Abstract
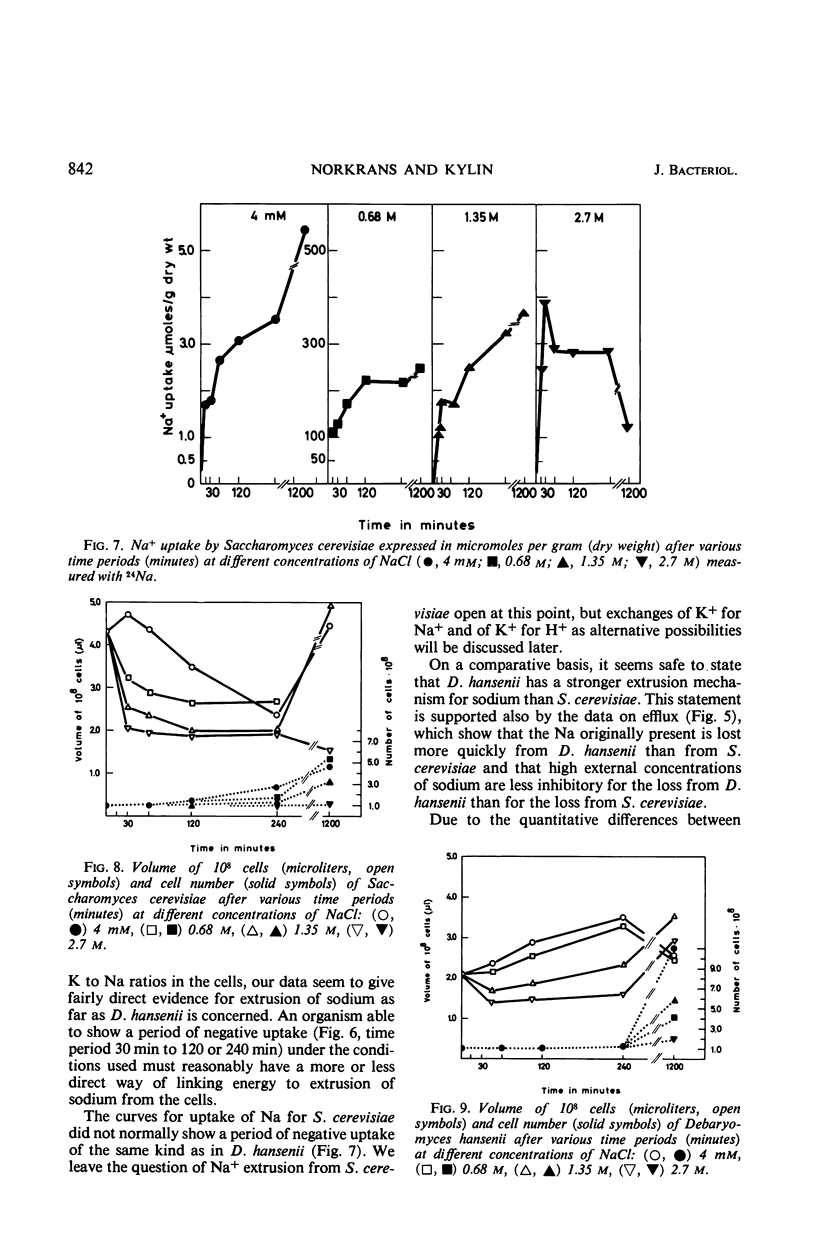
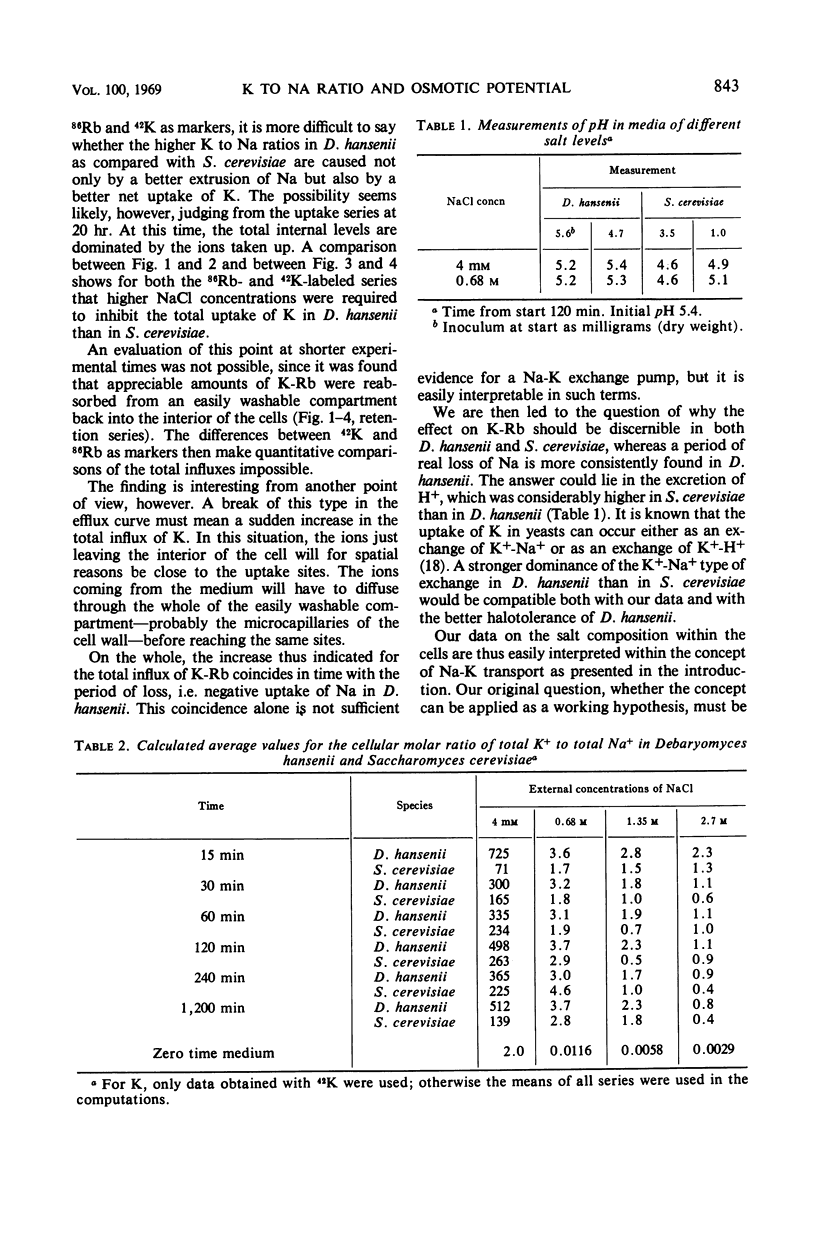
By using the isotope pairs 22Na-24Na and 42K-86Rb, the uptake and retention of Na and K was studied in the salt-tolerant Debaryomyces hansenii and in the less tolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae at NaCl levels of 4 mm and 0.68, 1.35, and 2.7 m in the medium. The ratio of K to Na is much higher in the cells than in the media, and higher in D. hansenii than in S. cerevisiae under comparable conditions. The difference between the two species is due to a better Na extrusion and a better uptake of K in D. hansenii. The kinetics of ion transport show that at about the time when extrusion of Na could be demonstrated in D. hansenii, K-Rb previously lost to an easily washable compartment of the cells was reabsorbed in both organisms. More H+ was given off from S. cerevisiae than from D. hansenii in the course of these events. The findings fit the working hypothesis tested, which regards salt tolerance as partly dependent on the ability to mobilize energy to extrude Na from the cells and to take up K. The volume changes in S. cerevisiae are greater and are more slowly overcome than those in D. hansenii. The total salt level of the cells is not sufficient to counteract the osmotic potential of the medium, so that additional osmoregulatory mechanisms must be involved in determining halotolerance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber J. Measurement of the membrane potential and evidence for active transport of ions in Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 11;150(4):618–625. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway E. J., Gaffney H. M. The further preparation of inorganic cationic yeasts and some of their chief properties. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):385–391. doi: 10.1042/bj1010385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylin A. Uptake and loss of Na, Rb, and Cs in relation to an active mechanism for extrusion of Na in Scenedesmus. Plant Physiol. 1966 Apr;41(4):579–584. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.4.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod J. G. The nutrition of the halophilic mould Sporendonema epizoum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Feb 1;56(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00406052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafaeli-Eshkol D. Studies on halotolerance in a moderately halophilic bacterium. Effect of growth conditions on salt resistance of the respiratory system. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):679–685. doi: 10.1042/bj1090679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


