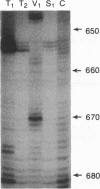
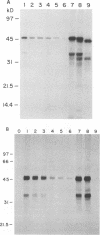
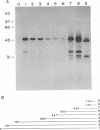
Abstract
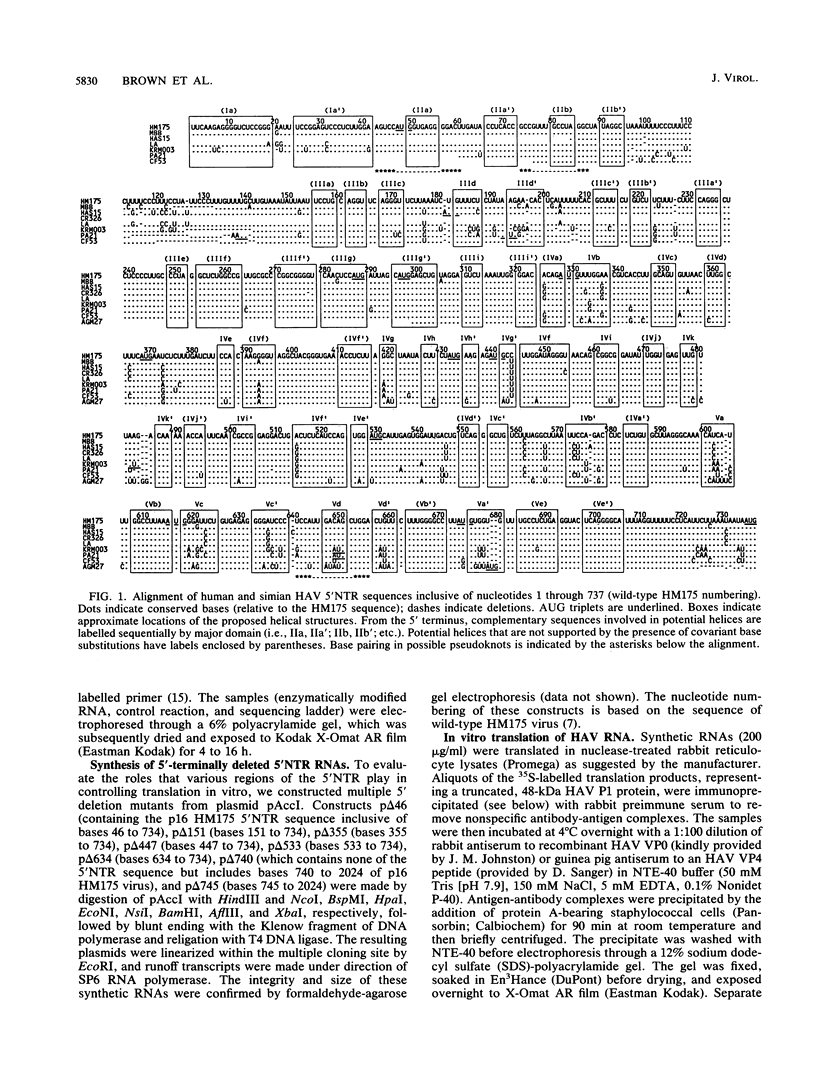
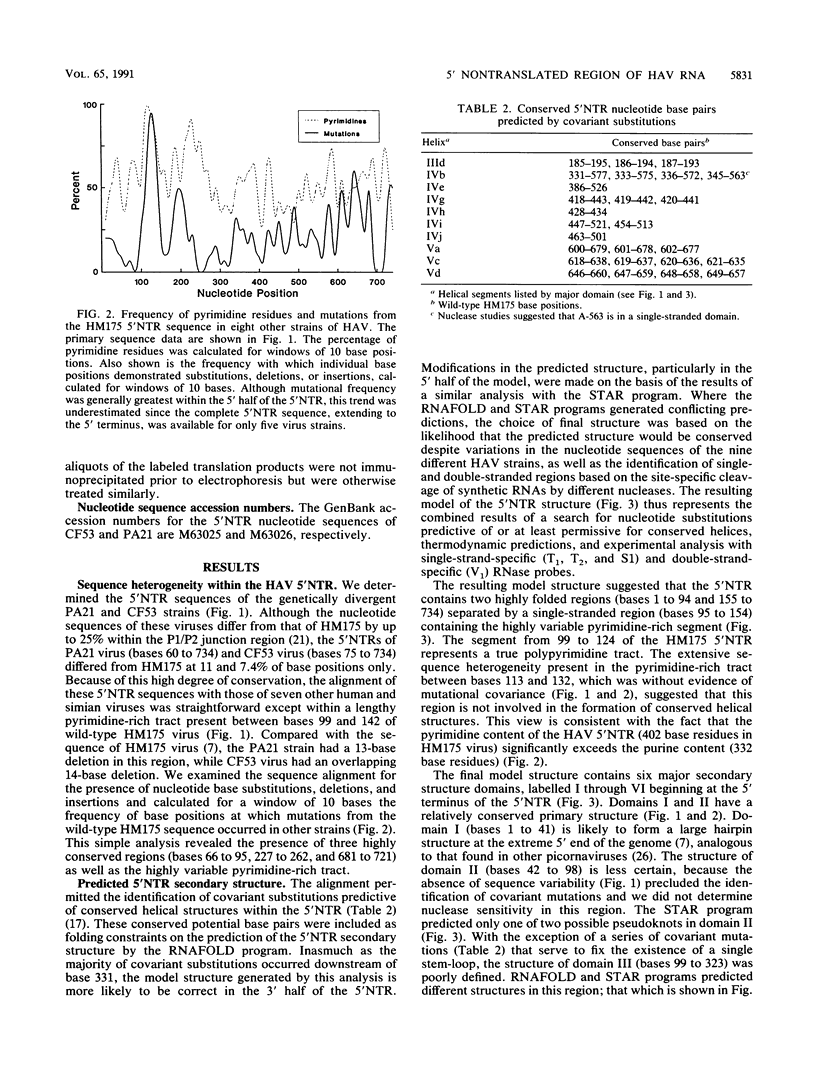
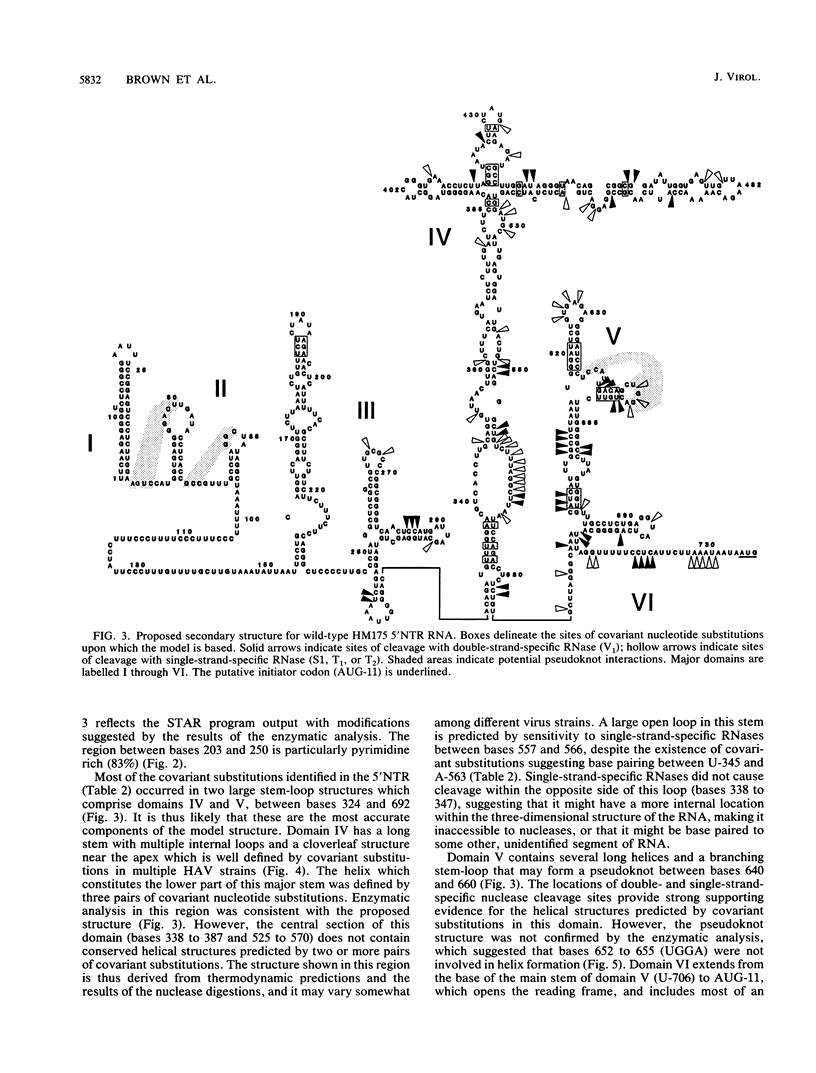
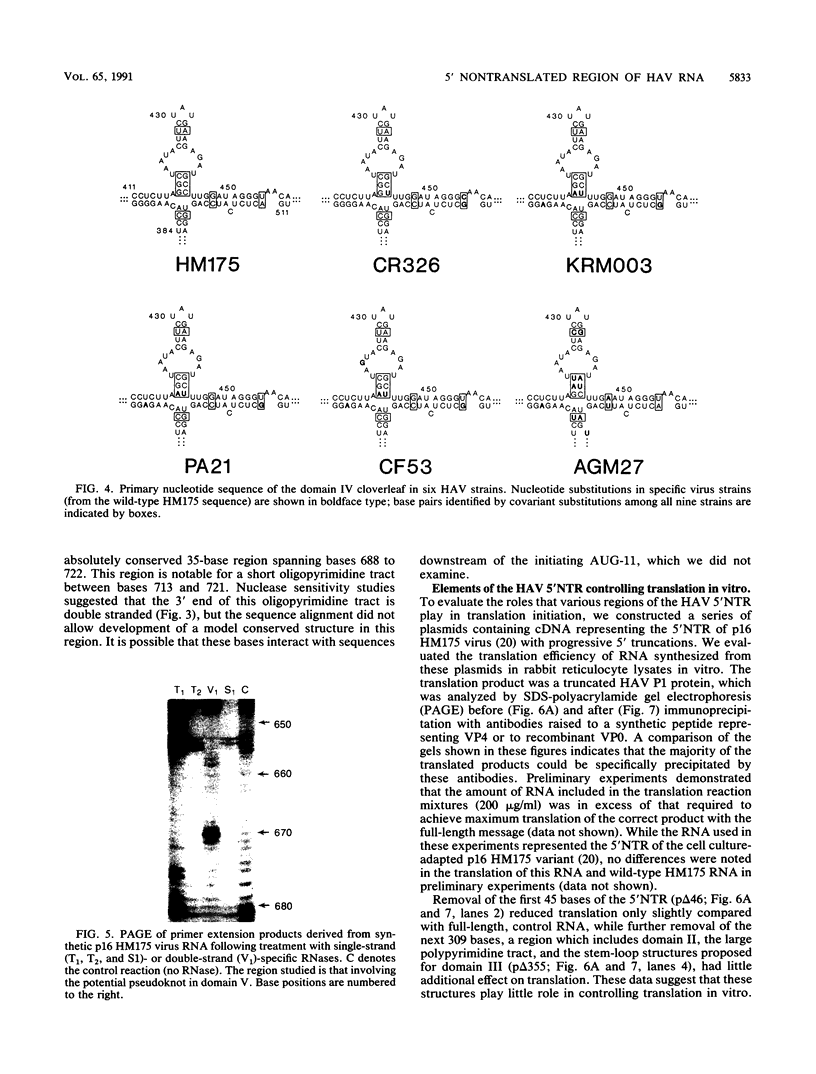
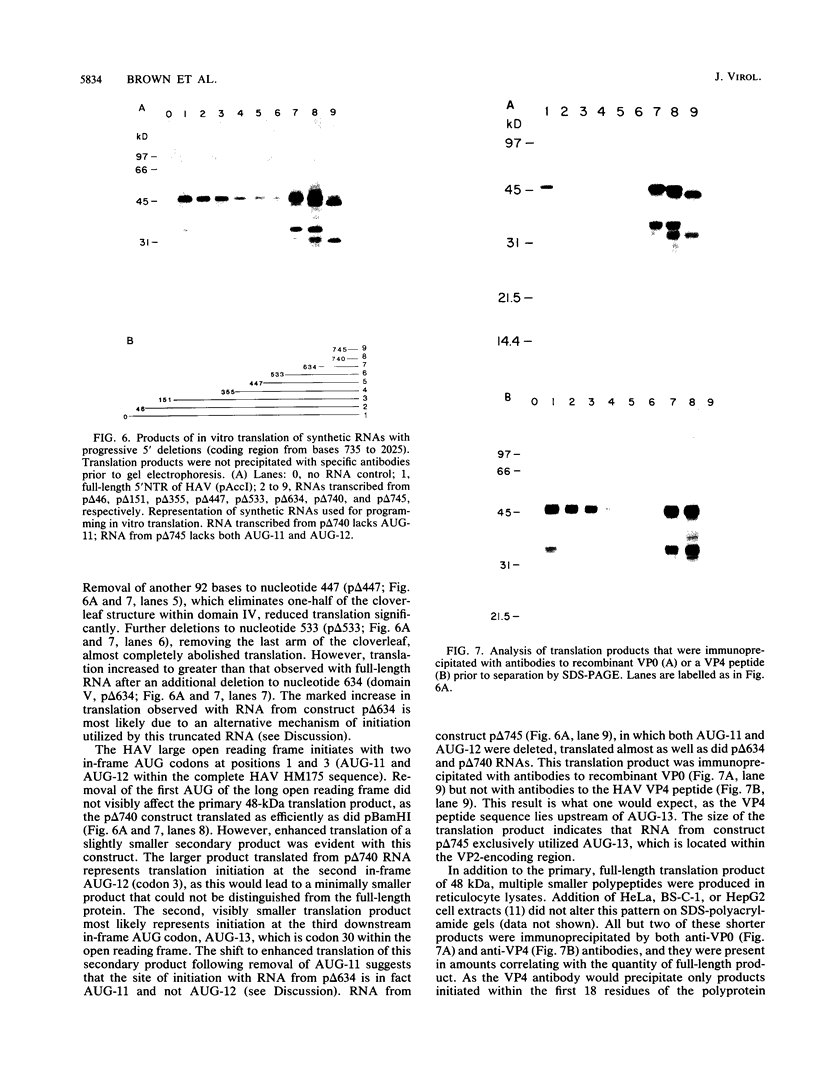
Although the lengthy 5' nontranslated regions (5'NTRs) of other picornaviral RNAs form highly ordered structures with important functions in viral translation, little is known about the 5'NTR of hepatitis A virus (HAV). We determined the nearly complete 5'NTR nucleotide sequences of two genetically divergent HAV strains (PA21 and CF53) and included these data in a comparative phylogenetic analysis of the HAV 5'NTR. We identified covariant nucleotide substitutions predictive of conserved secondary structures and used this information to develop a model of the 5'NTR secondary structure, which was further refined by thermodynamic predictions and nuclease digestion experiments. According to this model, the 5'NTR comprises six major structural domains. Domains I and II (bases 1 to 95) contain a 5'-terminal hairpin and two stem-loops followed by a single-stranded and highly variable pyrimidine-rich tract (bases 96 to 154). The remainder of the 5'NTR (domains III to VI, bases 155 to 734) contains several complex stem-loops, one of which may form a pseudoknot, and terminates in a highly conserved region containing an oligopyrimidine tract preceding the putative start codon by 13 bases. To determine which structural elements might function as