Abstract
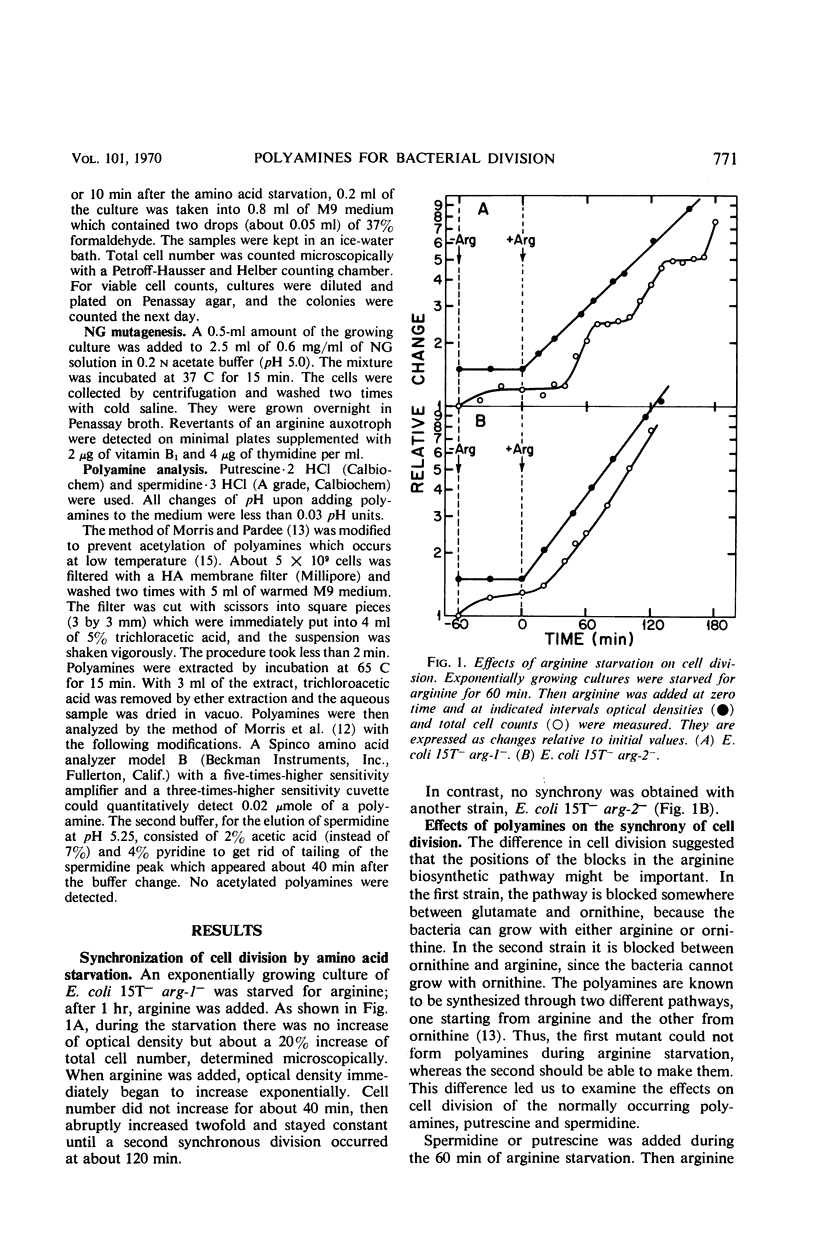
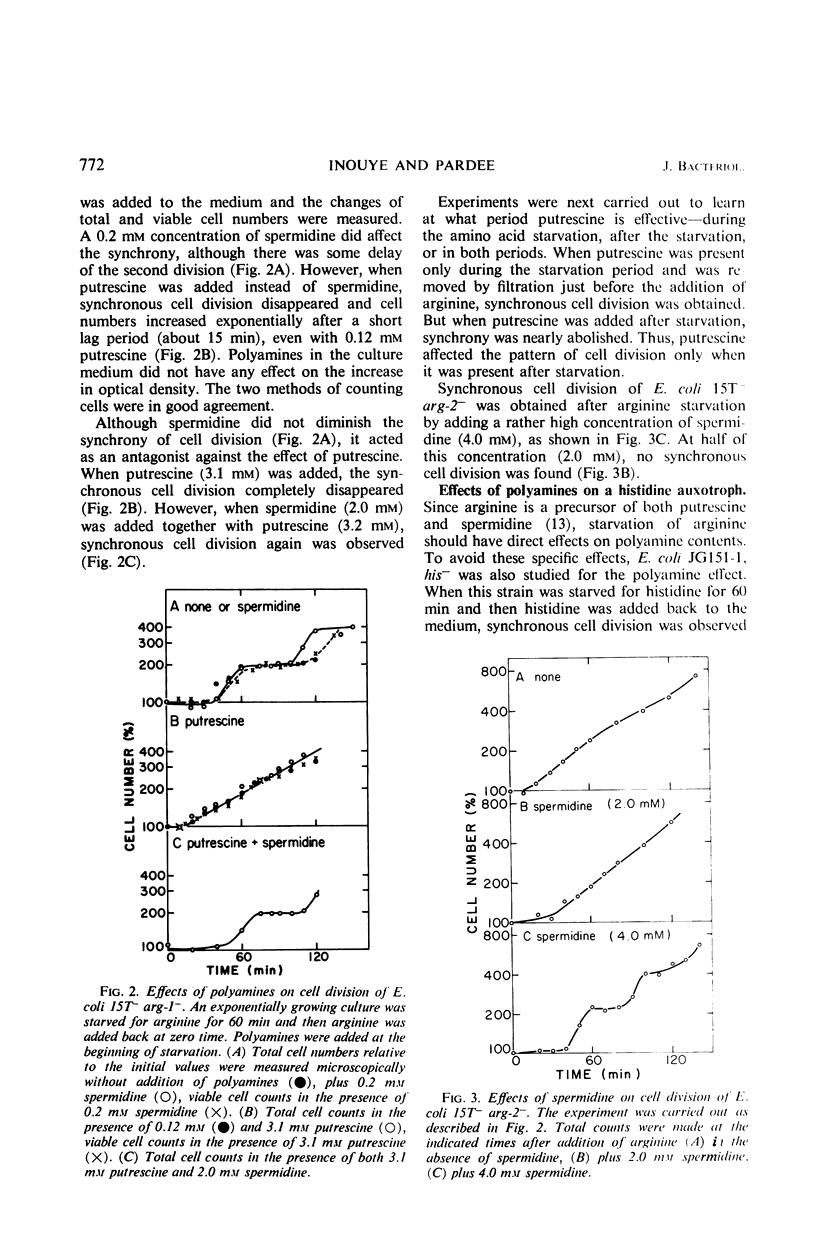
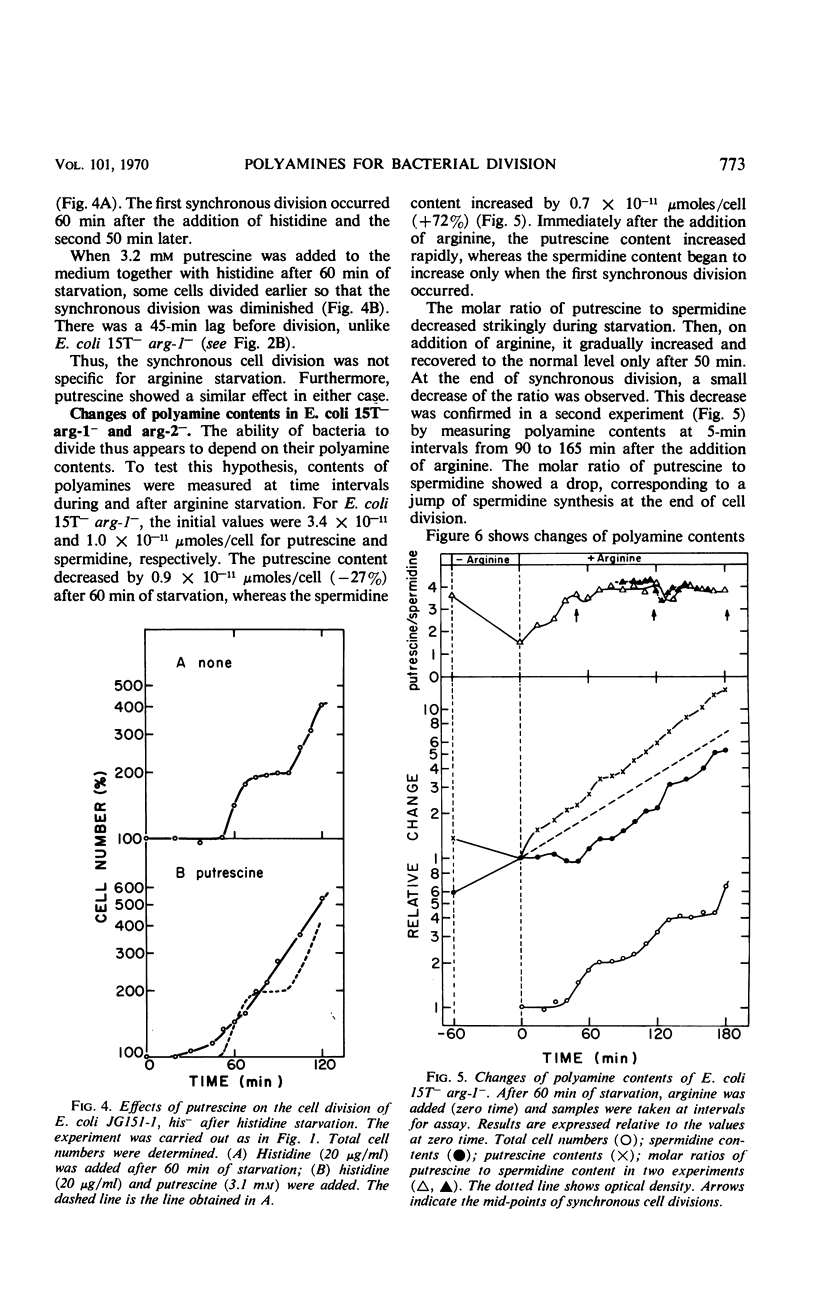
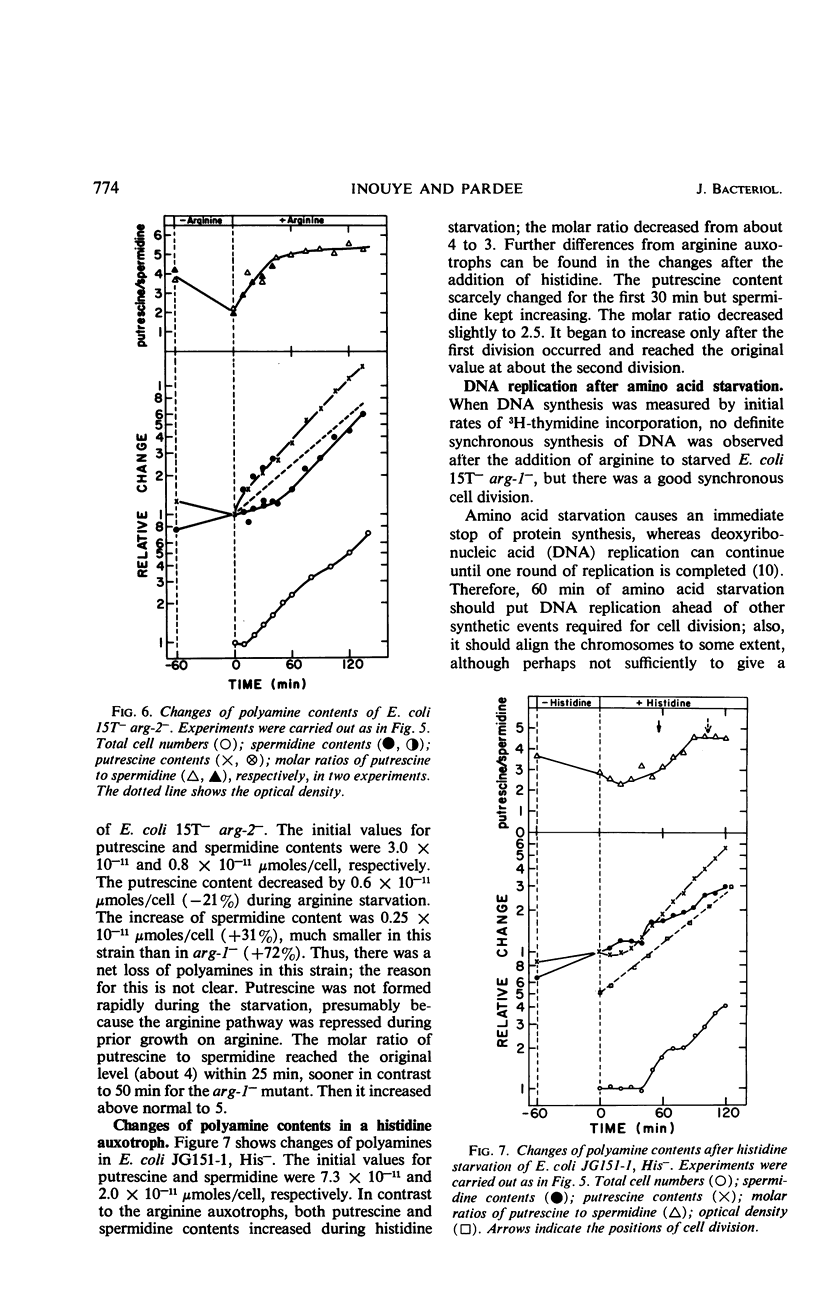
Synchronous cell division in an arginine auxotroph and a histidine auxotroph of Escherichia coli was obtained after starving for the required amino acid for 1 hr. However, cell division was not synchronized after starvation for 1 hr in another arginine auxotroph. This difference is proposed to depend on differences in the concentrations of polyamines in the cells. During amino acid starvation the ratio of putrescine concentration to spermidine concentration decreased in all strains, but it recovered afterward more rapidly in the third strain than in the other two. The cells divided when the ratio returned to normal in the Arg− mutants. Added putrescine permitted some of the cells of the first two mutants to divide sooner after amino acid starvation and thus eliminated synchrony. Spermidine added alone had no effect, but, when it was added together with putrescine, it restored synchronous division. Synchrony was established in the third mutant by adding spermidine after arginine starvation. Thus, both the variations in polyamine content and the effects of added polyamines suggest that the polyamines are essential in permitting cell division. We suggest