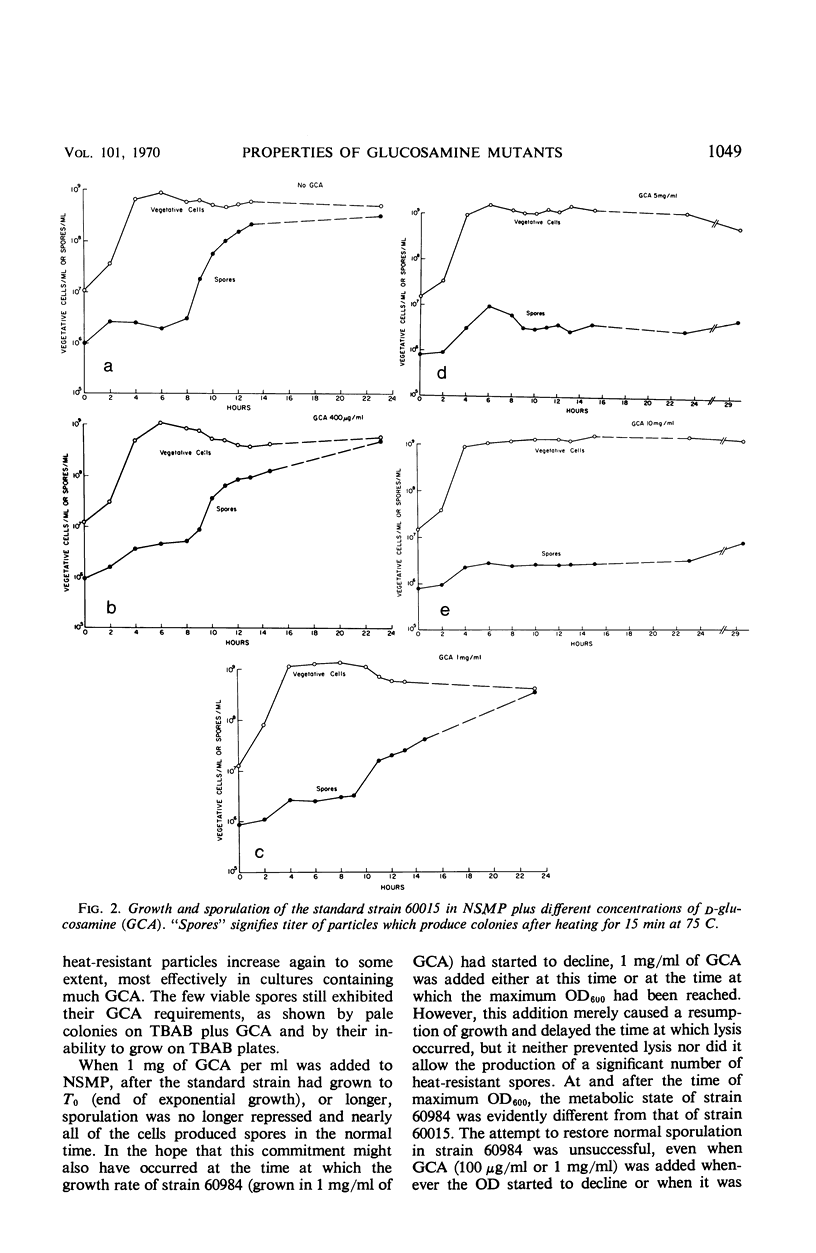
Abstract
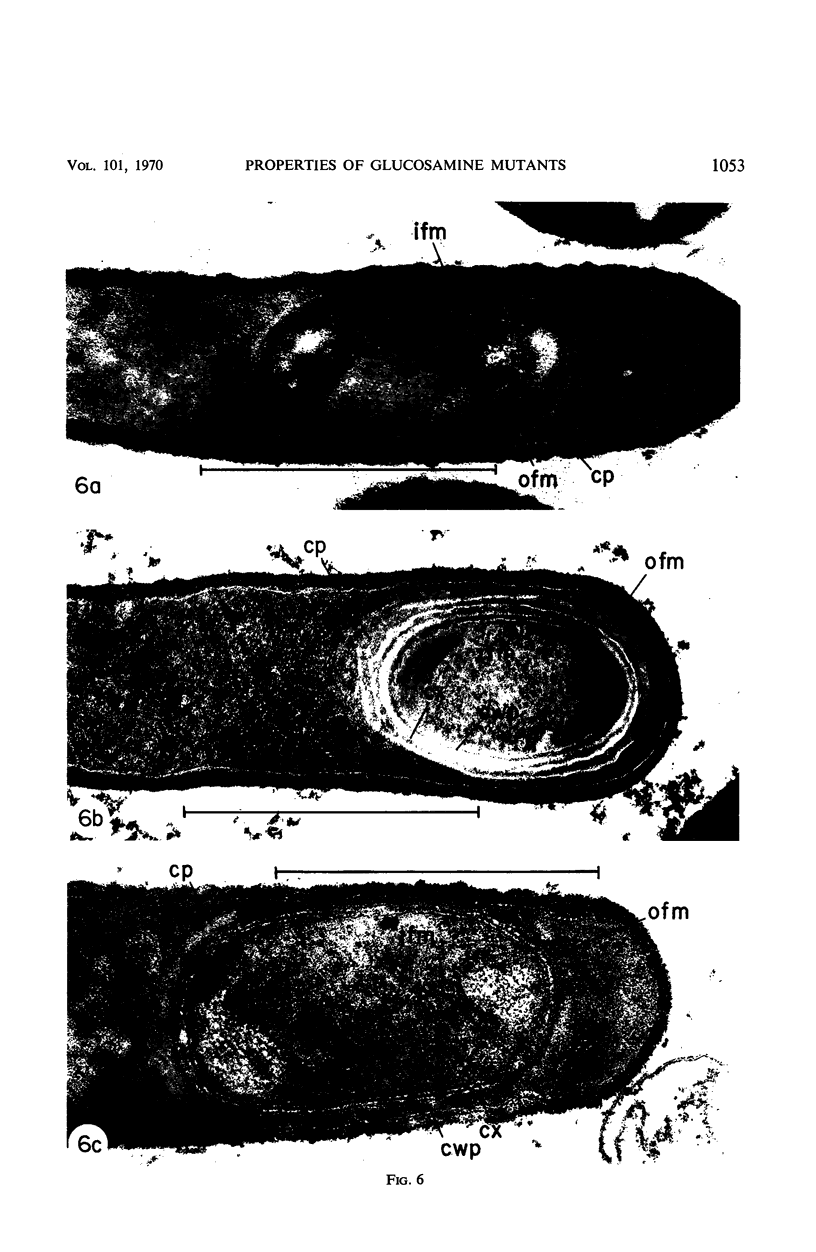
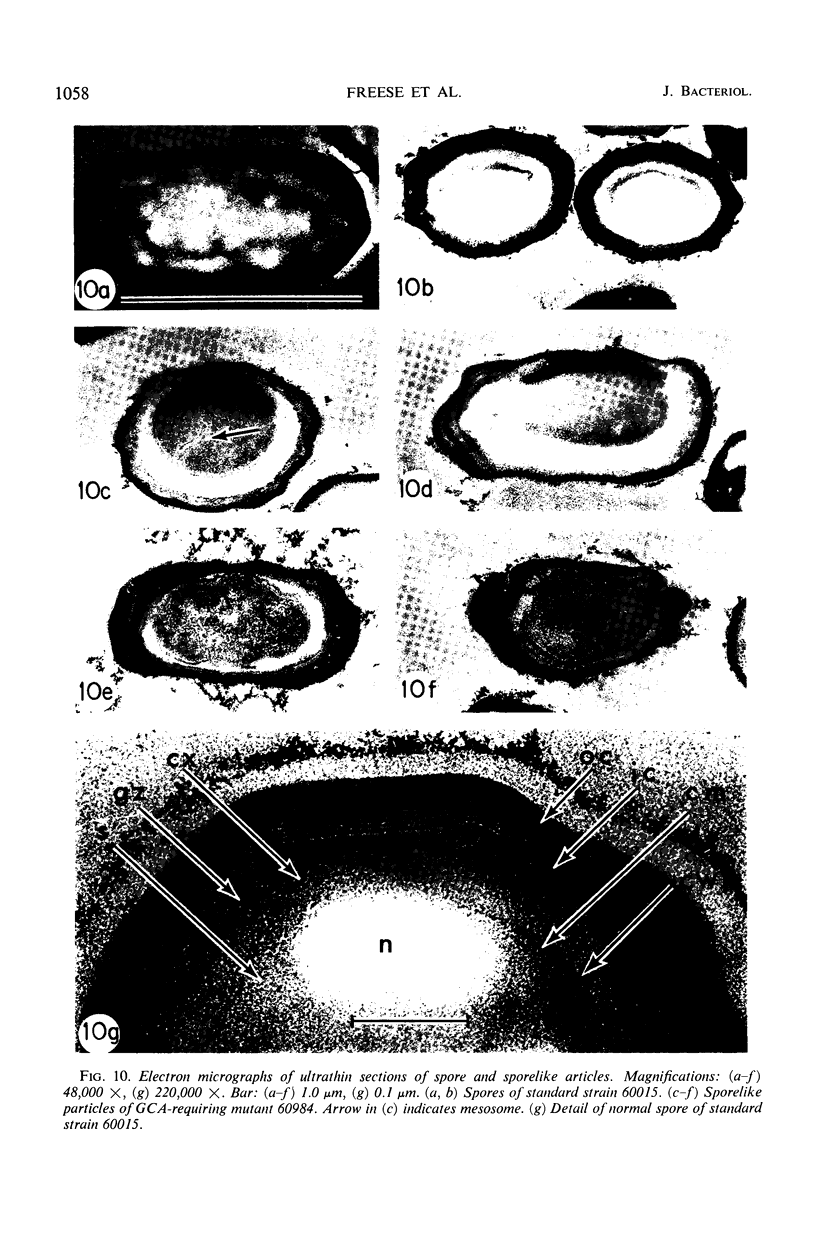
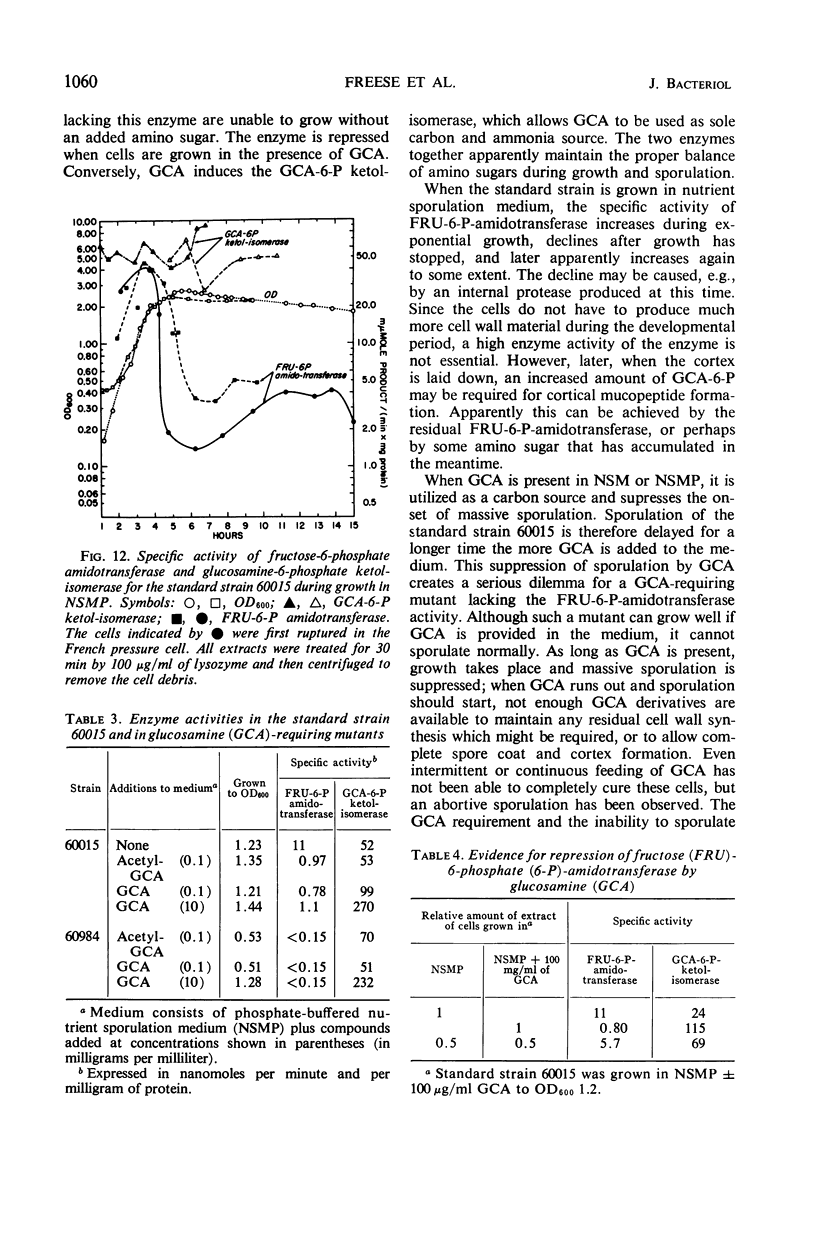
Two glucosamine (GCA)-requiring mutants have been isolated which grow on glucose minimal or nutrient sporulation medium only in the presence of either GCA or acetyl-GCA. They lack the l-glutamine-d-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.13), which is repressible by GCA and whose activity in the standard strain decreases after cessation of growth. But the mutants can grow on GCA as sole carbon and ammonia source, because GCA induces the synthesis of 2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucose-6-phosphate ketol-isomerase (deaminating) (EC 5.3.1.10). With respect to sporulation, the GCA-requiring mutants are in a serious dilemma, as GCA represses the onset of massive sporulation and yet a small amount of GCA-6-phosphate derivatives is necessary to allow sporulation. When GCA is continuously provided in small quantities, sporelike particles are produced which contain little or no spore cortex but a normal spore coat. Apparently, GCA derivatives are needed especially for cortex formation. Many of the sporelike particles can produce colonies after octanol, but not after heat treatment. When they are purified by treatment with lysozyme and sodium dodecylsulfate, they do not show the decrease in optical density at 600 nm typical of germination nor do they produce offspring.