Abstract
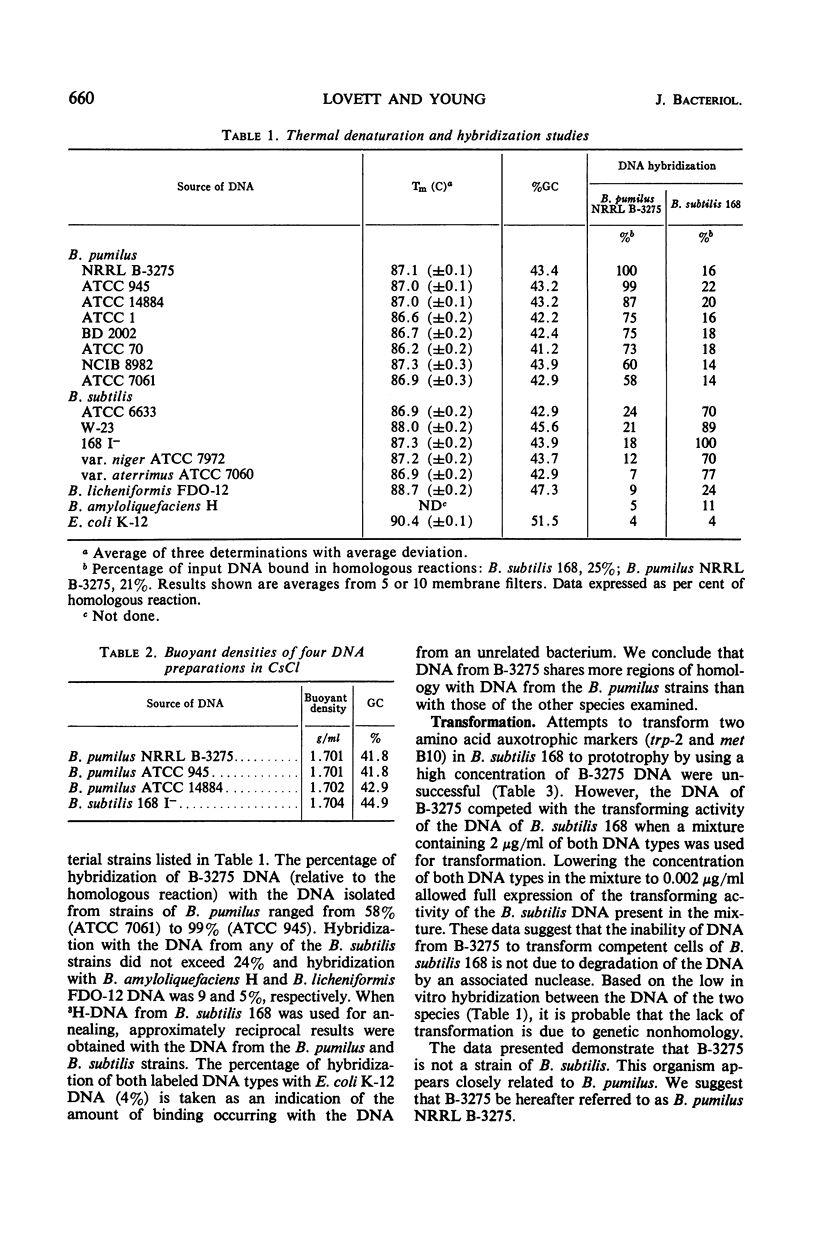
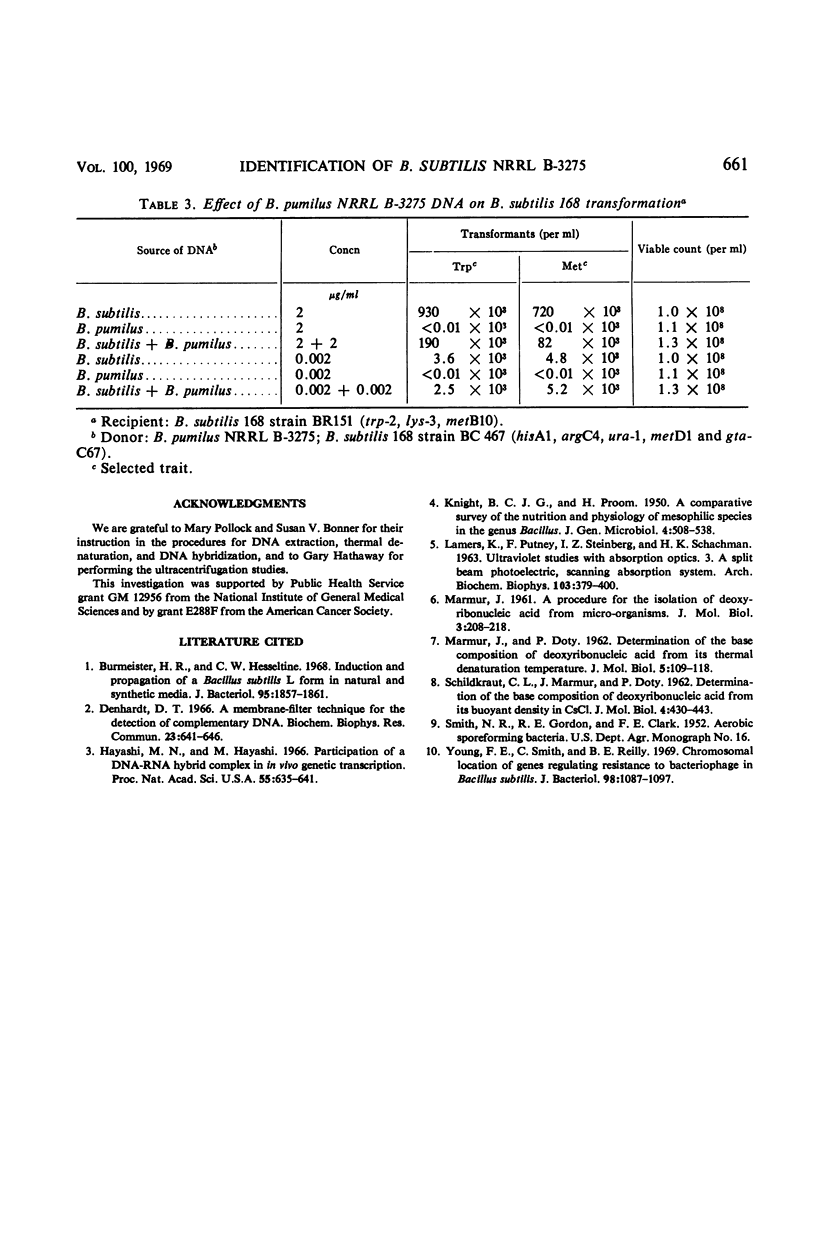
The physiological and biochemical properties of a species of Bacillus previously identified as B. subtilis NRRL B-3275 (B-3275) were compared with those of seven strains of B. pumilus and five strains of B. subtilis. The biotin requirement of B-3275, its inability to hydrolyze starch, and its failure to reduce nitrate indicate that the organism is more closely related to the B. pumilus strains than to those of B. subtilis. Hybridization of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from B-3275 with that of the strains of B. pumilus showed a binding efficiency (compared with the homologous reaction) of 58 to 99%, depending on the strain. Hybridization with the DNA from any of the strains of B. subtilis did not exceed 24%. DNA from B-3275 was unable to transform two amino acid auxotrophic markers to prototrophy in a highly competent strain of B. subtilis 168. We conclude that B-3275 is a strain of B. pumilus which we designate as B. pumilus NRRL B-3275.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burmeister H. R., Hesseltine C. W. Induction and propagation of a Bacillus subtilis L form in natural and synthetic media. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1857–1861. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1857-1861.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. Participation of a DNA-RNA hybrid complex in in vivo genetic transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):635–641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT B. C. J. G., PROOM H. A comparative survey of the nutrition and physiology of mesophilic species in the genus Bacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):508–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMERS K., PUTNEY F., STEINBERG I. Z., SCHACHMAN H. K. ULTRACENTRIFUGE STUDIES WITH ABSORPTION OPTICS. 3. A SPLIT-BEAM PHOTOELECTRIC, SCANNING ABSORPTION SYSTEM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Dec;103:379–400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E., Smith C., Reilly B. E. Chromosomal location of genes regulating resistance to bacteriophage in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1087–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1087-1097.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



