Abstract
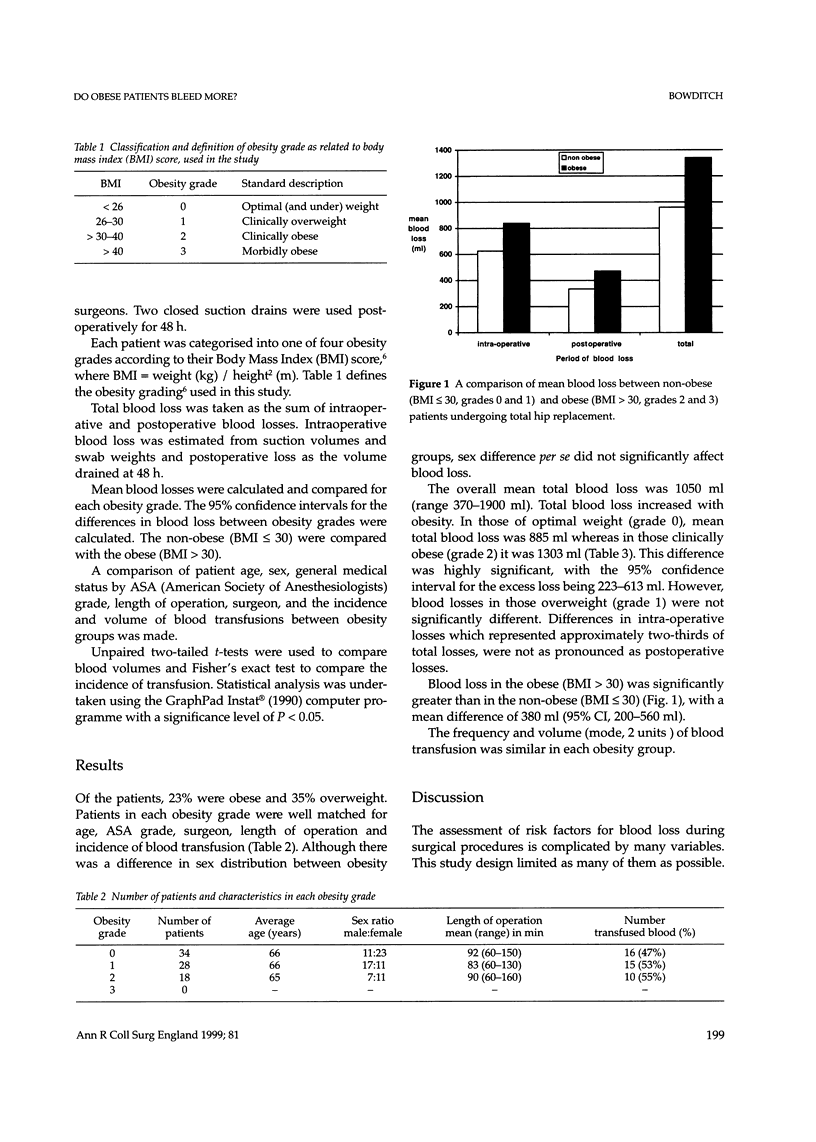
This study compares blood loss at total hip replacement in obese and non-obese patients. We made a prospective study of intra-operative and postoperative blood loss in 80 consecutive primary cemented hip replacements. Patients' obesity was classified according to body mass index (BMI). Overall mean total blood loss was 1050 ml. Obese patients (BMI > 30) bled significantly more (P < 0.0001) than those of optimal weight (BMI < 26), whereas those overweight (BMI 26-30) did not. The mean excess blood loss in obese patients was 380 ml (95% confidence interval, 200-560 ml). At a time when the prevalence of obesity is increasing, this study quantifies the risks of greater blood loss with respect to obesity and aids informed consent.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garrow J. S., Webster J. Quetelet's index (W/H2) as a measure of fatness. Int J Obes. 1985;9(2):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosflam J. M., Wright E. A., Cleary P. D., Katz J. N. Predictors of blood loss during total hip replacement surgery. Arthritis Care Res. 1995 Sep;8(3):167–173. doi: 10.1002/art.1790080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiganti J. J., Goldstein W. M., Williams C. S. A comparison of the perioperative morbidity in total joint arthroplasty in the obese and nonobese patient. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993 Apr;(289):175–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman D. E., Capello W. N., Feinberg J. R. Total hip arthroplasty without cement in obese patients. A minimum two-year clinical and radiographic follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994 Jun;76(6):854–862. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199406000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søballe K., Christensen F., Luxhøj T. Hip replacement in obese patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1987 Jun;58(3):223–225. doi: 10.3109/17453678709146470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