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayen H., Frehel C., Ryter A., Sebald M. Etude cytologique de la sporulation chez Clostridium histolyticum. Souche sporogène et mutants de sporulation. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Aug;113(2):163–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G., ROSEMAN S. Glucosamine metabolism. IV. Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):807–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. W. Morphogenesis in bacteria: some aspects of spore formation. Q Rev Biol. 1956 Jun;31(2):102–118. doi: 10.1086/401259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Fortnagel P. Analysis of sporulation mutants. I. Response of uracil incorporation to carbon sources, and other mutant properties. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1957–1969. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1957-1969.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRELET N. Le déterminisme de la sporulation de bacillus megatherium II. L'effet de la pénurie des constituants minéraux du milieu synthétique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Jan;82(1):66–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiragi Y., Iijima K., Kadota H. Hexagonal single crystal pattern from the spore coat of Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1967 Jul 8;215(5097):154–155. doi: 10.1038/215154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiragi Y., Iijima K., Kadota H. Splitting line of bacterial spore. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1392–1393. doi: 10.1038/2151392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAWATA T., INOUE T., TAKAGI A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF SPORE FORMATION AND GERMINATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Jpn J Microbiol. 1963 Jun;7:23–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1963.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R. Studies on L-glutamine D-fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase. I. Feedback inhibition by uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3135–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., MCALLAN A. The N-acetylation and estimation of hexosamines. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:127–132. doi: 10.1042/bj0730127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A. ETUDE MORPHOLOGIQUE DE LA SPORULATION DE BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jan;108:40–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau M., Fléchon J., Hermier J. Etude au microscope électronique de la germination de la spore chex Bacillus subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Aug;111(2):149–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Schaeffer P., Ionesco H. Classification cytologique, par leur stade de blocage, des mutants de sporulation de Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOKUYASU K., YAMADA E. Fine structure of Bacillus subtilis. II. Sporulation progress. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):129–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARTH A. D., OHYE D. F., MURRELL W. G. Location and composition of spore mucopeptide in Bacillus species. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:593–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wax R., Freese E., Cashel M. Separation of two functional roles of L-alanine in the initiation of Bacillus subtilis spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):522–529. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.522-529.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. E., JAMES P. C. Chemical and morphological studies of bacterial spore formation. IV. The development of spore refractility. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jan;12:115–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








