Abstract
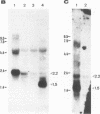
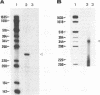
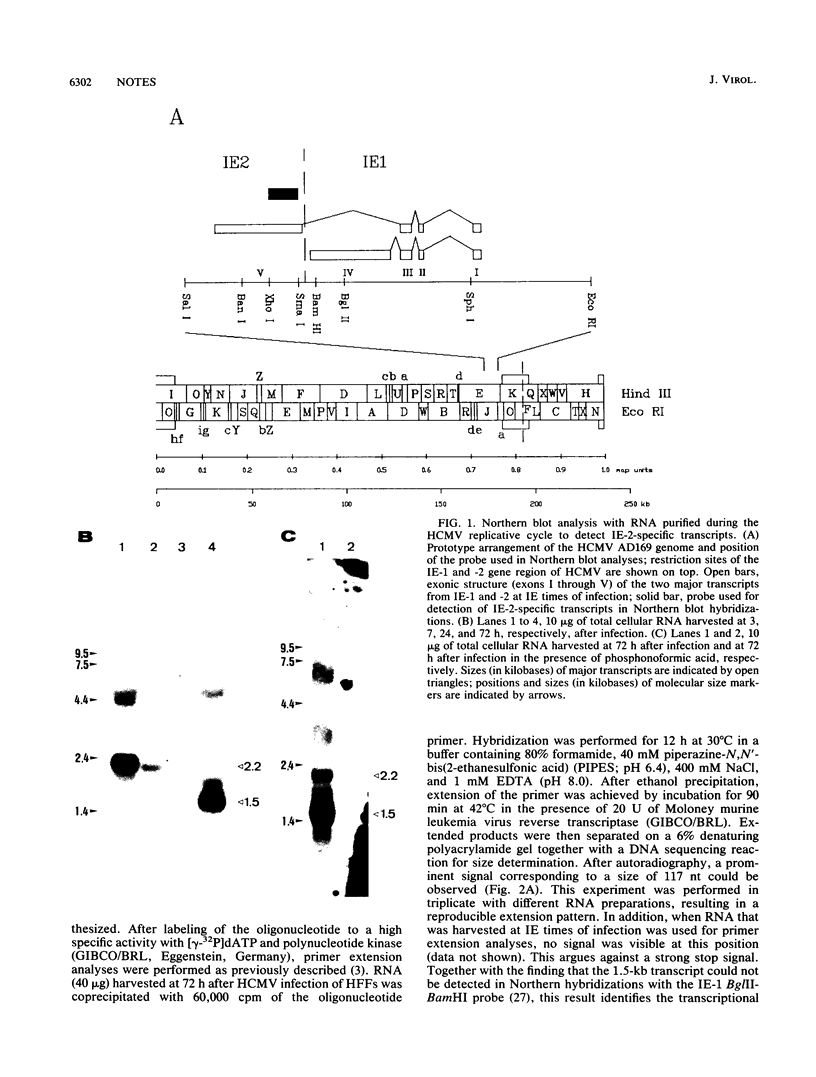
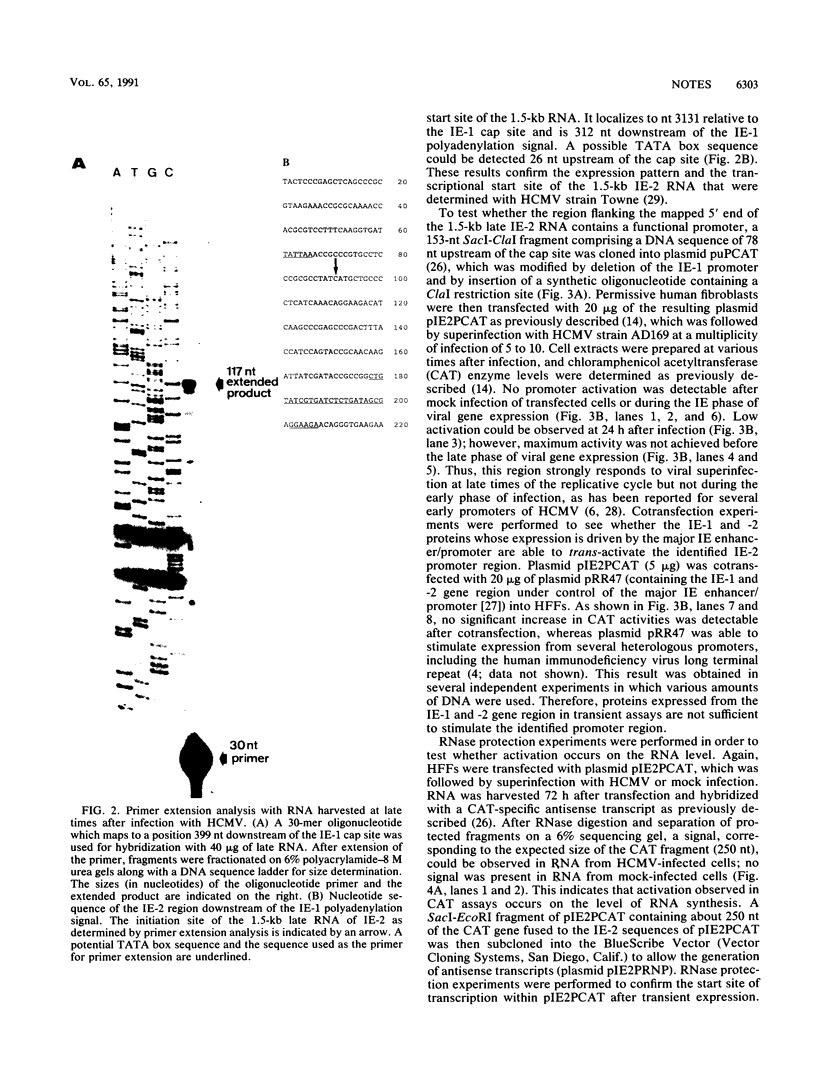
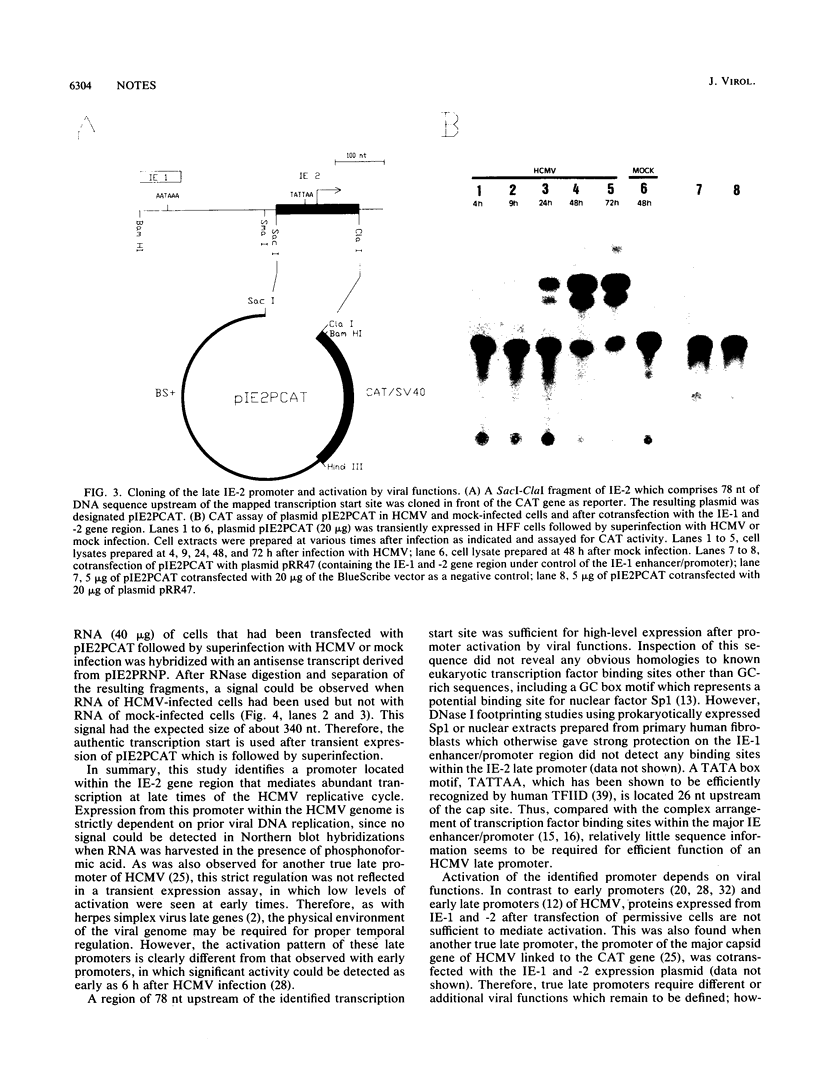
An abundant late transcript of 1.5 kb originates from the immediate-early 2 (IE-2) gene region of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) at late times after infection. The transcriptional start of this RNA was precisely mapped, and the putative promoter region was cloned in front of the CAT gene as reporter. This region, which comprises 78 nucleotides of IE-2 sequence upstream of the determined cap site, was strongly activated by viral superinfection at late times in the replicative cycle. As shown by RNase protection analyses, the authentic transcription start is used. No activation of this late promoter was observed after cotransfection with an expression plasmid containing the HCMV IE-1 and -2 gene region. This result suggests that, compared with early and early late promoters of HCMV, different or additional viral functions are required for the activation of true late promoters.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Wilkinson G. W., Oram J. D. The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenakis M., Tomasi L. F., Speziali V., Roizman B., Campadelli-Fiume G. Expression and regulation of glycoprotein C gene of herpes simplex virus 1 resident in a clonal L-cell line. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):367–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.367-376.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. A human cytomegalovirus early gene has three inducible promoters that are regulated differentially at various times after infection. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.281-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Khoury E. L., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie2 negatively regulates alpha gene expression via a short target sequence near the transcription start site. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):887–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.887-896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Schmidt C. A., Kaplan A. S. Patterns of transcription of human cytomegalovirus in permissively infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):277–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.277-286.