Abstract
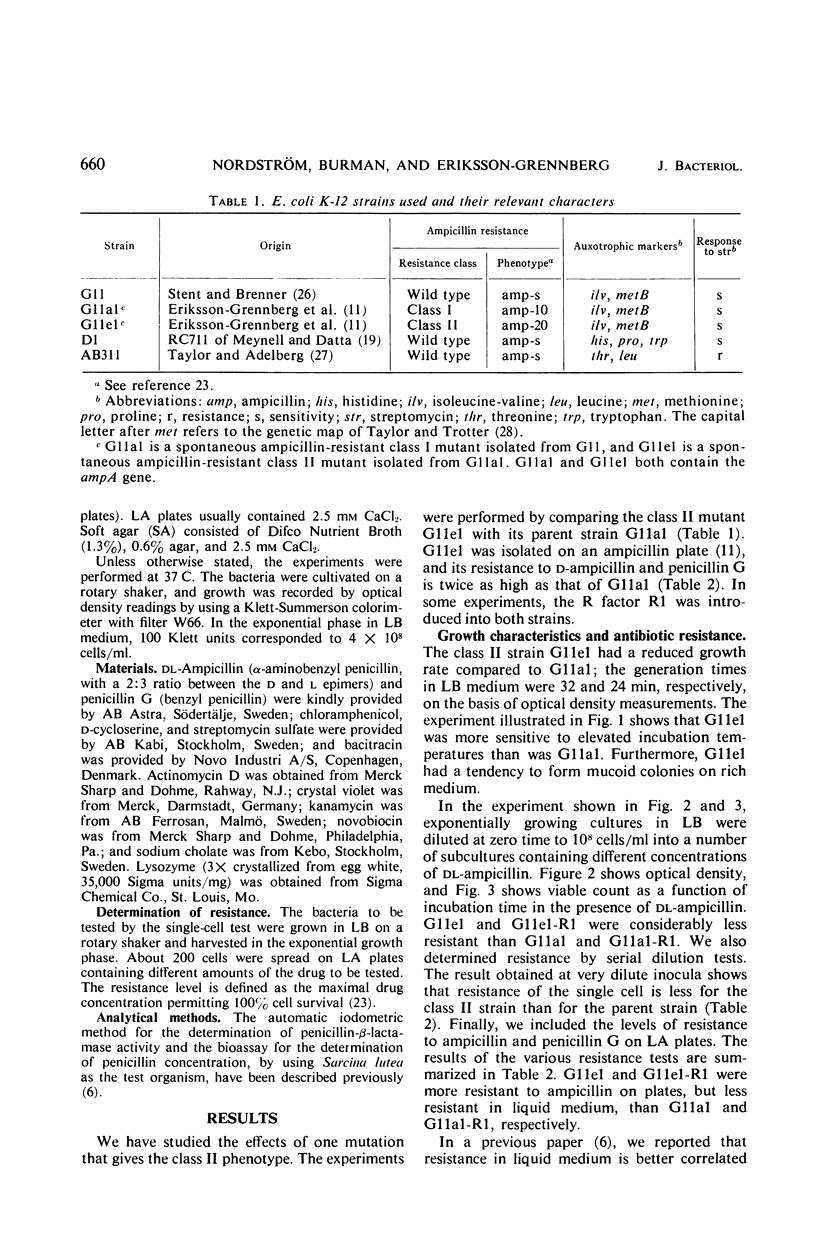
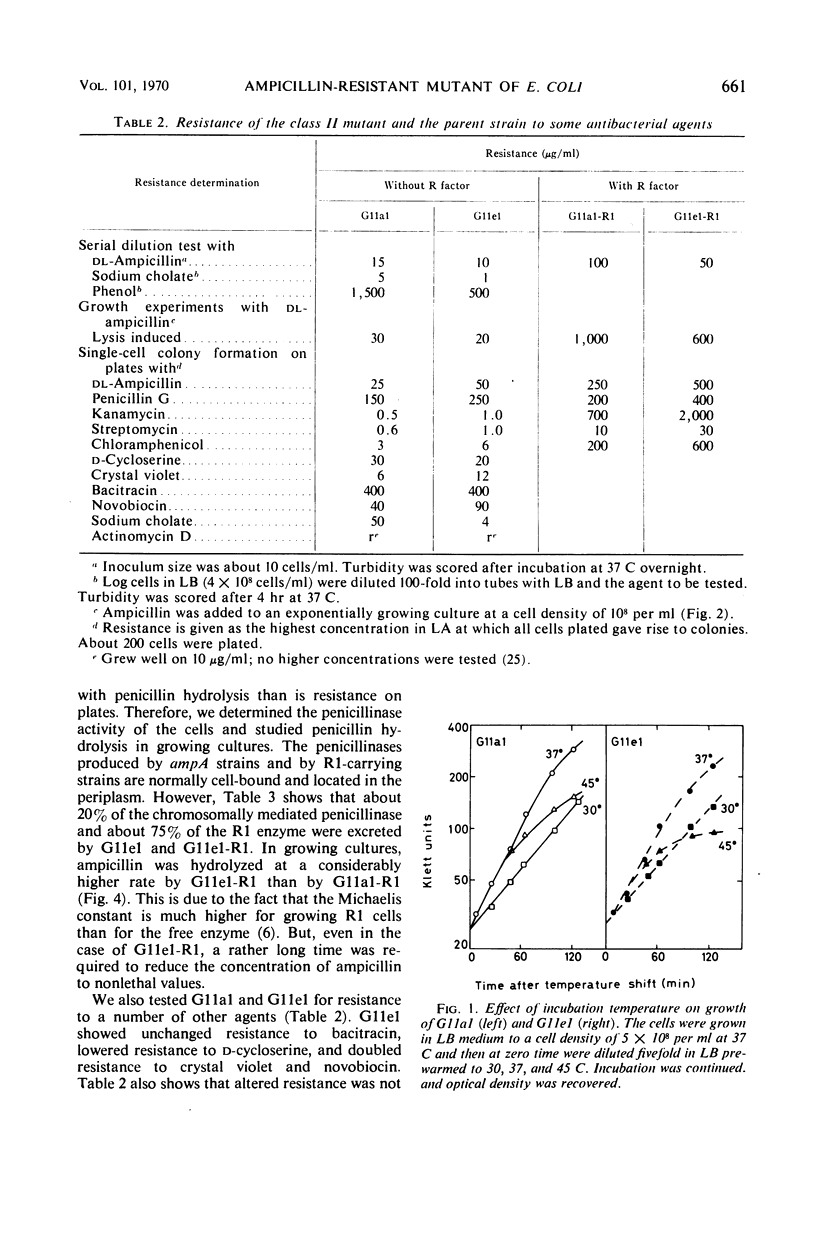
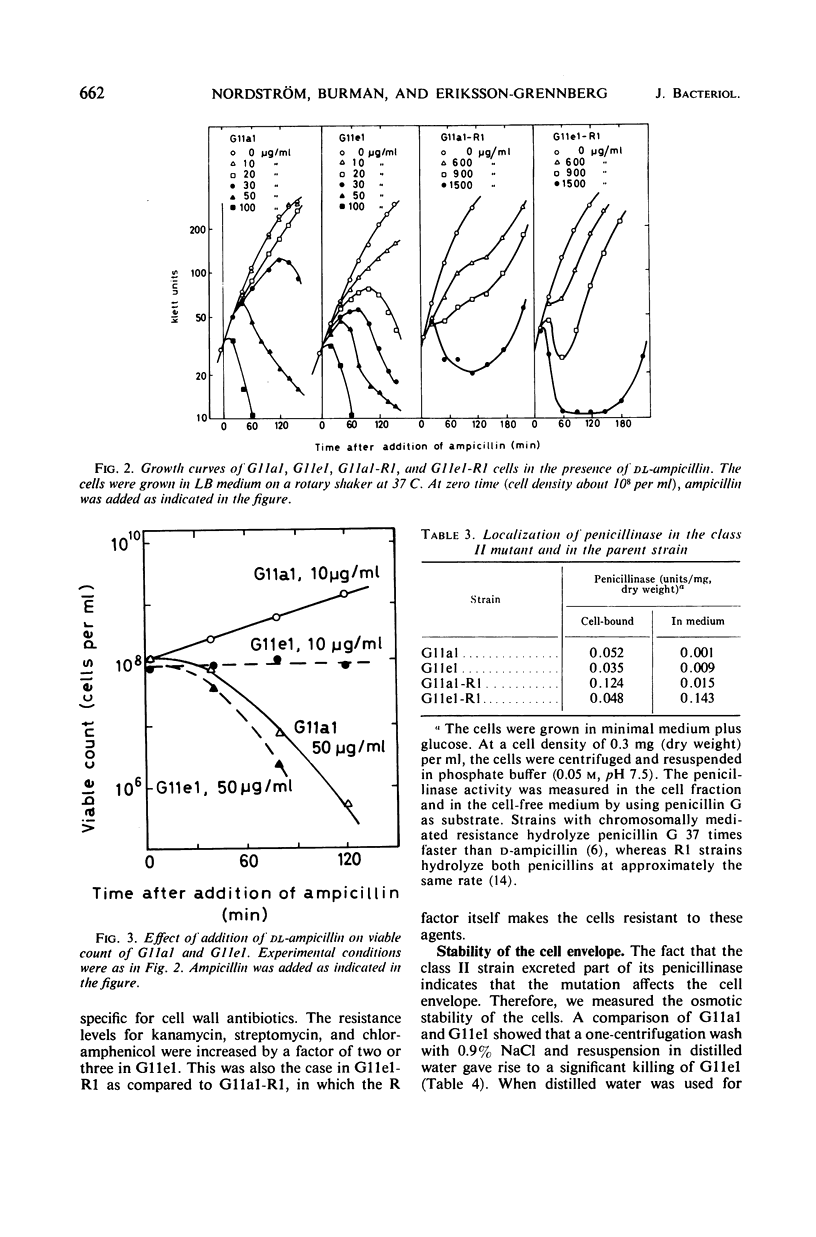
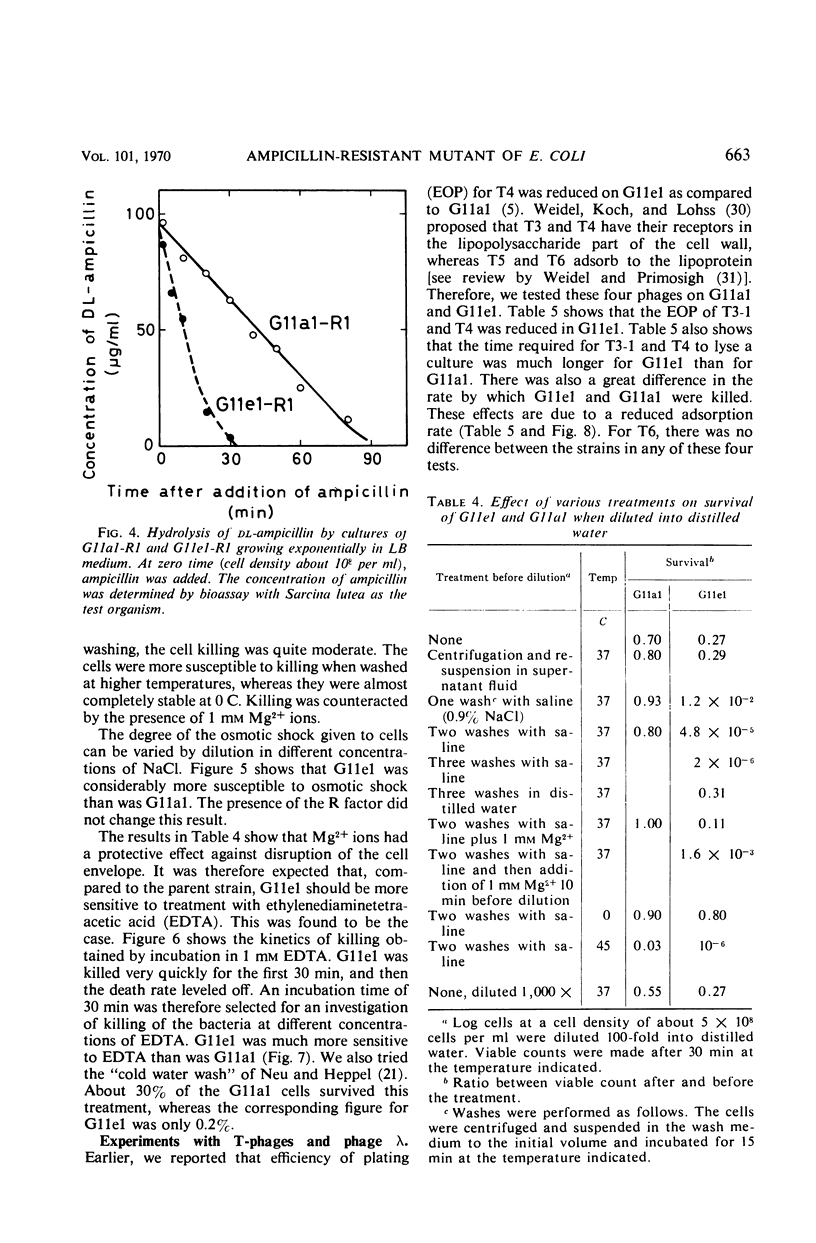
Class II ampicillin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli are defined as having a twofold increase in penicillinase-mediated ampicillin resistance when determined by colony formation tests on plates. In this paper, one class II mutant has been compared to its parent strain. In liquid medium, the mutant was less resistant than the parent strain both in the absence and in the presence of R1 and R-factor mediating penicillinase activity. The penicillinase activity was found to be almost completely bound to the cells in the parent strain, whereas it was excreted to a great extent in the class II mutant strain. In liquid medium, resistance was well correlated to the cell-bound penicillinase activity, whereas the excreted penicillinases were also of great importance for survival on ampicillin plates. The mutant also had a changed resistance to a great number of other antibacterial drugs. The mutant was found to be more sensitive than the parent strain to osmotic shock, especially when treated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or washed with sodium ions. However, the osmotic stability was restored by the presence of 1 mm Mg2+ ions. The class II mutant was more sensitive than the parent strain to sodium cholate, and it adsorbed the phages T4 and T3-1 at a slower rate than did the parent strain. The two strains adsorbed T6 at the same rate. The class II phenotype could be gradually reversed by increasing concentrations of divalent cations. The pleiotropic changes in the phenotype are apparently unrelated to the specific targets for the antibacterial agents tested. They are secondary consequences of a cell envelope mutation. The findings indicate that the class II mutation mediates a structural change in the lipopolysaccharide of the cell envelope.