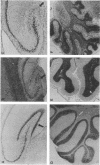
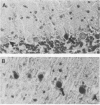
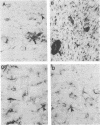
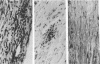
Abstract
Borna disease virus (BDV) is a negative-strand RNA virus which produces persistent infection in a variety of experimental animals. In the rat, the presence or absence of clinical signs of Borna disease, a characteristic, biphasic neurobehavioral illness, depends on host-related factors. A window of opportunity exists after birth wherein inoculation with BDV produces a persistently infected rat without signs of Borna disease or encephalitis (persistent, tolerant infection-newborn [PTI-NB] rat). Although immunopathological destruction of the nervous system does not occur in the PTI-NB rat, significant alterations in the development of the nervous system were noted, including site-specific lysis of neurons. Unlike the case with other pharmacologically produced, persistent, tolerant BDV infections, adoptive transfer of spleen cells from BDV-infected rats did not produce disease in the PTI-NB rats. PTI-NB rats developed Borna disease after being connected by parabiosis to rats with Borna disease. Bone marrow transplantation experiments revealed that bone marrow cells from PTI-NB rats produced Borna disease in lethally irradiated, BDV-infected recipient rats. Bone marrow from PTI-NB rats contained a complement of inflammatory cells capable of inducing Borna disease. Thus, the loss of BDV-specific cellular immunity appeared to occur after the release of cells from the bone marrow.
Full text
PDF




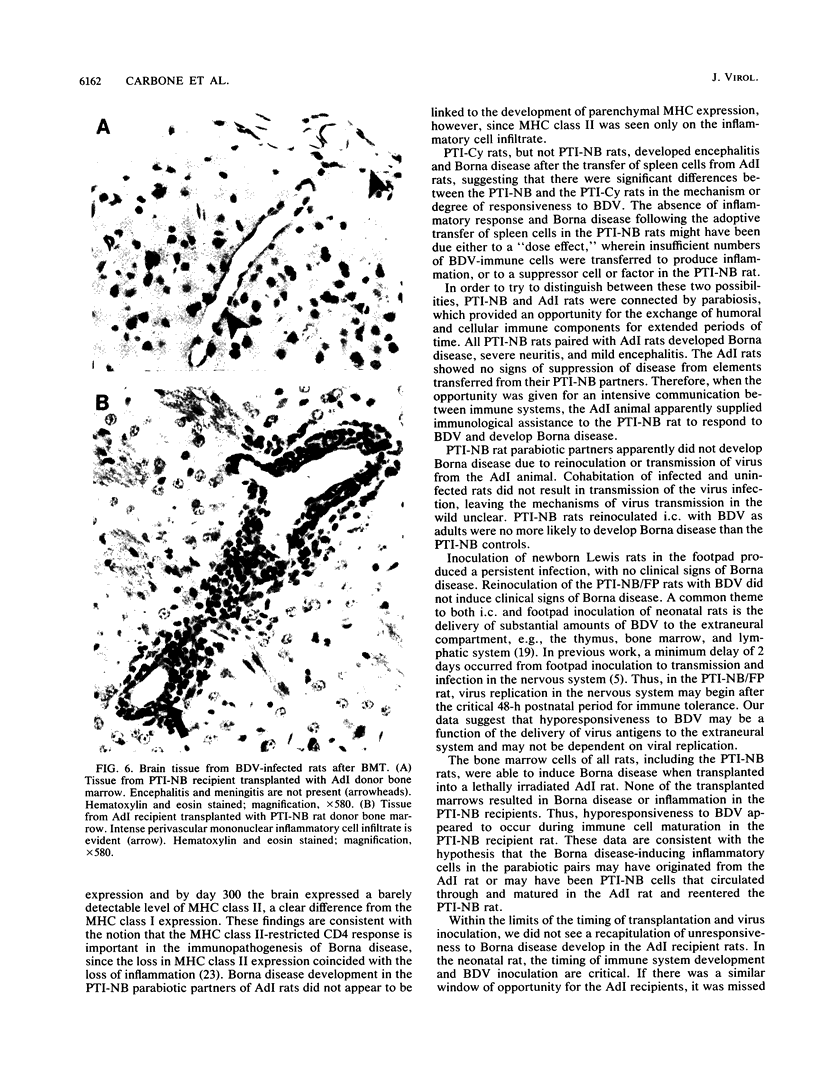


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Salmi A., Butler L. D., Chiller J. M., Oldstone M. B. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):521–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman J. Morphological and behavioral markers of environmentally induced retardation of brain development: an animal model. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Oct;74:153–168. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8774153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankamp B., Brinckmann U. G., Reich A., Niewiesk S., ter Meulen V., Liebert U. G. Measles virus nucleocapsid protein protects rats from encephalitis. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1695–1700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1695-1700.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. A., Thomson A. W., Whiting P. H., Davidson R. J., Simpson J. G. Immunosuppressive activity and toxicity of cyclosporin A in rats pretreated with high dose cyclophosphamide. Agents Actions. 1985 Oct;17(1):67–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01966684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Duchala C. S., Griffin J. W., Kincaid A. L., Narayan O. Pathogenesis of Borna disease in rats: evidence that intra-axonal spread is the major route for virus dissemination and the determinant for disease incubation. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3431–3440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3431-3440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Duchala C. S., Narayan O. Borna disease. An immunopathologic response to viral infection in the CNS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:661–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschl U., Stitz L., Herzog S., Frese K., Rott R. Determination of immune cells and expression of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen in encephalitic lesions of experimental Borna disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):41–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00662636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich W., Bode L., Ludwig H., Kao M., Schneider K. Learning deficiencies in Borna disease virus-infected but clinically healthy rats. Biol Psychiatry. 1989 Dec;26(8):818–828. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(89)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Laughlin M. A., Hoxie J. A., Wigdahl B., Gonzalez-Scarano F. CD4-independent infection of human neural cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2527–2533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2527-2533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog S., Frese K., Rott R. Studies on the genetic control of resistance of black hooded rats to Borna disease. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):535–540. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog S., Kompter C., Frese K., Rott R. Replication of Borna disease virus in rats: age-dependent differences in tissue distribution. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1984;173(4):171–177. doi: 10.1007/BF02122108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Kao M., Ludwig H. Persistent, tolerant or subacute infection in Borna disease virus-infected rats. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1521–1530. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson B. D., Ahmed R. T-cell tolerance: exposure to virus in utero does not cause a permanent deletion of specific T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2265–2268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. A., Chin L. T., Merriam G. R., Nelson L. M., Kruisbeck A. M. Failure of clonal deletion in neonatally thymectomized mice: tolerance is preserved through clonal anergy. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1277–1285. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Roehm N., Marrack P. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90568-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Travis G. H., Carbone K. M., Wilson M. C. Isolation and characterization of Borna disease agent cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4184–4188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A. Pathogenesis of viral infections of the fetus. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:194–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monjan A. A., Cole G. A., Gilden D. H., Nathanson N. Pathogenesis of cerebellar hypoplasia produced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of neonatal rats. 1. Evolution of disease following infection at 4 days of age. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Jan;32(1):110–124. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197301000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Viruses can cause disease in the absence of morphologic evidence of cell injury: pathology in the absence of cell lysis--implication for pathologists' future study of disease. Monogr Pathol. 1990;(32):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richt J. A., Stitz L., Wekerle H., Rott R. Borna disease, a progressive meningoencephalomyelitis as a model for CD4+ T cell-mediated immunopathology in the brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riond J. L., Cullen J. M., Godfrey V. L., Hunt E. L., Anderson K. L. Bovine viral diarrhea virus-induced cerebellar disease in a calf. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1990 Dec 15;197(12):1631–1632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidorenko A. V., Gubrii I. B., Andrianova L. F., Macsijuk T. V., Butenko G. M. Functional rearrangement of lymphohemopoietic system in heterochronically parabiosed mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 1986 Sep;36(1):41–56. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(86)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitz L., Soeder D., Deschl U., Frese K., Rott R. Inhibition of immune-mediated meningoencephalitis in persistently Borna disease virus-infected rats by cyclosporine A. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutschka P. J. The role of the thymus in regulating tolerance to self and nonself. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):486–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsang G. B., Hess A. D., Gordon G., Santos G. W. Treatment and prevention of acute graft-versus-host disease with thalidomide in a rat model. Transplantation. 1986 May;41(5):644–647. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198605000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Walker D. G., Akiyama H., McGeer P. L. Herpes simplex virus type I infection of the CNS induces major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on rat microglia. J Neurosci Res. 1990 May;26(1):55–65. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Denaro F. J., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Localization of cytomegalovirus proteins and genome during fulminant central nervous system infection in an AIDS patient. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Mar;45(2):127–139. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198603000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Carbone K. M., Lipkin W. I. Molecular characterization of the Borna disease agent. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):853–856. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90154-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]