that the molar ratio of putrescine to spermidine can be a critical factor for cell division. This effect of polyamines seems to be specific for cell division. Amino acid starvation does not induce delays in subsequent mass increase or deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Possible mechanisms of polyamine action are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONHOEFFER F., SCHALLER H. A METHOD FOR SELECTIVE ENRICHMENT OF MUTANTS BASED ON THE HIGH UV SENSITIVITY OF DNA CONTAINING 5-BROMOURACIL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 18;20:93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdá-Olmedo E., Hanawalt P. C., Guerola N. Mutagenesis of the replication point by nitrosoguanidine: map and pattern of replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):705–719. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J. Regulation of deoxyribonucleic acid replication and cell division in Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1214–1224. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1214-1224.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekiel D. H., Brockman H. Effect of spermidine treatment on amino acid availability in amino acid-starved Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C. E. DNA synthesis during the division cycle of rapidly growing Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):507–518. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C. E., Pierucci O. Cell division during inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1627-1633.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Ryter A., Jacob F. Thermosensitive mutants of E. coli affected in the processes of DNA synthesis and cellular division. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:677–693. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M. Unlinking of cell division from deoxyribonucleic acid replication in a temperature-sensitive deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):842–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.842-850.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi M., Hirota Y. Hybridization between Escherichia coli K-12 and 15T- and thymineless death of their derivatives. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1496–1497. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1496-1497.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAALOE O., HANAWALT P. C. Thymine deficiency and the normal DNA replication cycle. I. J Mol Biol. 1961 Apr;3:144–155. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matney T. S., Suit J. C. Synchronously dividing bacterial cultures. I. Synchrony following depletion and resupplementation of a required amino acid in Escerichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):960–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.960-966.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Koffron K. L., Okstein C. J. An automated method for polyamine analysis. Anal Biochem. 1969 Sep;30(3):449–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Pardee A. B. Multiple pathways of putrescine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3129–3135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina A., Cohen S. S. Polyamines and RNA synthesis in a polyauxotrophic strain of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1587–1593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR H., TABOR C. W. SPERMIDINE, SPERMINE, AND RELATED AMINES. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Sep;16:245–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W. The effects of temperature on the acetylation of spermidine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 26;30(4):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90747-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. B., Glaser D. A. Origin and direction of DNA synthesis in E. coli B-r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):881–886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