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depto A. S., Stenberg R. M. Regulated expression of the human cytomegalovirus pp65 gene: octamer sequence in the promoter is required for activation by viral gene products. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1232-1238.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickenscher H., Stamminger T., Rüger R., Fleckenstein B. The role of a repetitive palindromic sequence element in the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early enhancer. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jan;70(Pt 1):107–123. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Hennighausen L. Specific interactions between transcription factors and the promoter-regulatory region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1076–1079. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1076-1079.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early two protein region involved in negative regulation of the major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3532–3536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3532-3536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Knust E., Schmolla H., Sarre T., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K., Fleckenstein B. Predominant immediate-early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus AD 169. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.363-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Hermiston T. W., Stinski M. F. A cis-acting element in the major immediate-early (IE) promoter of human cytomegalovirus is required for negative regulation by IE2. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):897–903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.897-903.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone C. L., Vesole D. H., Stinski M. F. Transactivation of a human cytomegalovirus early promoter by gene products from the immediate-early gene IE2 and augmentation by IE1: mutational analysis of the viral proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1498-1506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H., Bankier A. T., Landini M. P., Brown C. M., Barrell B. G., Rüger B., Mach M. Identification and procaryotic expression of the gene coding for the highly immunogenic 28-kilodalton structural phosphoprotein (pp28) of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2243–2250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2243-2250.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Hayward G. S. The IE2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus specifically down-regulate expression from the major immediate-early promoter through a target sequence located near the cap site. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6154–6165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6154-6165.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Stamminger T., Jahn G. Transcriptional analysis of the eight-kilobase mRNA encoding the major capsid protein of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5167–5172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5167-5172.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Fickenscher H., Fleckenstein B. Cell type-specific induction of the major immediate early enhancer of human cytomegalovirus by cyclic AMP. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):105–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Puchtler E., Fleckenstein B. Discordant expression of the immediate-early 1 and 2 gene regions of human cytomegalovirus at early times after infection involves posttranscriptional processing events. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2273–2282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2273-2282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Oberg B. Inhibition of cytomegalovirus late antigens by phosphonoformate. Intervirology. 1980;12(6):335–339. doi: 10.1159/000149093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Temporal regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription at immediate early and early times after infection. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.446-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. W., Akrigg A., Greenaway P. J. Transcription of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1984;1(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]