Abstract
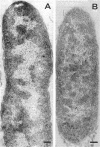
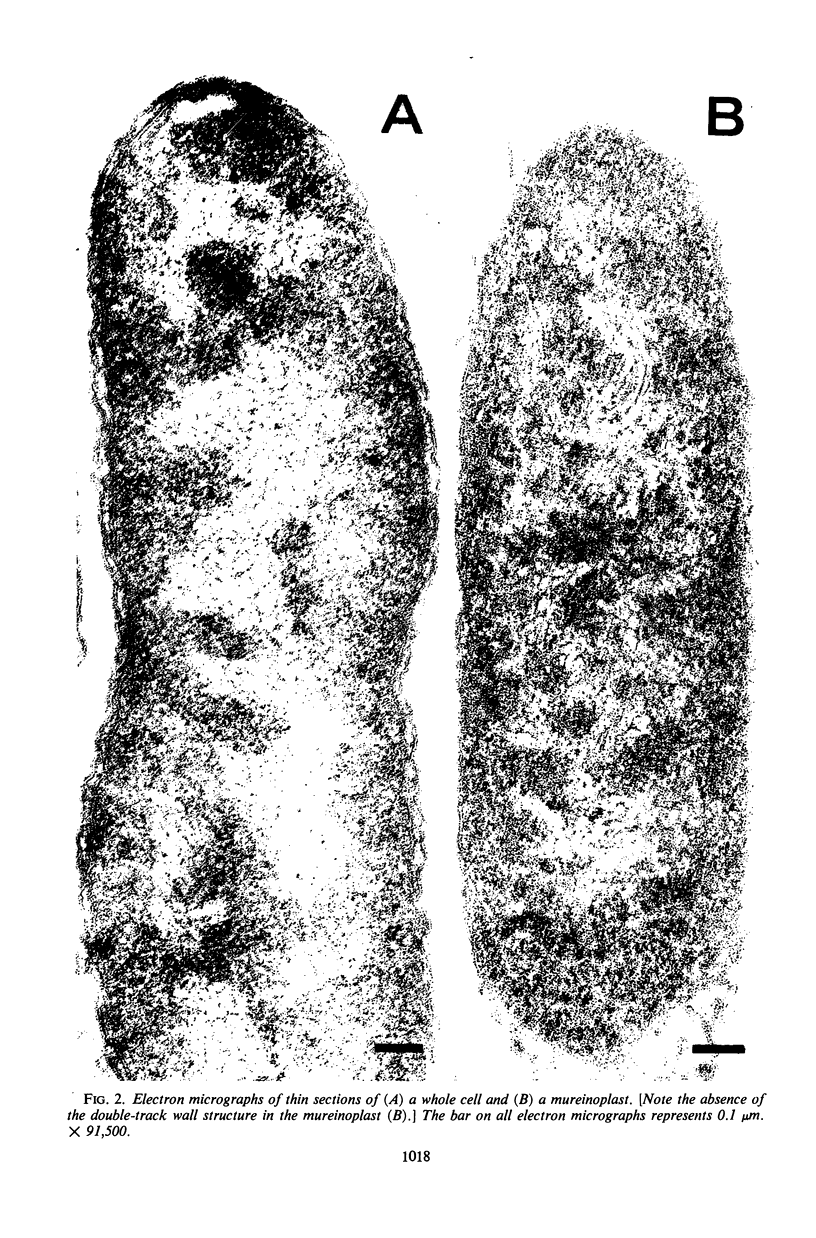
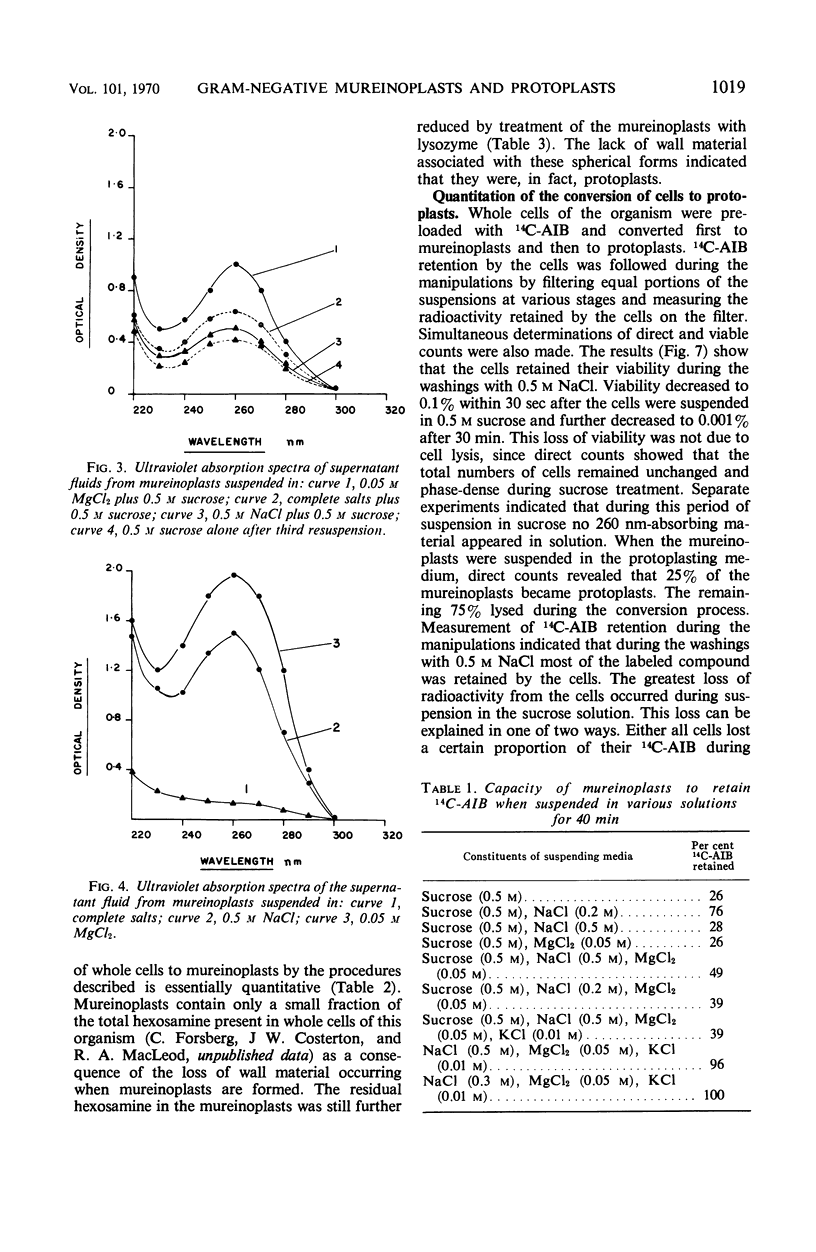
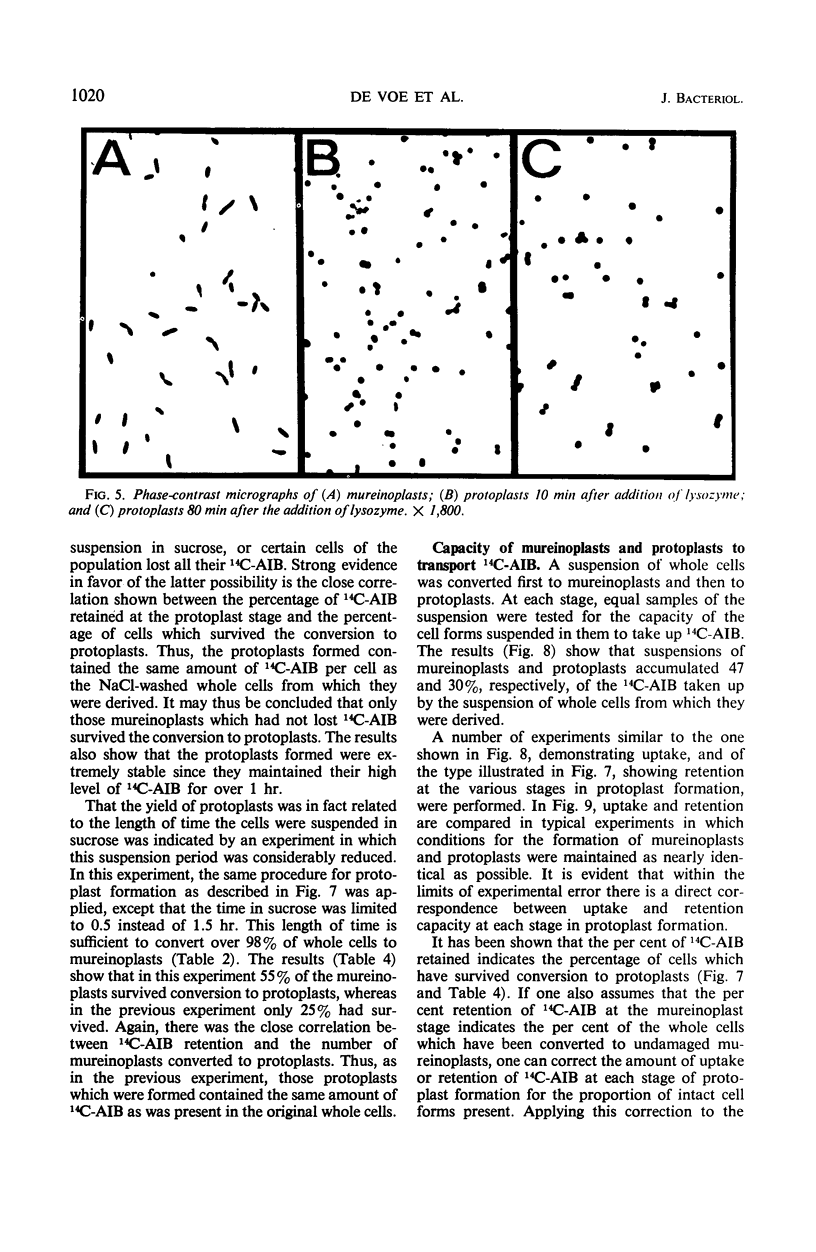
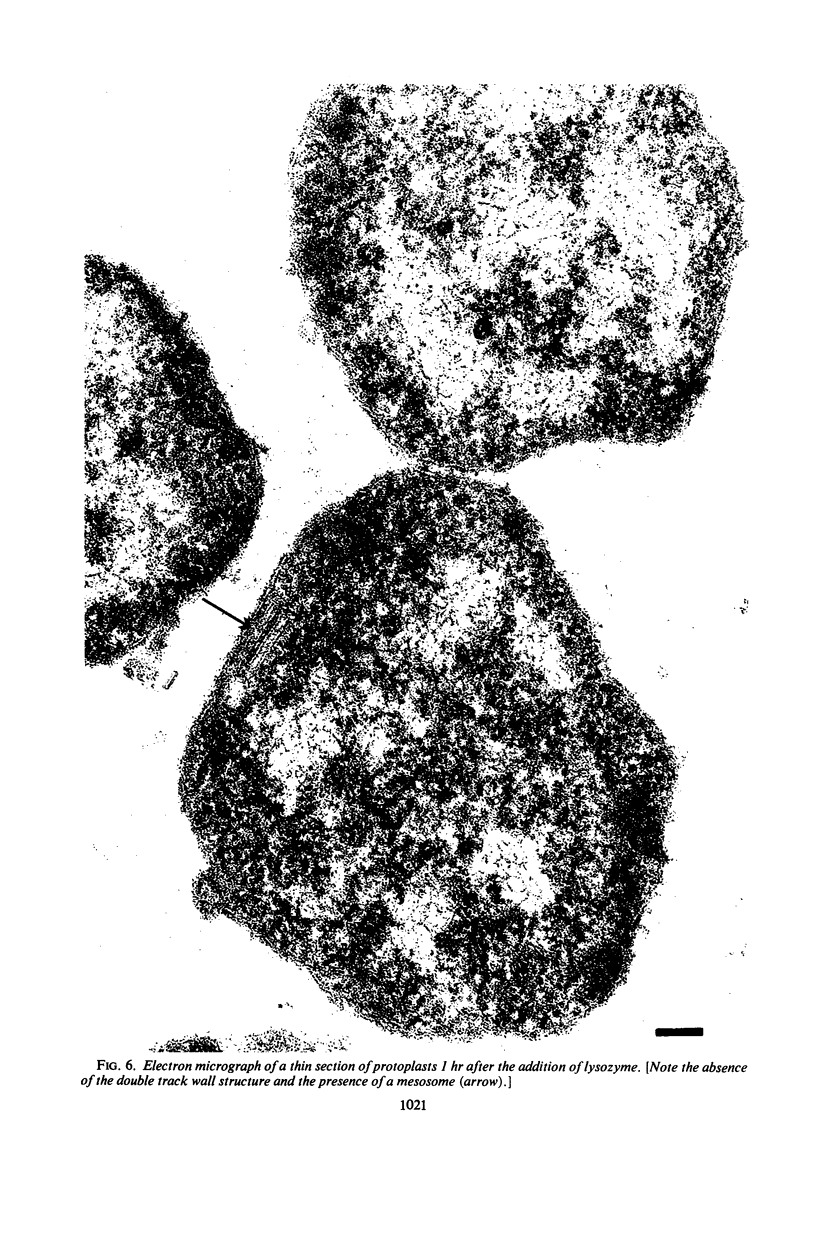
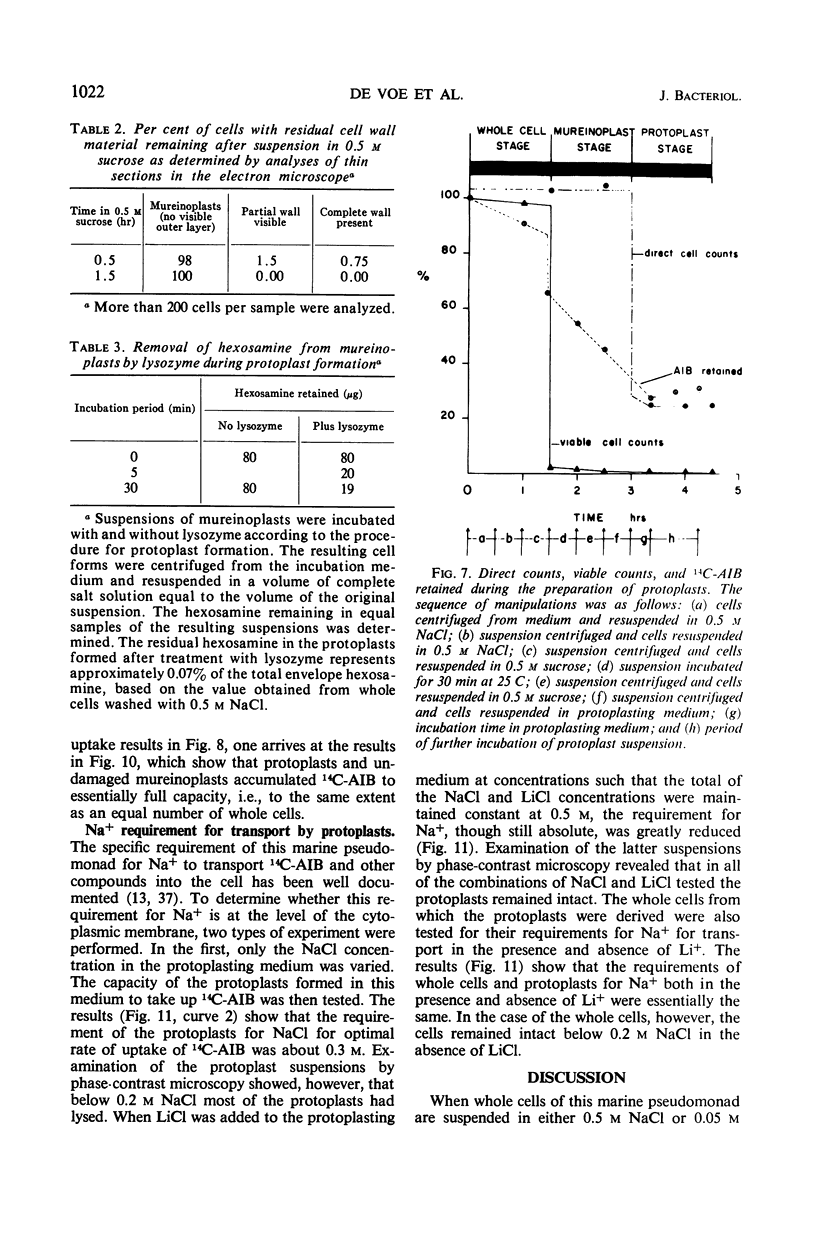
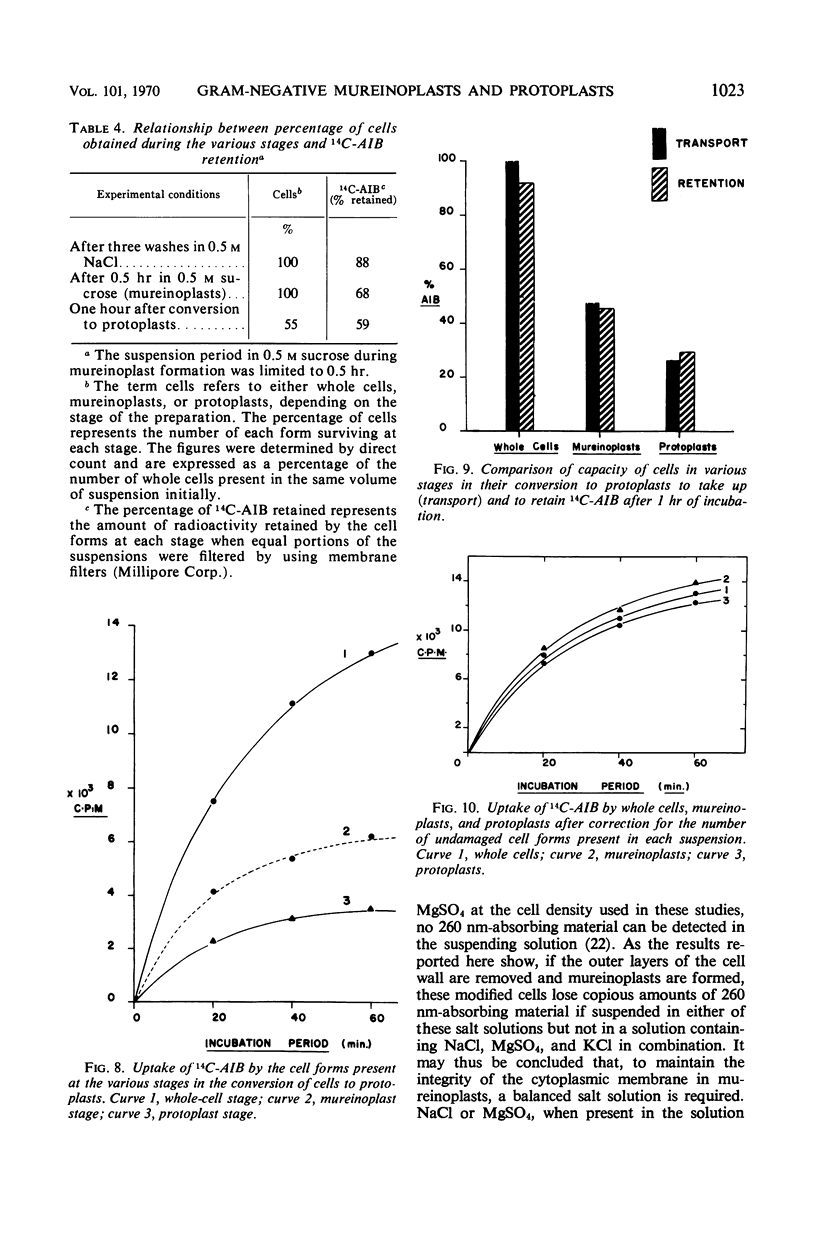
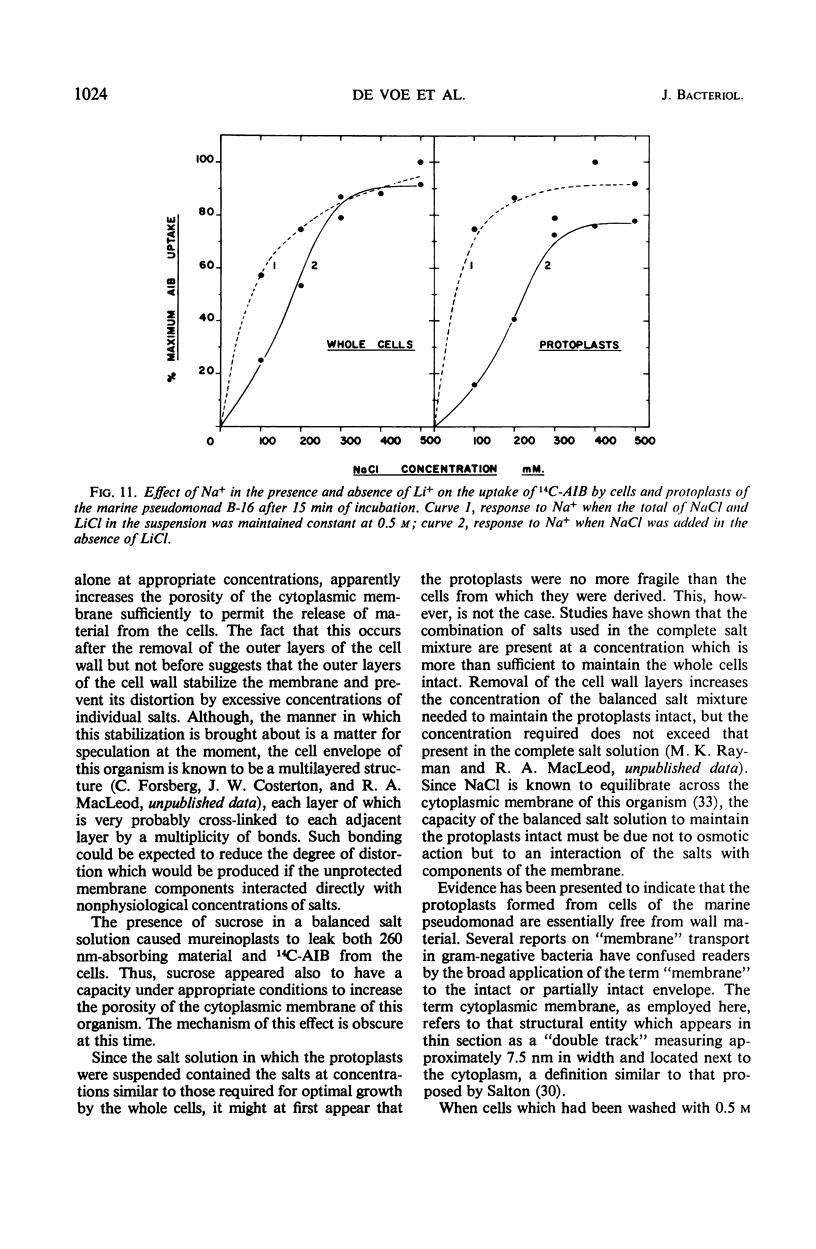
The outer layers of the cell envelope of a pseudomonad of marine origin were removed by washing the cells in 0.5 m NaCl followed by suspension in 0.5 m sucrose. The term mureinoplast has been suggested for the rod-shaped forms which resulted from this treatment. As previously established, these forms lacked the outer cell wall layers but still retained a rigid peptidoglycan structure. Mureinoplasts remained stable if suspended in a balanced salt solution containing 0.3 m NaCl, 0.05 m MgSO4, and 0.01 m KCl but, unlike whole cells, lost ultraviolet (UV)-absorbing material if suspended in 0.5 m NaCl or 0.05 m MgCl2. Sucrose added to the balanced salt solution