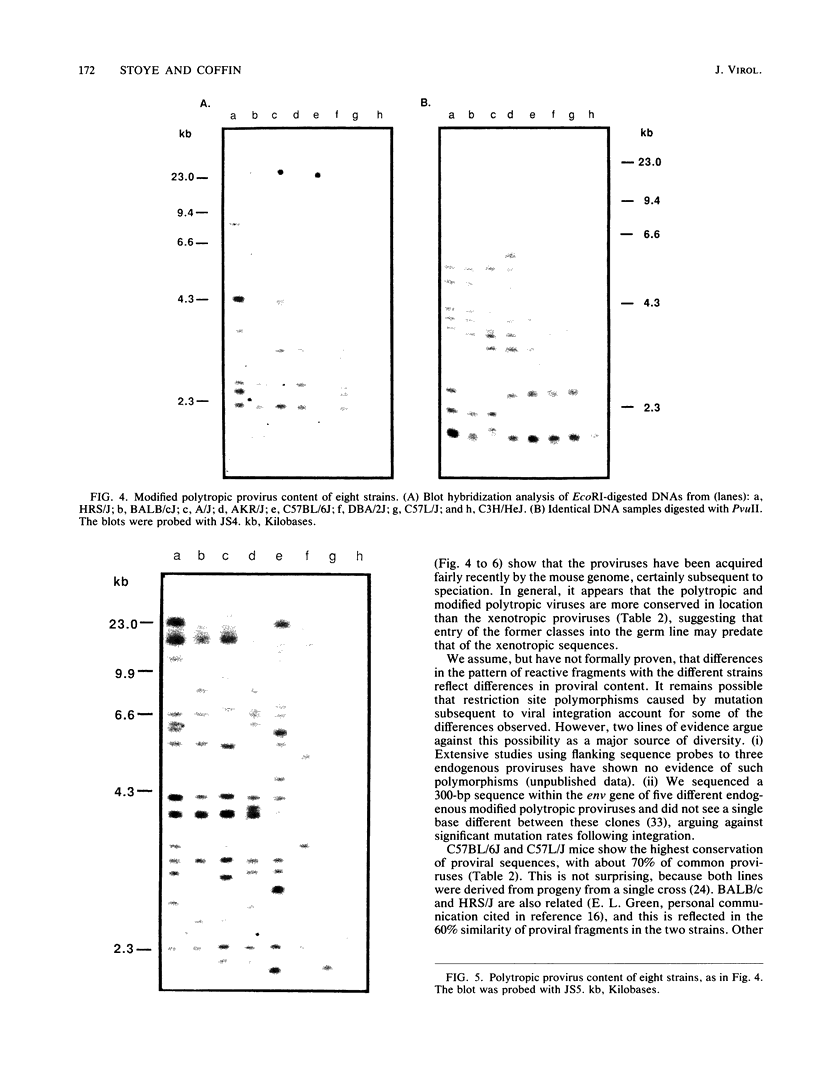
Abstract
Inbred mice contain three classes of endogenous nonecotropic murine leukemia virus-related sequences, namely xenotropic, polytropic, and modified polytropic proviruses. Oligonucleotide probes specific for the three different classes were prepared and used to examine the diversity of endogenous sequences present in eight different strains of mice: HRS/J, BALB/cJ, A/J, AKR/J, C57BL/6J, DBA/2J, C57L/J, and C3H/HeJ. A high degree of polymorphism was observed. Overall, the strains showed between 17% (A/J and HRS/J) and 65% (C57BL/6J and C57L/J) shared proviruses, and only four proviruses were present in all eight strains. The similarity among the strains is due in part to the few proviruses present in all of the strains but also represents the independent assortment of a limited set of proviruses. These oligonucleotides provide a basis for determining the stability, distribution, and mutagenic potential of nonecotropic proviruses within the mouse genome.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Mileham K., Haas M., Nesbitt M. N., Harper M. E., Simon M. I. Chromosomal mapping of the mink cell focus-inducing and xenotropic env gene family in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6298–6302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., Hoggan M. D., Chan H. W., Sears J. F., Khan A. S., Moore J. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Cloning and characterization of an envelope-specific probe from xenotropic murine leukemia proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.228-236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Hutchison K. W., Jenkins N. A. Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Lee B. K. Association of the lethal yellow (Ay) coat color mutation with an ecotropic murine leukemia virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):247–249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolberg D. S., Bacheler L. T., Fan H. Endogenous type C retroviral sequences of mice are organized in a small number of virus-like classes and have been acquired recently. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):96–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.96-106.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris S. D., Sage R. D., Wilson A. C. Evidence from mtDNA sequences that common laboratory strains of inbred mice are descended from a single female. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):163–165. doi: 10.1038/295163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Atchley W. R. Evolution in inbred strains of mice appears rapid. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1169–1175. doi: 10.1126/science.4001935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., O'Neill R. R., Kozak C. A. Nonecotropic murine leukemia viruses in BALB/c and NFS/N mice: characterization of the BALB/c Bxv-1 provirus and the single NFS endogenous xenotrope. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):980–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.980-986.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Wozney J., Hopkins N. Nucleotide sequence of the gp70 gene of murine retrovirus MCF 247. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.413-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. High frequency germline acquisition of ecotropic MuLV proviruses in SWR/J-RF/J hybrid mice. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Martin M. A. Endogenous murine leukemia proviral long terminal repeats contain a unique 190-base-pair insert. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2699–2703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-inducing loci in five mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):219–228. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A. Susceptibility of wild mouse cells to exogenous infection with xenotropic leukemia viruses: control by a single dominant locus on chromosome 1. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):690–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.690-695.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lerner R. A., Wilson M. C. Normal expression of polymorphic endogenous retroviral RNA containing segments identical to mink cell focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):691–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.691-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meruelo D., Rossomando A., Offer M., Buxbaum J., Pellicer A. Association of endogenous viral loci with genes encoding murine histocompatibility and lymphocyte differentiation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5032–5036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Buckler C. E., Theodore T. S., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Envelope and long terminal repeat sequences of a cloned infectious NZB xenotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.100-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Khan A. S., Hoggan M. D., Hartley J. W., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Specific hybridization probes demonstrate fewer xenotropic than mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus env-related sequences in DNAs from inbred laboratory mice. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.359-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou C. Y., Boone L. R., Yang W. K. A novel sequence segment and other nucleotide structural features in the long terminal repeat of a BALB/c mouse genomic leukemia virus-related DNA clone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5603–5620. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A. Interference grouping of murine leukemia viruses: a distinct receptor for the MCF-recombinant viruses in mouse cells. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mice induced by retrovirus insertion into the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):315–320. doi: 10.1038/304315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Russell L. B., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Allelic variation within the Emv-15 locus defines genomic sequences closely linked to the agouti locus on mouse chromosome 2. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):85–92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Mural R., Cowing D., Mielcarz J., Young J., Roblin R. Most of the murine leukemia virus sequences in the DNA of NIH/swiss mice consist of two closely related proviruses, each repeated several times. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.127-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. The four classes of endogenous murine leukemia virus: structural relationships and potential for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2659–2669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2659-2669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Moroni C. Endogenous retrovirus expression in stimulated murine lymphocytes. Identification of a new locus controlling mitogen induction of a defective virus. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1660–1674. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wejman J. C., Taylor B. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Endogenous xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related sequences map to chromosomal regions encoding mouse lymphocyte antigens. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):237–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.237-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]