Abstract
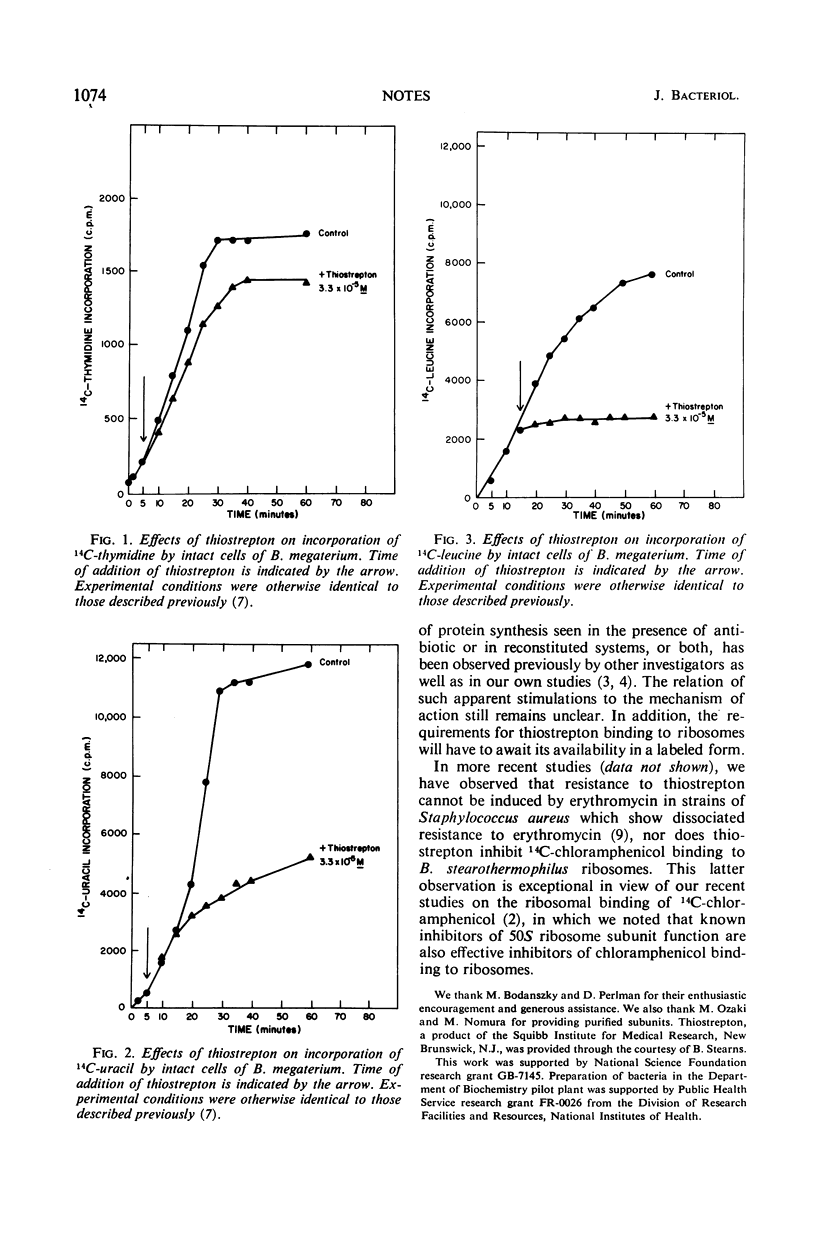
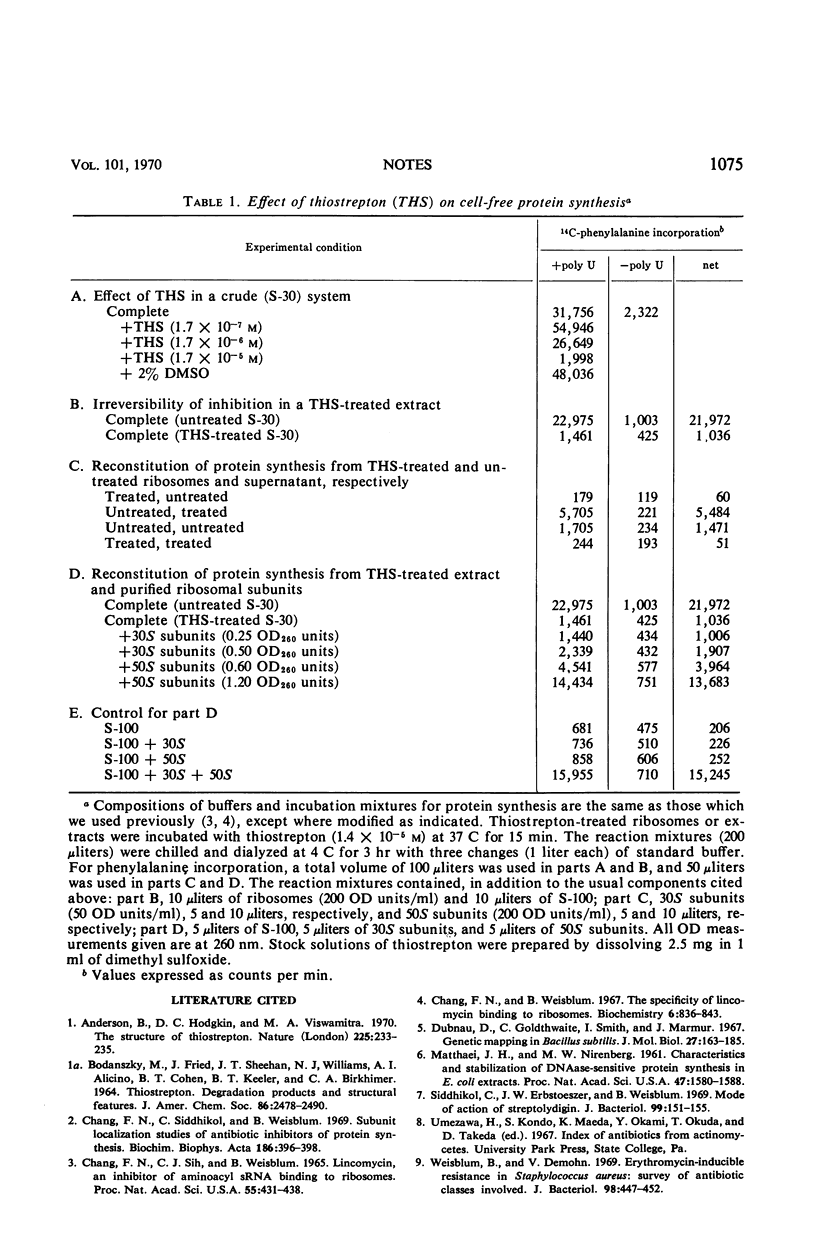
Thiostrepton inhibits 14C-leucine incorporation by intact cells of Bacillus megaterium as well as 14C-phenylalanine incorporation by a poly U-directed extract of Escherichia coli. Extracts of E. coli which are pretreated by incubation with thiostrepton cannot be reactivated by dialysis to more than 5% of their former activity. The 50S ribosome subunit appears to be the site of thiostrepton action, since protein-synthesizing activity can be restored to dialyzed pretreated extracts by supplementation with 50S ribosome subunits but not with 30S ribosome subunits. This technique also provides a simple sensitive method for detection of the biological activity of very small amounts of 50S ribosome subunits.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B., Hodgkin D. C., Viswamitra M. A. The structure of thiostrepton. Nature. 1970 Jan 17;225(5229):233–235. doi: 10.1038/225233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Siddhikol C., Weisblum B. Subunit localization studies of antibiotic inhibitors of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 20;186(2):396–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Sih C. J., Weisblum B. Lincomycin, an inhibitor of aminoacyl sRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):431–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Weisblum B. The specificity of lincomycin binding to ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):836–843. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Goldthwaite C., Smith I., Marmur J. Genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):163–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddhikol C., Erbstoeszer J. W., Weisblum B. Mode of action of streptolydigin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.151-155.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: survey of antibiotic classes involved. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):447–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.447-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