also enhanced the loss of UV-absorbing material. Addition of lysozyme to suspensions of mureinoplasts in the balanced salt solution produced spherical forms which, by electron microscopy and the analysis of residual cell wall material, appeared to be true protoplasts. Only undamaged mureinoplasts, as judged by their capacity to fully retain α-aminoisobutyric acid, were capable of being converted to protoplasts. Protoplasts and undamaged mureinoplasts retained 100% transport capacity when compared to an equal number of whole cells. The Na+ requirement for transport of α-aminoisobutyric acid and the sparing action of Li+ on this Na+ requirement were the same for both protoplasts and whole cells. These observations indicate that, in this gram-negative bacterium, the cell wall does not participate in the transport process though it does stabilize the cytoplasmic membrane against changes in porosity produced by unbalanced salt solutions. The results also indicate that the requirements for Na+ for transport and for the retention of intracellular solutes are manifested at the level of the cytoplasmic membrane.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anraku Y. The reduction and restoration of galactose transport in osmotically shocked cells of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. 3. Studies on the restoration of active transport. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3128–3135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIBB W. R., STRAUGHN W. R. INDUCIBLE TRANSPORT SYSTEM FOR CITRULLINE IN STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:815–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.815-822.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., MOO-PENN G. An amino acid transport system in Streptococcus faecium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Aug;98:183–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIN G., COHEN G. N., MONOD J., RICKENBERG H. V. La galactoside-perméase