Abstract
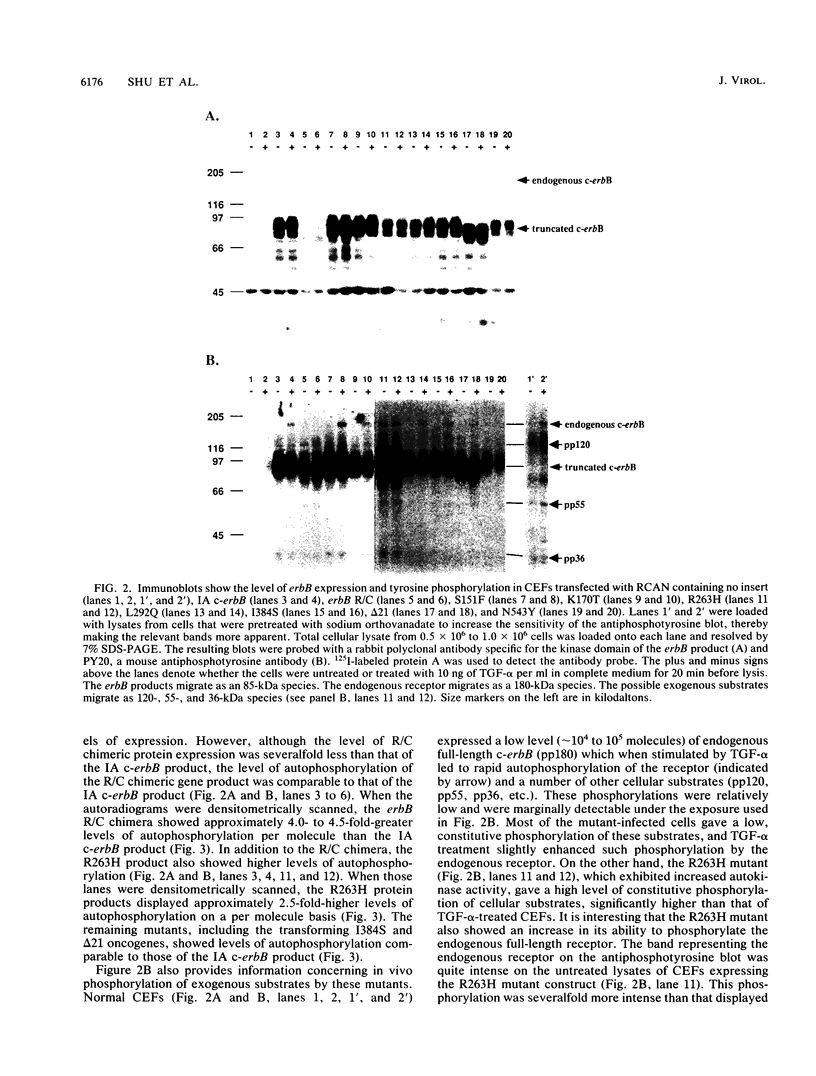
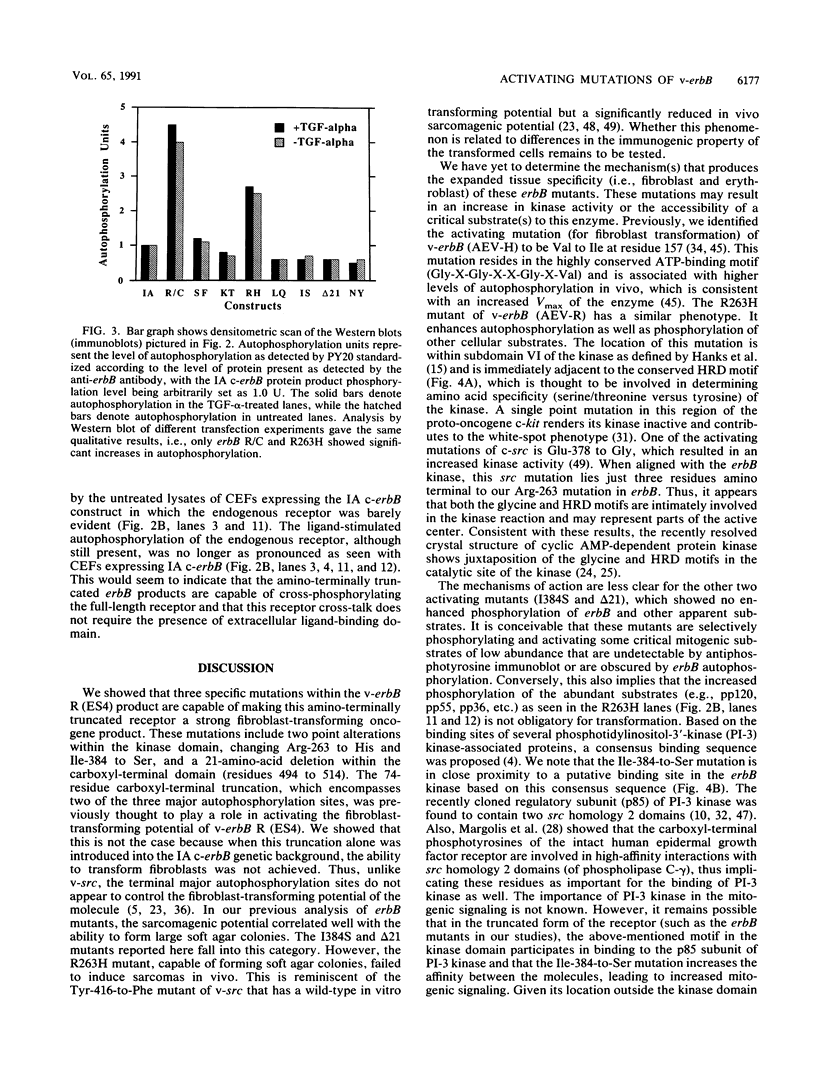
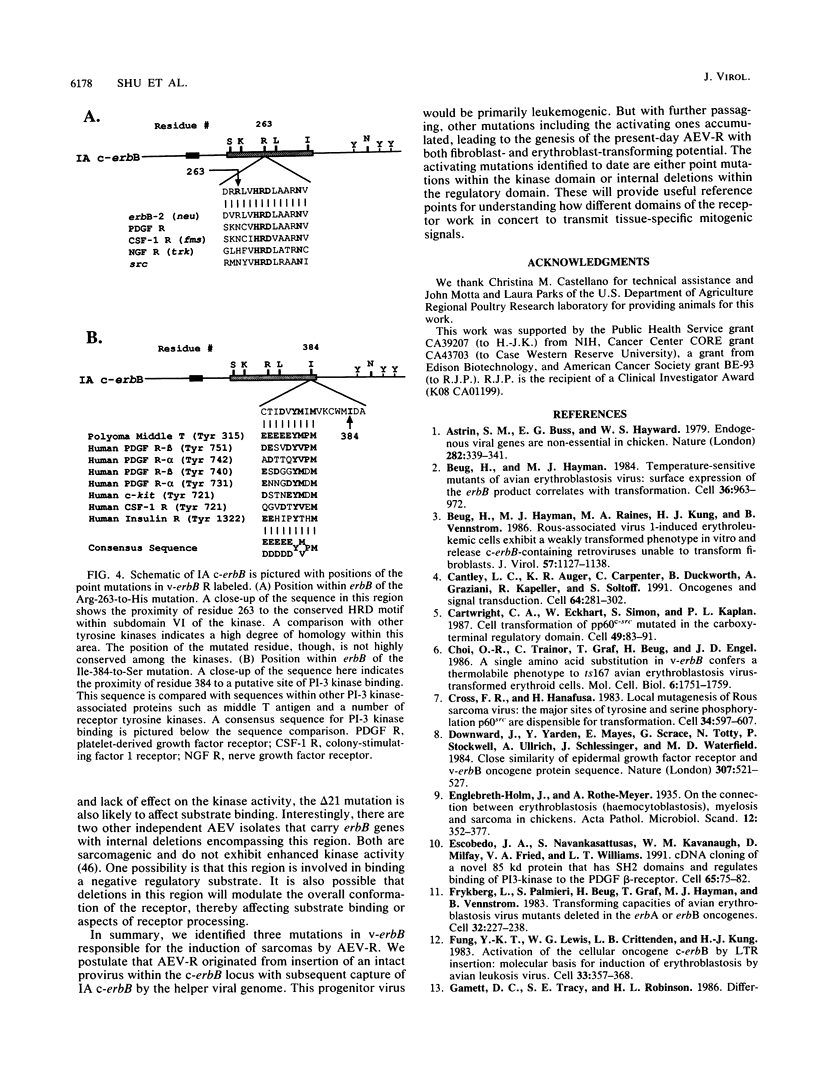
The v-erbB oncogene isolated from the R (or ES4) strain of avian erythroblastosis virus is capable of inducing erythroleukemia and fibrosarcomas. This oncogene differs from the proto-oncogene c-erbB, the avian homolog of the epidermal growth factor receptor, by its lack of an intact ligand-binding domain as well as additional alterations in its cytoplasmic coding sequences. By contrast, the insertionally activated c-erbB, a variant oncogene, which encodes a product that also lacks the ligand-binding domain but is otherwise unaltered in its cytoplasmic coding sequences, is capable of inducing leukemia but cannot induce sarcomas. In this report, we show that the critical changes for activating the sarcomagenic potential displayed by v-erbB R are two point mutations within the tyrosine kinase domain and an internal deletion of 21 amino acids in the carboxyl-terminal regulatory domain. The removal of the carboxyl-terminal autophosphorylation sites is not obligatory. These activating mutations (Arg-263 to His, Ile-384 to Ser, and the deletion of residues 494 to 514), when introduced singly into the insertionally activated c-erbB, all dramatically increase fibroblast-transforming potential. Arg-263 resides near the highly conserved HRD motif of the kinase domain, and its mutation to His increases the autophosphorylation activity. The other two mutations do not alter the intrinsic kinase activity and presumably affect other aspects of the receptor involved in growth signaling. Therefore, the high transforming potential of v-erbB R is a consequence of synergism among multiple activating mutations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrin S. M., Buss E. G., Haywards W. S. Endogenous viral genes are non-essential in the chicken. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):339–341. doi: 10.1038/282339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J., Raines M. B., Kung H. J., Vennström B. Rous-associated virus 1-induced erythroleukemic cells exhibit a weakly transformed phenotype in vitro and release c-erbB-containing retroviruses unable to transform fibroblasts. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1127–1138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1127-1138.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J. Temperature-sensitive mutants of avian erythroblastosis virus: surface expression of the erbB product correlates with transformation. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Trainor C., Graf T., Beug H., Engel J. D. A single amino acid substitution in v-erbB confers a thermolabile phenotype to ts167 avian erythroblastosis virus-transformed erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frykberg L., Palmieri S., Beug H., Graf T., Hayman M. J., Vennström B. Transforming capacities of avian erythroblastosis virus mutants deleted in the erbA or erbB oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Royer-Pokora B., Schubert G. E., Beug H. Evidence for the multiple oncogenic potential of cloned leukemia virus: in vitro and in vitro studies with avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Beug H. Identification of a form of the avian erythroblastosis virus erb-B gene product at the cell surface. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):460–462. doi: 10.1038/309460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Ramsay G. M., Savin K., Kitchener G., Graf T., Beug H. Identification and characterization of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB gene product as a membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Yamamoto H., Shimohira H., Arai K., Shimizu T. Avian erythroblastosis virus isolated from chick erythroblastosis induced by lymphatic leukemia virus subgroup A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 May;70(5):891–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Most of the substrates of oncogenic viral tyrosine protein kinases can be phosphorylated by cellular tyrosine protein kinases in normal cells. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):105–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Johnson A., Howk R., Sap J., Bellot F., Winkler M., Ullrich A., Vennstrom B., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Chicken epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor: cDNA cloning, expression in mouse cells, and differential binding of EGF and transforming growth factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maihle N. J., Raines M. A., Flickinger T. W., Kung H. J. Proviral insertional activation of c-erbB: differential processing of the protein products arising from two alternate transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4868–4876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain B., Woods C. M., Saez J., Flickinger T., Raines M., Peyrol S., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Kung H. J., Jurdic P. EGF-R as a hemopoietic growth factor receptor: the c-erbB product is present in chicken erythrocytic progenitors and controls their self-renewal. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90405-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. J., Maihle N. J., Boerkoel C., Shu H. K., Carter T. H., Moscovici C., Kung H. J. Disease tropism of c-erbB: effects of carboxyl-terminal tyrosine and internal mutations on tissue-specific transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. J., Moscovici C., Hughes S., Kung H. J. Proviral-activated c-erbB is leukemogenic but not sarcomagenic: characterization of a replication-competent retrovirus containing the activated c-erbB. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1840–1844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1840-1844.