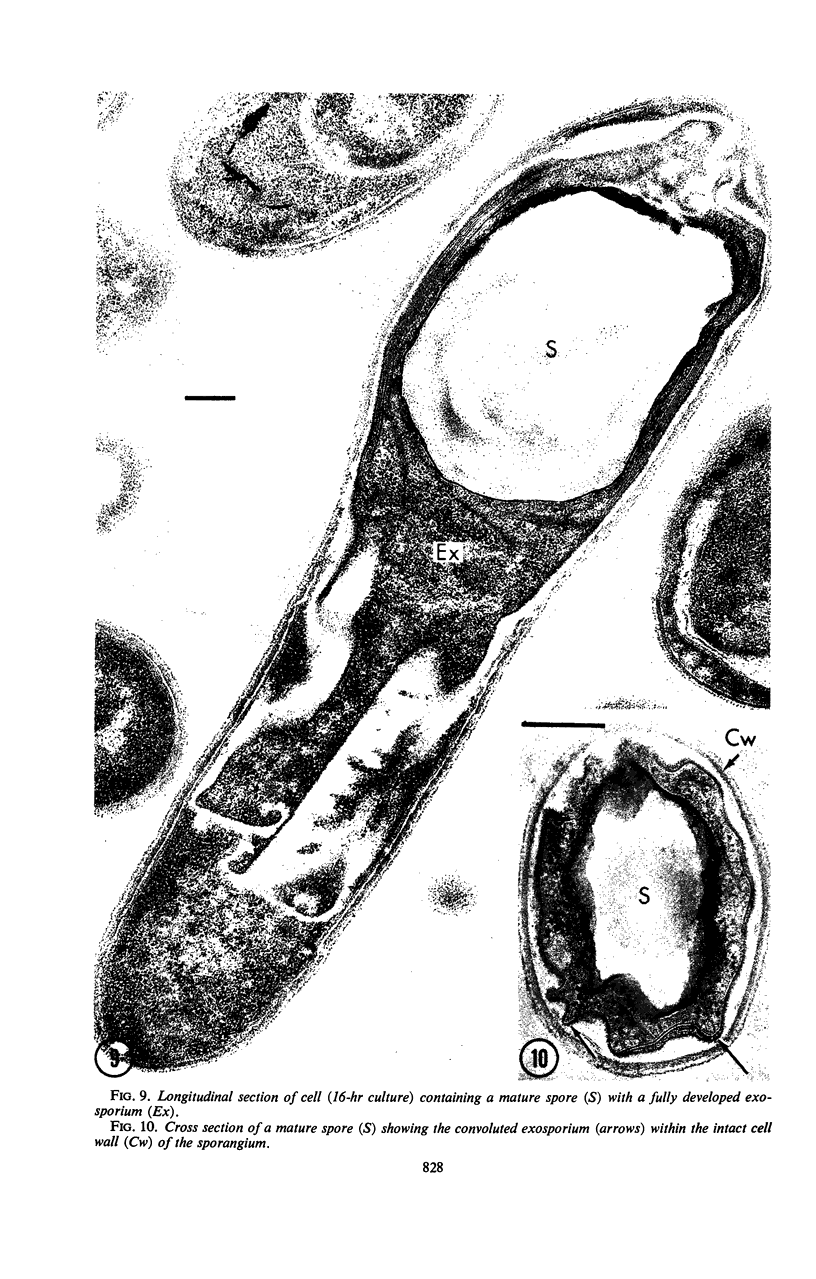



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPMAN G. B., HILLIER J. Electron microscopy of ultra-thin sections of bacteria I. Cellular division in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):362–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.362-373.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellar D. J., Lundgren D. G. Fine structure of sporulation in Bacillus cereus grown in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1748–1764. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1748-1764.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. C. Participation of the cytoplasmic membrane in the growth and spore fromation of bacilli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:507–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz-James P. C. MORPHOLOGY OF SPORE DEVELOPMENT IN CLOSTRIDIUM PECTINOVORUM. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84(1):104–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.1.104-114.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka R. S., Frank H. A. Nutritional requirements for germination, outgrowth, and vegetative growth of putrefactive anaerobe 3679 in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1515-1520.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., RIBI E. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE EXOSPORIUM ENVELOPING SPORES OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1774–1789. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1774-1789.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachisuka Y., Kojima K., Sato T. Fine filaments on the outside of the exosporium of Bacillus anthracis spores. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2382–2384. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2382-2384.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkiss W., Ordal Z. J., Cann D. C. The comparative morphology of the spores of Clostridium botulinum type E and the spores of the "OS mutant". Can J Microbiol. 1966 Dec;12(6):1283–1284. doi: 10.1139/m66-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkiss W., Ordal Z. J., Cann D. C. The morphology and ultrastructure of the spore and exosporium of some Clostridium species. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):213–225. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkiss W., Ordal Z. J. Morphology of the spore of some strains of Clostridium botulinum type E. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2031–2036. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2031-2036.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAWATA T., INOUE T., TAKAGI A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF SPORE FORMATION AND GERMINATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Jpn J Microbiol. 1963 Jun;7:23–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1963.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope L., Yolton D. P., Rode L. J. Appendages of Clostridium bifermentans spores. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1206–1215. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1206-1215.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A. ETUDE MORPHOLOGIQUE DE LA SPORULATION DE BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jan;108:40–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Lundgren D. G. Multiple septation in variants of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1426–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1426-1431.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Schaeffer P., Ionesco H. Classification cytologique, par leur stade de blocage, des mutants de sporulation de Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T. Electron microscopic aspects of membrane alterations during bacterial cell lysis. Exp Cell Res. 1967 May;46(2):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI A., KAWATA T., YAMAMOTO S. Electron microscope studies on ultrathin sections of spores of the Clostridium group, with special reference to the sporulation and germination process. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jul;80:37–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.1.37-46.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI A., KAWATA T., YAMAMOTO S., KUBO T., OKITA S. Electron microscopic studies on ultrathin sections of spores of Clostridium tetani and Clostridium histolyticum, with special reference to sporulation and spore germination process. Jpn J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;4:137–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1960.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOKUYASU K., YAMADA E. Fine structure of Bacillus subtilis. II. Sporulation progress. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):129–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi A., Nakamura K., Ueda M. Electron microscope studies of the intracytoplasmic membrane system in Clostridium tetani and Clostridium botulinum. Jpn J Microbiol. 1965 Sep;9(3):131–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1965.tb00282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UEHARA M., FUJIOKA R. S., FRANK H. A. METHOD FOR OBTAINING CLEANED PUTREFACTIVE ANAEROBE 3679 SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:929–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.929-930.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara M., Frank H. A. Sequence of events during germination of putrefactive anaerobe 3679 spores. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):506–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.506-511.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. E. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN ABORTIVELY DISPORIC VARIANT OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:242–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.242-254.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]