d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):829–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XIV. On the mechanism of lysis of a marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Aug;11(4):677–691. doi: 10.1139/m65-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MONOD J. Bacterial permeases. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Sep;21(3):169–194. doi: 10.1128/br.21.3.169-194.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Forsberg C., Matula T. I., Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVI. Formation of protoplasts, spheroplasts, and related forms from a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1764–1777. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1764-1777.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Antagonistic effect of monovalent cations in maintenance of cellular integrity of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1355–1367. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1355-1367.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Cation interactions and biochemical composition of the cell envelope of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1368–1377. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1368-1377.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Kennedy E. P. Specific labeling and partial purification of the M protein, a component of the beta-galactoside transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):891–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. THE ROLE OF PERMEASE IN TRANSPORT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:177–200. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Stadtman E. R. Proline uptake by an isolated cytoplasmic membrane preparation of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):920–927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., McLELLAN W. L., Jr, HORECKER B. L. Galactose transport in Escherichia coli. III. The effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol on entry and accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2585–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. Membrane transport proteins. Proteins that appear to be parts of membrane transport systems are being isolated and characterized. Science. 1968 Nov 8;162(3854):632–637. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3854.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E. L'inclusion au polyester pour l'ultramicrotomie. J Ultrastruct Res. 1958 Dec;2(2):200–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(58)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Finkelstein A. Membrane biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:463–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R. Structure and function of bacterial cell membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:417–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A., Rumley M. K., Kennedy E. P. The function of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the lactose transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):951–958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz E. W., Hochster R. M. Active transport of L-valine by Streptococcus diacetilactis. J Dairy Sci. 1965 Oct;48(10):1282–1286. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(65)88448-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKACS F. P., MATULA T. I., MACLEOD R. A. NUTRITION AND METABOLISM OF MARINE BACTERIA. XIII. INTRACELLULAR CONCENTRATIONS OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IONS IN A MARINE PSEUDOMONAD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.510-518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe W. J., Chapman G. B. Fine structure of selected marine pseudomonads and achromobacters. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1862–1873. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1862-1873.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]