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Bishop J. M. Proteins specified by avian erythroblastosis virus: coding region localization and identification of a previously undetected erb-B polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of the v-erb-B protein, the product of a transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Sealy L., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB locus is a glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1257–1267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Maihle N. J., Moscovici C., Crittenden L., Kung H. J. Mechanism of c-erbB transduction: newly released transducing viruses retain poly(A) tracts of erbB transcripts and encode C-terminally intact erbB proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2437–2443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2437-2443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Maihle N. J., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Kung H. J. Molecular characterization of three erbB transducing viruses generated during avian leukosis virus-induced erythroleukemia: extensive internal deletion near the kinase domain activates the fibrosarcoma- and hemangioma-inducing potentials of erbB. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2444–2452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2444-2452.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Privalsky M. L., Moscovici G., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Site-specific mutagenesis of avian erythroblastosis virus: erb-B is required for oncogenicity. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):155–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. K., Pelley R. J., Kung H. J. Tissue-specific transformation by epidermal growth factor receptor: a single point mutation within the ATP-binding pocket of the erbB product increases its intrinsic kinase activity and activates its sarcomagenic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9103–9107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M. A mutation at the major phosphotyrosine in pp60v-src alters oncogenic potential. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Phosphorylation of tyrosine-416 is not required for the transforming properties and kinase activity of pp60v-src. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S. E., Woda B. A., Robinson H. L. Induction of angiosarcoma by a c-erbB transducing virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):304–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.304-310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Hihara H., Nishida T., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. A new avian erythroblastosis virus, AEV-H, carries erbB gene responsible for the induction of both erythroblastosis and sarcomas. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]