Abstract
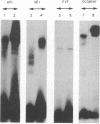
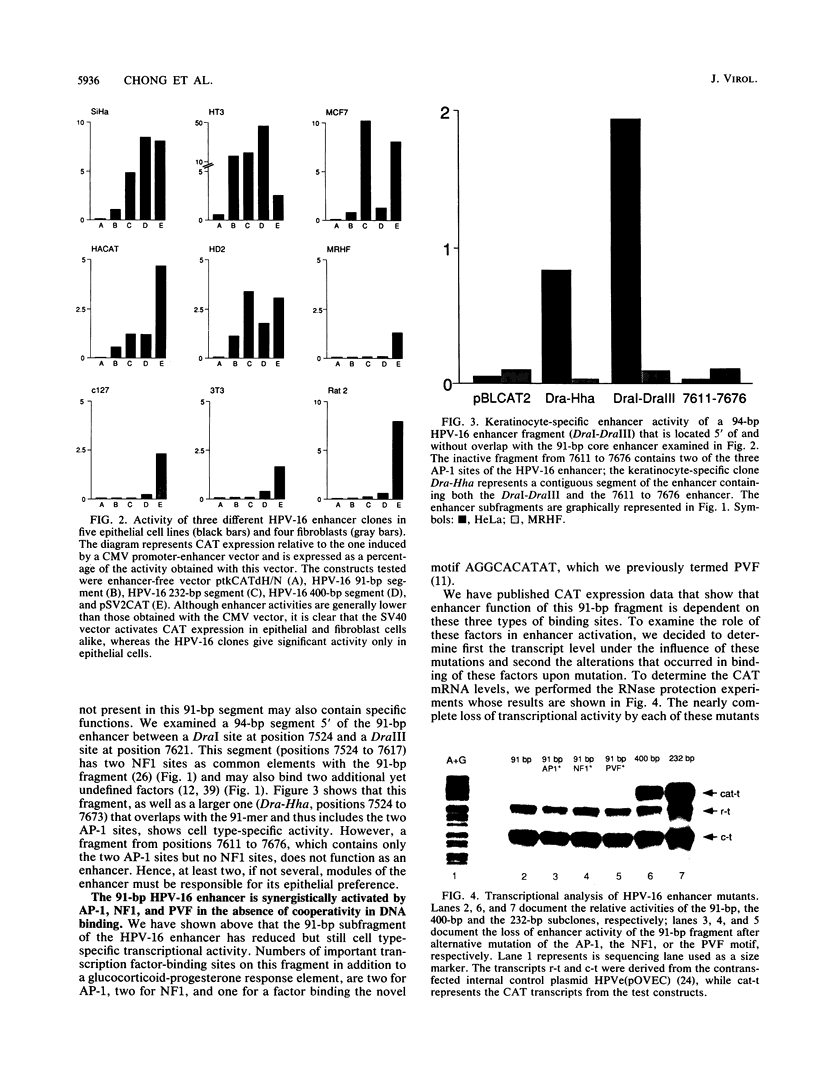
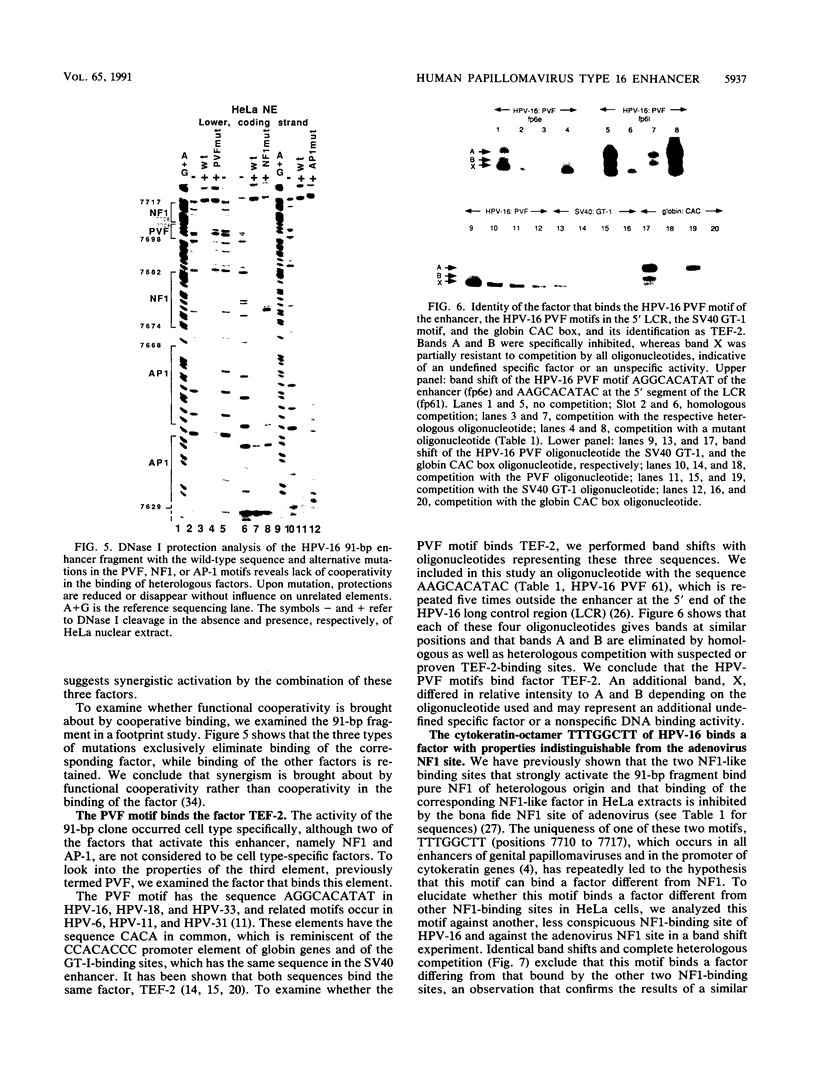
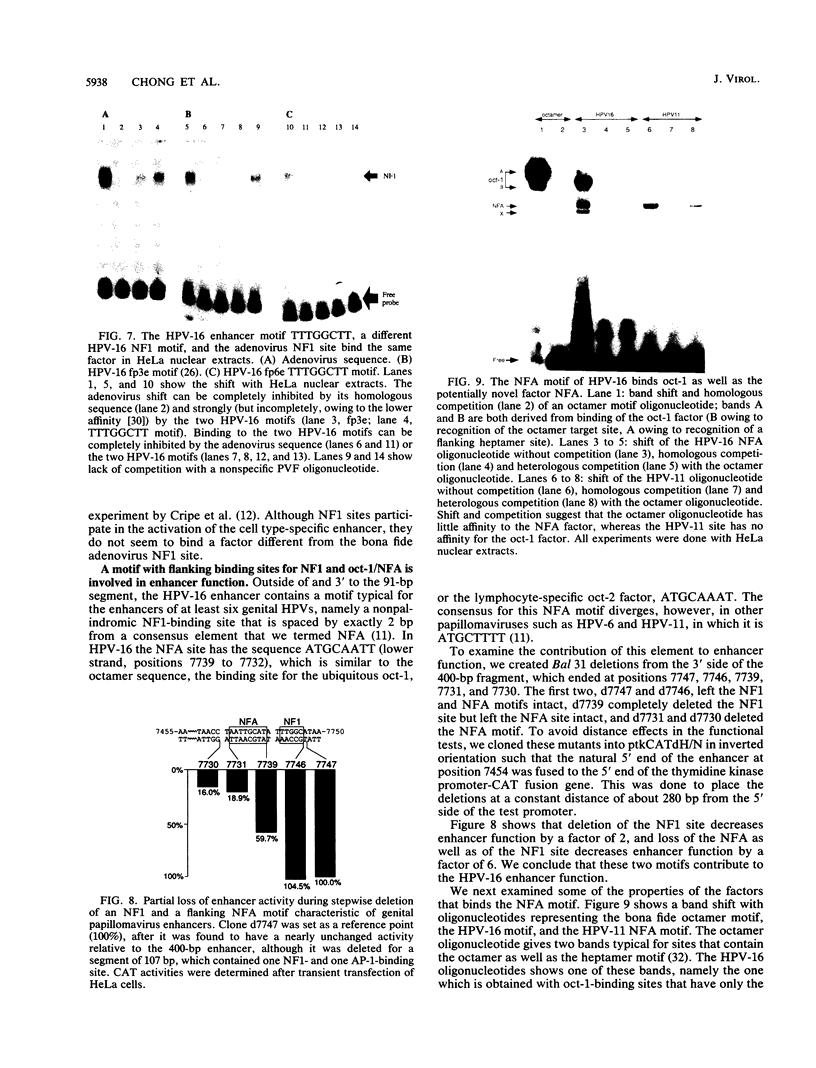
The enhancer of human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) is considered to be specific for epithelial cells, in particular for cervical carcinoma-derived cell lines. We reexamined this hypothesis with the complete enhancer as well as nonoverlapping subclones and found all clones to be active in epithelial cell lines derived from the epidermis and from carcinomas of the cervix, mammary gland, and colon, but inactive in fibroblast, lymphoma, and embryonal carcinoma cells. Although the virus infects only human mucosal epithelia, enhancer activity was independent of the exact type or of the species of origin of the transfected epithelial cell. In spite of epithelial cell specificity, we found that the activity of the HPV-16 enhancer varied strongly from a cytomegalovirus enhancer and the simian virus 40 enhancer in a cell line-dependent manner. This suggests varying quantitative contributions of enhancer elements rather than regulation by an all-or-none switch. Cell type specificity was maintained by a 91-bp subclone of the 400-bp enhancer. Most of the enhancer activity of this fragment was eliminated by alternative mutations in binding sites for the ubiquitous factors AP-1, nuclear factor 1 (NF1), or TEF-2. These three types of factors bind this 91-bp enhancer without cooperation, although activation appears to be synergistic. Outside the 91-bp fragment, a motif typical for papillomavirus enhancers, namely an octamerlike sequence flanked by an NF1-binding site, contributes to enhancer function, as the activity was strongly reduced upon its deletion. In HPV-16, this motif is bound by the oct-1 factor as well as by a probably novel factor, NFA, whereas a related motif of HPV-11 is recognized only by NFA. On examination, none of the five types of transcription factors involved in HPV enhancer activation was restricted to epithelial cells, but NF1, AP-1, and oct-1 were present in higher concentration in HeLa cells than in fibroblasts. Only NF1 showed some qualitative cell type-specific differences. We propose that the epithelial specificity of the HPV-16 enhancer is brought about via binding sites for supposed ubiquitous transcription factors. The mechanism of this activation apparently involves synergism between factors that vary in concentration and may include cell-specific functional differences residing outside the DNA-binding domain of these factors.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Oltersdorf T., Seedorf K. Expression of the human papillomavirus type 18 E7 gene by a cassette-vector system for the transcription and translation of open reading frames in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):133–138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessing M., Zentgraf H., Jorcano J. L. Differentially expressed bovine cytokeratin genes. Analysis of gene linkage and evolutionary conservation of 5'-upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):567–575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Petrussevska R. T., Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Markham A., Fusenig N. E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Chong T., Bernard H. U., Klock G. Transcription of the transforming genes of the oncogenic human papillomavirus-16 is stimulated by tumor promotors through AP1 binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):763–769. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Klock G., Bernard H. U. Progesterone and glucocorticoid response elements occur in the long control regions of several human papillomaviruses involved in anogenital neoplasia. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3261–3269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3261-3269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin M. T., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Identification of a novel constitutive enhancer element and an associated binding protein: implications for human papillomavirus type 11 enhancer regulation. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2967–2976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2967-2976.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Chan W. K., Bernard H. U. Transcriptional activation of human papillomavirus 16 by nuclear factor I, AP1, steroid receptors and a possibly novel transcription factor, PVF: a model for the composition of genital papillomavirus enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Alderborn A., Anderson R. D., Parkkinen S., Bergman P., Haugen T. H., Pettersson U., Turek L. P. Transcriptional activation of the human papillomavirus-16 P97 promoter by an 88-nucleotide enhancer containing distinct cell-dependent and AP-1-responsive modules. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):450–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Haugen T. H., Turk J. P., Tabatabai F., Schmid P. G., 3rd, Dürst M., Gissmann L., Roman A., Turek L. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6-E7 promoter by a keratinocyte-dependent enhancer, and by viral E2 trans-activator and repressor gene products: implications for cervical carcinogenesis. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3745–3753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusenig N. E., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Breitkreutz D. Phenotypic and cytogenetic characteristics of different stages during spontaneous transformation of mouse keratinocytes in vitro. Carcinog Compr Surv. 1985;9:293–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carranca A., Thierry F., Yaniv M. Interplay of viral and cellular proteins along the long control region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4321–4330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4321-4330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U., Seedorf K., Klock G. The upstream regulatory region of the human papilloma virus-16 contains an E2 protein-independent enhancer which is specific for cervical carcinoma cells and regulated by glucocorticoid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3735–3743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U. The E6/E7 promoter of human papillomavirus type 16 is activated in the absence of E2 proteins by a sequence-aberrant Sp1 distal element. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5577–5584. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5577-5584.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
