Abstract
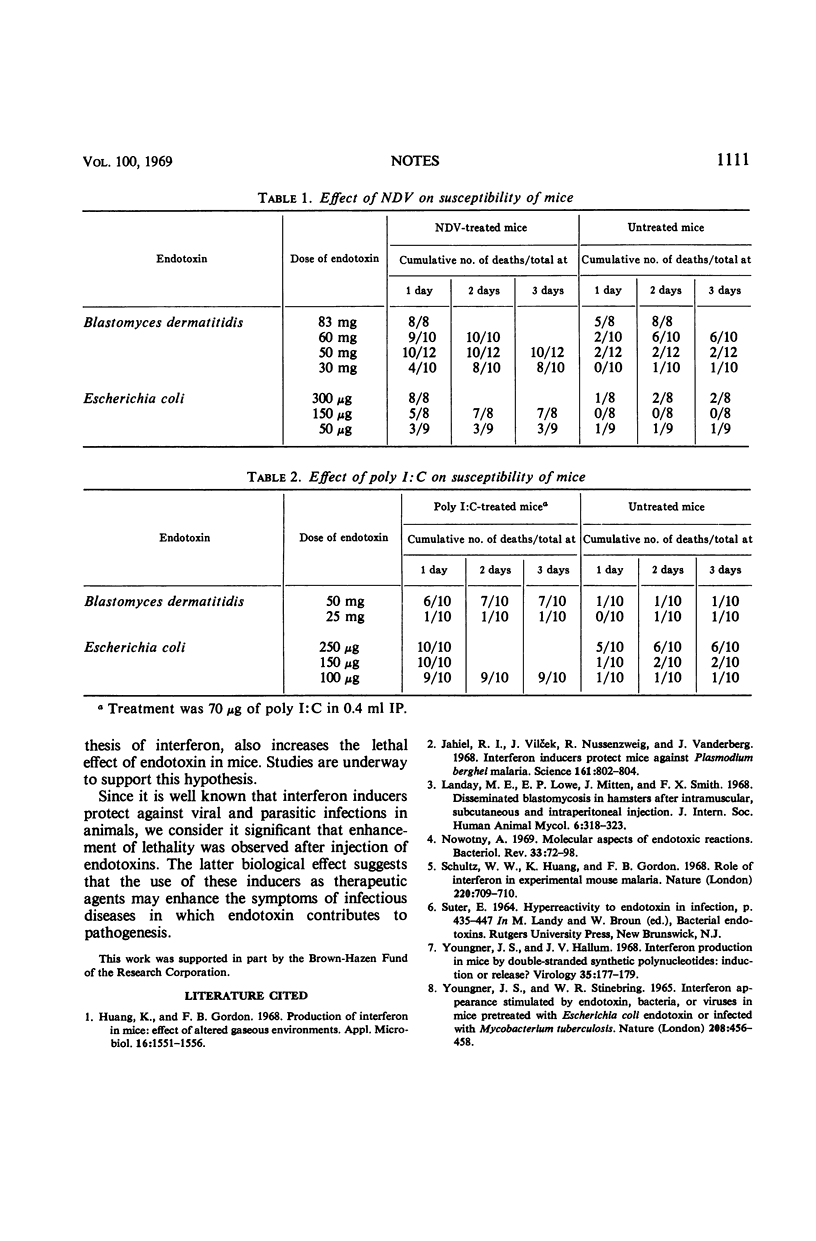
Prior treatment of mice with poly I:C or NDV enhanced the lethal effect of E. coli or B. dermatitidis endotoxins.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Production of interferon in mice: effect of altered gaseous environments. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1551–1556. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1551-1556.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R., Vanderberg J. Interferon inducers protect mice against plasmodium berghei malaria. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay M. E., Lowe E. P., Mitten J., Smith F. X. Disseminated blastomycosis in hamsters after intramuscular, subcutaneous and intraperitoneal injection. Sabouraudia. 1968 Oct;6(4):318–323. doi: 10.1080/00362176885190621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A. Molecular aspects of endotoxic reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Mar;33(1):72–98. doi: 10.1128/br.33.1.72-98.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz W. W., Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Role of interferon in experimental mouse malaria. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):709–710. doi: 10.1038/220709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Hallum J. V. Interferon production in mice by double-stranded synthetic polynucleotides: induction or release? Virology. 1968 May;35(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R. Interferon appearance stimulated by endotoxin, bacteria, or viruses in mice pre-treated with Escherichia coli endotoxin or infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature. 1965 Oct 30;208(5009):456–458. doi: 10.1038/208456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



