Abstract
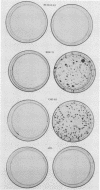
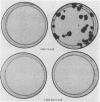
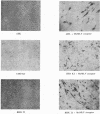
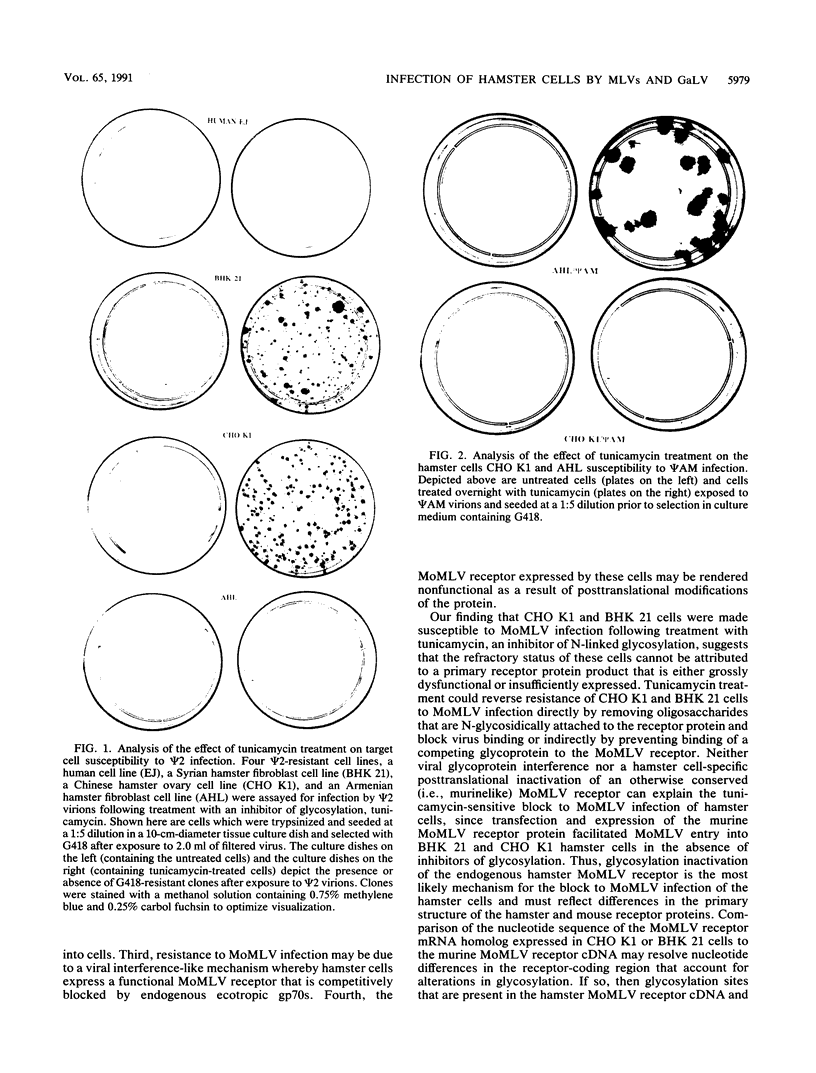
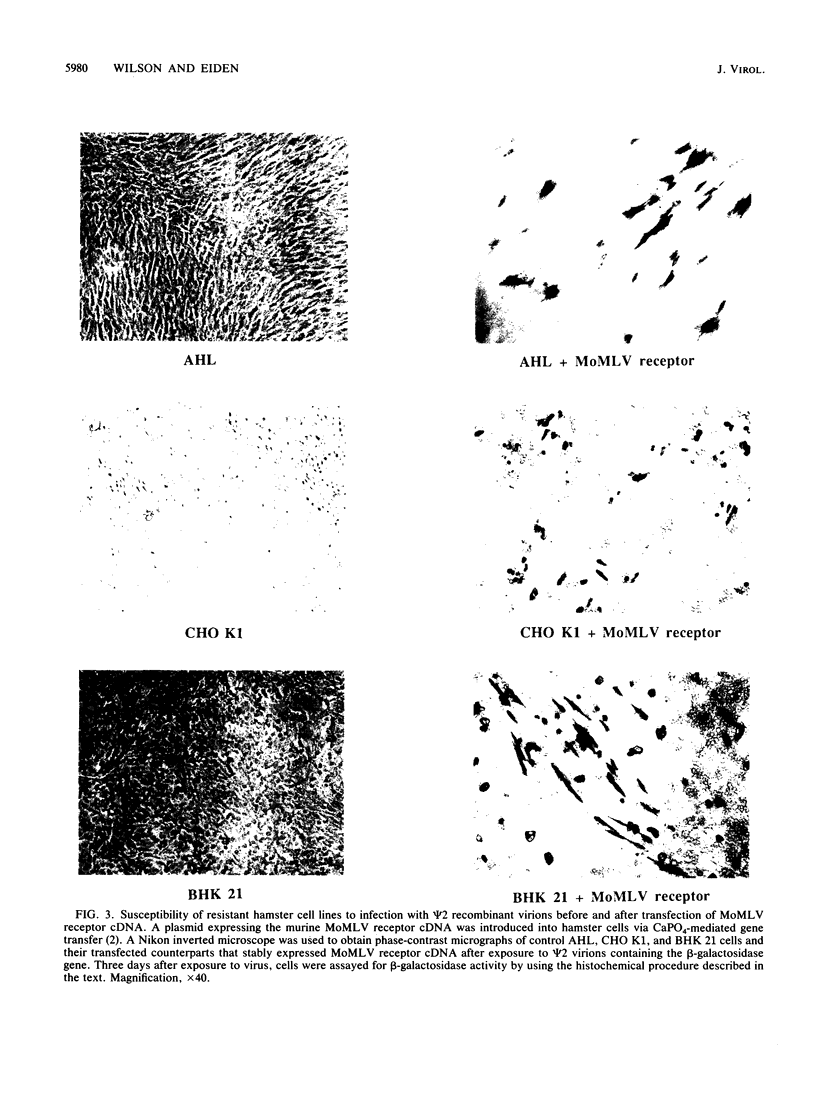
Hamster cells are resistant to infection by most retroviruses, including Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMLV) and gibbon ape leukemia viruses (GaLVs). We have constructed MoMLV-GaLV hybrid virions to identify viral and cellular determinants responsible for the inability of GaLV and MoMLV to infect hamster cells. The substitution of MoMLV core components for GaLV core components circumvents the resistance of hamster cells to infection by GaLV, demonstrating that hamster cells have receptors for GaLV but are not efficiently infected by this primate retrovirus because of a postpenetration block. In contrast, hamster cells are apparently resistant to MoMLV infection because although they bear a receptor for MoMLV, the receptor is nonfunctional. Treatment of CHO K1 or BHK 21 hamster cells with the glycosylation inhibitor tunicamycin allows the cells to be infected by MoMLV. The construction of MoMLV-GaLV hybrid virions that can efficiently infect resistant cells has allowed the identification of viral and cellular factors responsible for restricting infection of hamster cells by MoMLV and GaLV.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. Different mechanisms account for the relative resistance of KG-1 and HL-60 cell lines to retrovirus infection. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4346–4348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4346-4348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Physical mapping of the Fv-1 tropism host range determinant of BALB/c murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):685–696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.685-696.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuer G., Taketo M., Hanecak R. C., Fan H. Two blocks in Moloney murine leukemia virus expression in undifferentiated F9 embryonal carcinoma cells as determined by transient expression assays. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2317–2324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2317-2324.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Bancuk J. E. Polyoma genome in hamster BHK-21-C13 cells: integration into cellular DNA and induction of the viral replication. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):133–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.133-141.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Receptor affinities as major determinants of enterovirus tissue tropisms in humans. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:312–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifetz A., Keenan R. W., Elbein A. D. Mechanism of action of tunicamycin on the UDP-GlcNAc:dolichyl-phosphate Glc-NAc-1-phosphate transferase. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2186–2192. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P. The Fv-1 gene of the mouse and its control of murine leukemia virus replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;86:67–122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67341-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Garcia J. V., von Suhr N., Lynch C. M., Wilson C., Eiden M. V. Construction and properties of retrovirus packaging cells based on gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2220-2224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou C. Y., Boone L. R., Koh C. K., Tennant R. W., Yang W. K. Nucleotide sequences of gag-pol regions that determine the Fv-1 host range property of BALB/c N-tropic and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):779–784. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.779-784.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen R., Kempler G., Barklis E. A stem cell-specific silencer in the primer-binding site of a retrovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1214–1221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H. GENETIC CONTROL OF CELLULAR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO PSEUDOTYPES OF ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1965 Jun;26:270–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed S., Gardner M. B., Chan E. Amphotropic host range of naturally occuring wild mouse leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):13–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.13-18.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Schultz A. M., Bader J. P., Bassin R. H. Inhibitors of glycosylation reverse retroviral interference. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. A VIRUS IN CHICK EMBRYOS WHICH INDUCES RESISTANCE IN VITRO TO INFECTION WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1105–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Martin G. R., Lowy D. R. Virus infection of murine teratocarcinoma stem cell lines. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallagher R. E., Gillespie D. H., Gallo R. C. Infective transmission and characterisation of a C-type virus released by cultured human myeloid leukaemia cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):551–555. doi: 10.1038/256551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Wong A. L. Phenotypic mixing between avian and mammalian RNA tumor viruses: I. Envelope pseudotypes of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):826–834. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada J. Pseudotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus with the coat of murine leukaemia and of avian myeloblastosis viruses. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jun;15(3):183–191. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-3-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]