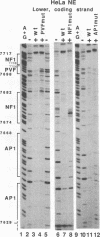
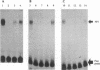
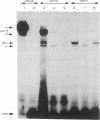
- Gloss B., Chong T., Bernard H. U. Numerous nuclear proteins bind the long control region of human papillomavirus type 16: a subset of 6 of 23 DNase I-protected segments coincides with the location of the cell-type-specific enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1142–1152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1142-1152.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Yeo-Gloss M., Meisterenst M., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Bernard H. U. Clusters of nuclear factor I binding sites identify enhancers of several papillomaviruses but alone are not sufficient for enhancer function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3519–3533. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal N., Knox J., Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of multiple forms of nuclear factor I in human and murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1041–1048. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Bucher E., Seipel K., Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W. Promoters with the octamer DNA motif (ATGCAAAT) can be ubiquitous or cell type-specific depending on binding affinity of the octamer site and Oct-factor concentration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):237–242. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schreiber E., Müller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2001–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberti C., Morrissey L. C., Grossman S. R., Androphy E. J. Transcriptional activation by the papillomavirus E6 zinc finger oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1907–1913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M., Ptashne M., Green M. R. How different eukaryotic transcriptional activators can cooperate promiscuously. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):359–361. doi: 10.1038/345359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Vass W. C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Velu T. J. The bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein can stimulate the transforming activity of EGF and CSF-1 receptors. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakshatri H., Pater M. M., Pater A. Ubiquitous and cell-type-specific protein interactions with human papillomavirus type 16 and type 18 enhancers. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):92–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90382-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord E. A., Beard P. A member of the activator protein 1 family found in keratinocytes but not in fibroblasts required for transcription from a human papillomavirus type 18 promoter. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4792–4798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4792-4798.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Fulton R., Breimer L., Stewart M., Willison K., Neil J. C. Nuclear factor 1 activates the feline leukemia virus long terminal repeat but is posttranscriptionally down-regulated in leukemia cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1991–1999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1991-1999.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Roeder R. G. Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):747–756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan R. A., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Achtstätter T., Moll R., Jorcano J. L., Magin T. M., Franke W. W. Patterns of expression and organization of cytokeratin intermediate filaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:282–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Thierry F., Howley P. M. Mutational analysis of cis elements involved in E2 modulation of human papillomavirus type 16 P97 and type 18 P105 promoters. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2849–2859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2849-2859.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer H. D., Freyaldenhoven M. P., Napierski I., Spitkovsky D. D., Bauknecht T., Dathan N. Delineation of human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer binding proteins: the intracellular distribution of a novel octamer binding protein p92 is cell cycle regulated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2363–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Dürst M., Demankowski C., Lattermann O., Zech R., Wolfsperger E., Suhai S., zur Hausen H. DNA sequence and genome organization of genital human papillomavirus type 6b. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R. Multiple nuclear proteins in liver cells are bound to hepatitis B virus enhancer element and its upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbet G. J., Campo M. S. Multiple interactions between cellular factors and the non-coding region of human papillomavirus type 16. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2699–2707. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Pol S. B., Howley P. M. A bovine papillomavirus constitutive enhancer is negatively regulated by the E2 repressor through competitive binding for a cellular factor. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5420–5429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5420-5429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., van den Heuvel S. J., van der Vliet P. C. Contactpoint analysis of the HeLa nuclear factor I recognition site reveals symmetrical binding at one side of the DNA helix. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):161–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBoer E., Antoniou M., Mignotte V., Wall L., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin promoter; nuclear protein factors and erythroid specific induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4203–4212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]