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. Role of Multivalent Cations in the Organization, Structure, and Assembly of the Cell Wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):380–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.380-387.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Normark S., Matsson E. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. IV. Genetic study of mutants resistant to D,L-ampicillin concentrations o 100 mu-g-ml. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):169–185. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Nordström K., Boman H. G. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. V. Physiological comparison of two isogenic strains, one with chromosomally and one with episomally mediated ampicillin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):438–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.438-446.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson K. J., Eagon R. G. Lysozyme sensitivity of the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Further evidence for the role of the non-peptidoglycan components in cell wall rigidity. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):105–108. doi: 10.1139/m66-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox S. T., Jr, Eagon R. G. Action of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane, and lysozyme on cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Aug;14(8):913–922. doi: 10.1139/m68-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGON R. G., CARSON K. J. LYSIS OF CELL WALLS AND INTACT CELLS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA BY ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRAACETIC ACID AND BY LYSOZYME. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:193–201. doi: 10.1139/m65-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Boman H. G., Jansson J. A., Thorén S. Resistance of Escherichia coli to Penicillins I. Genetic Study of Some Ampicillin-Resistant Mutants. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):54–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.54-62.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson-Grennberg K. G. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. II. An improved mapping of the ampA gene. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):147–156. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Shovlin V. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Physical, chemical, and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide released from Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6384–6391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist R. C., Nordström K. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. VII. Purification and characterization of a penicillinase mediated by the R factor R1. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.232-239.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linström E. B., Boman H. G., Steele B. B. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. VI. Purification and characterization of the chromosomally mediated penicillinase present in ampA-containing strains. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):218–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.218-231.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Selection of sucrose-dependent Escherichia coli to obtain envelope mutants and fragile cultures. Science. 1966 Aug 19;153(3738):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3738.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz A., Lieberman M. M., Rosenbaum N. Derepression of phosphomannose isomerase by regulator gene mutations involved in capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1497–1501. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1497-1501.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz A., Rosenbaum N. A regulator gene that is dominant on an episome and recessive on a chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1084–1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meynell E., Datta N. The relation of resistance transfer factors to the F-factor (sex-factor) of Escherichia coli K12. Genet Res. 1966 Feb;7(1):134–140. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Boman H. G. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. 3. AmpB, a locus affecting episomally and chromosomally mediated resistance to ampicillin and chlorampheincol. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):157–168. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve E. C. Genetic analysis of some mutations causing resistance to tetracycline in Escherichia coli K12. Genet Res. 1968 Jun;11(3):303–309. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Iida S. Mutants of Escherichia coli permeable to actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2315–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A L, Adelberg E A. Linkage Analysis with Very High Frequency Males of Escherichia Coli. Genetics. 1960 Sep;45(9):1233–1243. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.9.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Revised linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):332–353. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.332-353.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PRIMOSIGH J. Biochemical parallels between lysis by virulent phage and lysis by penicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):513–517. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