an internal ribosome entry site, RNA transcripts representing the HAV 5'NTR with progressive 5' deletions were translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. The translation product was truncated, unprocessed P1 polyprotein. Removal of the 5'-terminal 354 bases of the 5'NTR had little effect on translation. However, deletion to base 447 slightly decreased translation, while deletion to base 533 almost completely abolished it. These data indicate that sequences 3' of base 355 play an important role in the translation mechanism utilized by genomic-length HAV RNA. Significantly, this region shares several conserved structural features with the internal ribosome entry site element of murine encephalomyocarditis virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams J. P., van den Berg M., van Batenburg E., Pleij C. Prediction of RNA secondary structure, including pseudoknotting, by computer simulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3035–3044. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90170-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Ehrenfeld E. An internal 5'-noncoding region required for translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3068–3072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3068-3072.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Jansen R. W., Lemon S. M. Characterization of a simian hepatitis A virus (HAV): antigenic and genetic comparison with human HAV. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4932–4937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4932-4937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Rosenblum B., Feinstone S. M., Ticehurst J., Purcell R. H. Attenuation and cell culture adaptation of hepatitis A virus (HAV): a genetic analysis with HAV cDNA. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5364–5370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5364-5370.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Rosenblum B., Ticehurst J. R., Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of an attenuated hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2497–2501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Cann A. J., Stanway G., Almond J. W., Currey K., Maizel J. V., Jr Increased neurovirulence associated with a single nucleotide change in a noncoding region of the Sabin type 3 poliovaccine genome. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):548–550. doi: 10.1038/314548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss-Müller V., Deinhardt F. Effect of hepatitis A virus infection on cell metabolism in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Jan;175(1):10–15. doi: 10.3181/00379727-175-41757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Dideoxy sequencing of RNA using reverse transcriptase. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:121–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic comparative analysis of RNA secondary structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:227–239. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cell culture-adapted variant of hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus with restricted capacity for in vitro replication. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Siegl G., Lemon S. M. Molecular epidemiology of human hepatitis A virus defined by an antigen-capture polymerase chain reaction method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2867–2871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Howell M. T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: the authentic initiation site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3753–3759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Carbon P. A guide for probing native small nuclear RNA and ribonucleoprotein structures. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:212–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Stable hairpin structure within the 5'-terminal 85 nucleotides of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):328–335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.328-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Martin-Gallardo A., Hughes J. V., Young A., Mitra S. W. Molecular cloning and partial sequencing of hepatitis A viral cDNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.247-255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luz N., Beck E. A cellular 57 kDa protein binds to two regions of the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81182-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. A cellular protein that binds to the 5'-noncoding region of poliovirus RNA: implications for internal translation initiation. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1026–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najarian R., Caput D., Gee W., Potter S. J., Renard A., Merryweather J., Van Nest G., Dina D. Primary structure and gene organization of human hepatitis A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2627–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Kräusslich H. G., Toyoda H., Dunn J. J., Wimmer E. Poliovirus polypeptide precursors: expression in vitro and processing by exogenous 3C and 2A proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. V., Tada H., von der Helm K., Wissel T., Kiehn R., Wimmer E., Deinhardt F. The entire nucleotide sequence of the genome of human hepatitis A virus (isolate MBB). Virus Res. 1987 Aug;8(2):153–171. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
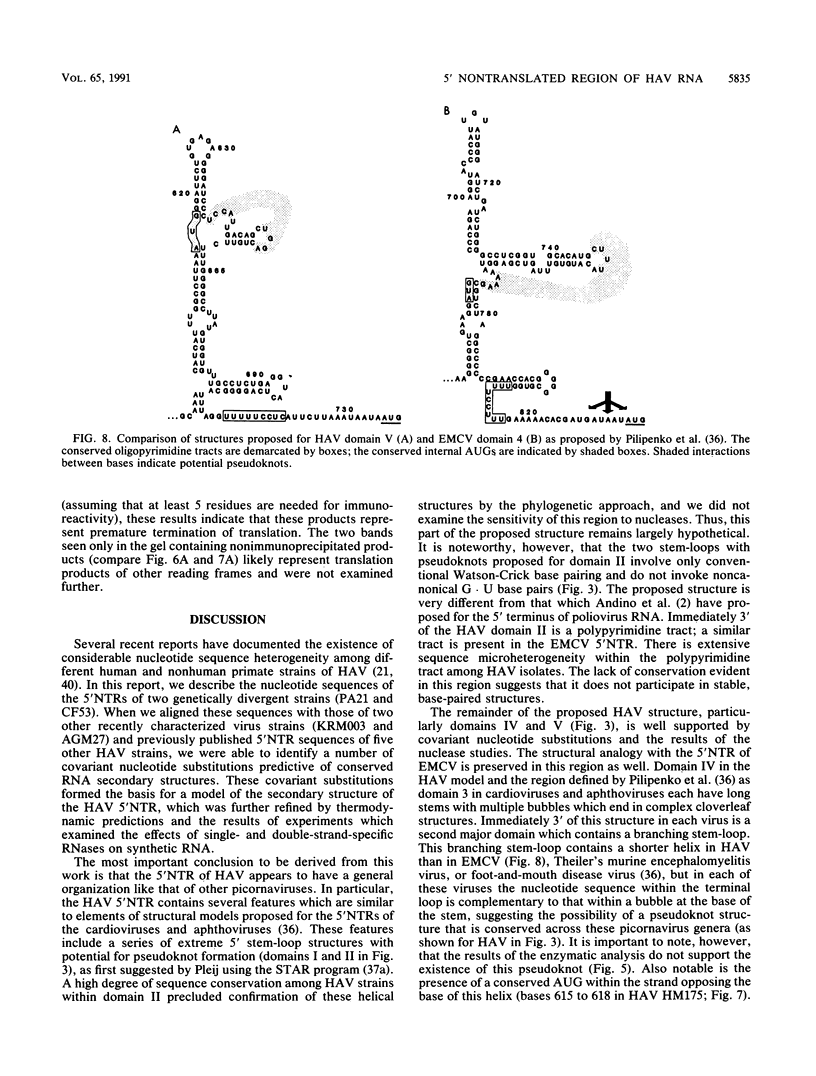
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Chernov B. K., Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V. I. Conservation of the secondary structure elements of the 5'-untranslated region of cardio- and aphthovirus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5701–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Romanova L. I., Sinyakov A. N., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Conserved structural domains in the 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes: an analysis of the segment controlling translation and neurovirulence. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Welsh J. D., Maizel J. V., Jr Comparative sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of the enteroviruses and rhinoviruses. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90656-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Anderson B. N., Edwards P. C., Gust I. D. Nucleotide sequence of high-passage hepatitis A virus strain HM175: comparison with wild-type and cell culture-adapted strains. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2805–2810. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoes E. A., Sarnow P. An RNA hairpin at the extreme 5' end of the poliovirus RNA genome modulates viral translation in human cells. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):913–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.913-921.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Racaniello V. R., Dunn G., Cooper J., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. New model for the secondary structure of the 5' non-coding RNA of poliovirus is supported by biochemical and genetic data that also show that RNA secondary structure is important in neurovirulence. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Translation in mammalian cells of a gene linked to the poliovirus 5' noncoding region. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):445–448. doi: 10.1126/science.2839901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Angel R. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Fernández-Tomás C., Silverstein S. J., Racaniello V. R. Cell proteins bind to multiple sites within the 5' untranslated region of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8299–8303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]