Abstract
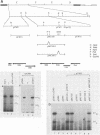
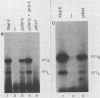
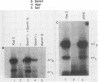
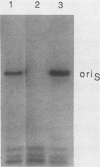
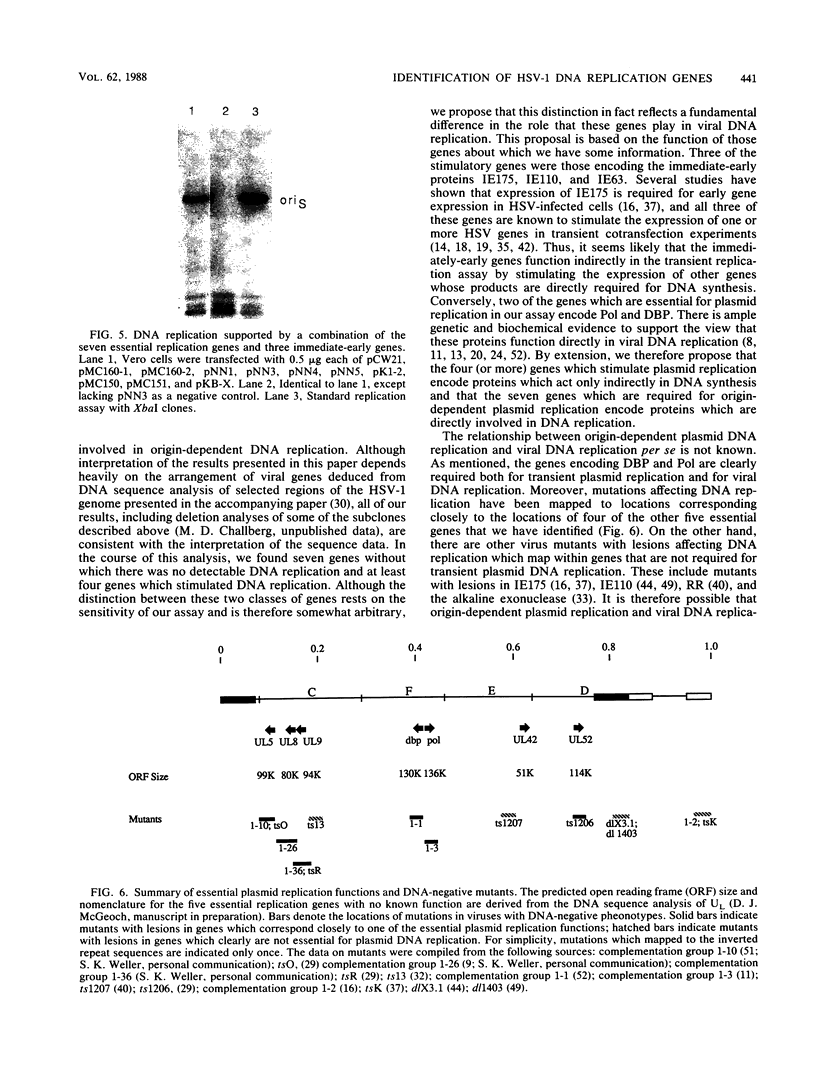
The herpes simplex virus (HSV) genome contains both cis- and trans-acting elements which are important in viral DNA replication. The cis-acting elements consist of three origins of replication: two copies of oriS and one copy of oriL. It has previously been shown that five cloned restriction fragments of HSV-1 DNA together can supply all of the trans-acting functions required for the replication of plasmids containing oriS or oriL when cotransfected into Vero cells (M. D. Challberg, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 83:9094-9098, 1986). These observations provide the basis for a complementation assay with which to locate all of the HSV sequences which encode trans-acting functions necessary for origin-dependent DNA replication. Using this assay in combination with the data from large-scale sequence analysis of the HSV-1 genome, we have now identified seven HSV genes which are necessary for transient replication of plasmids containing either oriS or oriL. As shown previously, two of these genes encode the viral DNA polymerase and single-stranded DNA-binding protein, which are known from conventional genetic analysis to be essential for viral DNA replication in infected cells. The functions of the products of the remaining five genes are unknown. We propose that the seven genes essential for plasmid replication comprise a set of genes whose products are directly involved in viral DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss G. J., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Herpes simplex virus proteins: DNA-binding proteins in infected cells and in the virus structure. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Dym H., Sarov I. Herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1968 Oct;36(2):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of paar mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 by intertypic marker rescue. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):265–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.265-276.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Timbury M. C., Hay J., Moss H. Mutant of herpes simplex virus type 2 with temperature-sensitive lesions affecting virion thermostability and DNase activity: identification of the lethal mutation and physical mapping of the nuc-lesion. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.140-146.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. T., Parris D. S., Dixon R. A., Farber F. E., Schaffer P. A. Hydroxylamine mutagenesis of HSV DNA and DNA fragments: introduction of mutations into selected regions of the viral genome. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):168–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., McLauchlan J., McGeoch D. J. Orientation of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):77–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Aschman D. P., Gelep P. T., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Schaffer P. A. Fine mapping and molecular cloning of mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):236–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.236-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H. Ribonucleotide reductase activity of synchronized KB cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):408–418. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.408-418.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The products of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate early genes 1, 2 and 3 can activate HSV-1 gene expression in trans. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2507–2513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 that are resistant to phosphonoacetic acid induce altered DNA polymerase activities in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):145–148. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R. Acquisition of thymidine kinase activity by herpes simplex-infected mouse fibroblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 2;11:55–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz B., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Preston V. G. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 using cloned restriction endonuclease fragments. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2261–2270. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
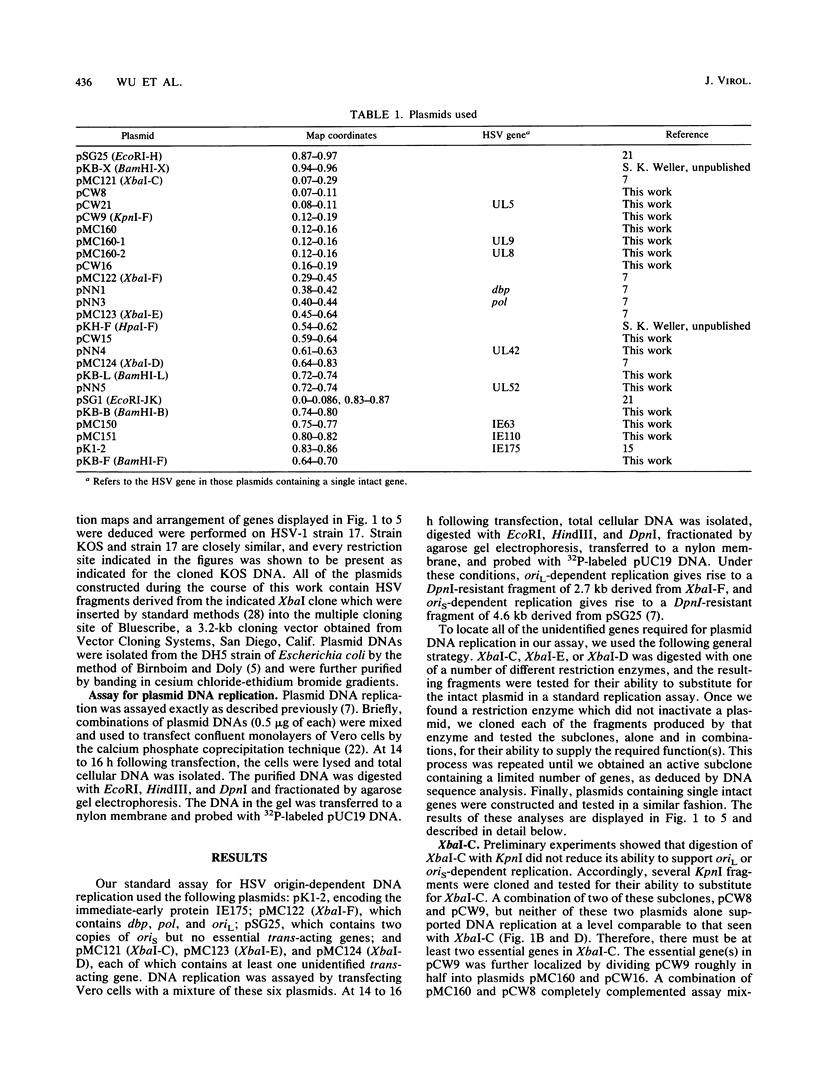
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. M., Keir H. M. A new DNA-exonuclease in cells infected with herpes virus: partial purification and properties of the enzyme. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):337–347. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss H. The herpes simplex virus type 2 alkaline DNase activity is essential for replication and growth. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1173–1178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
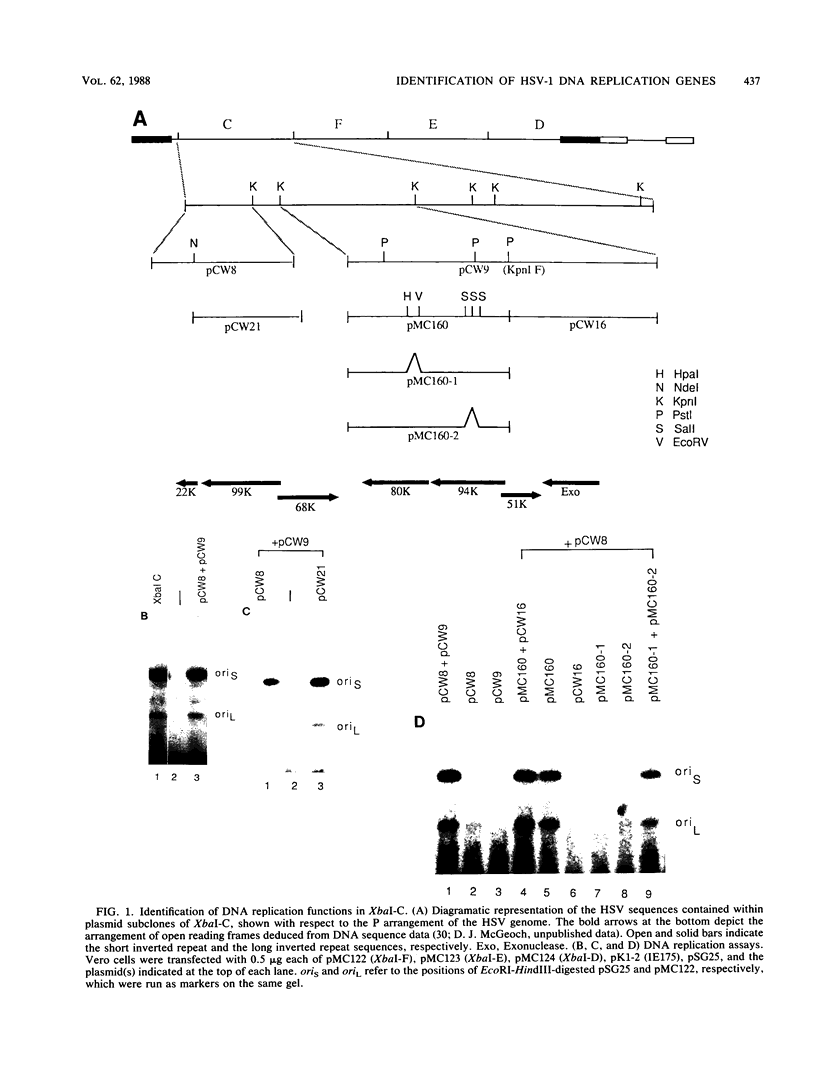
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polvino-Bodnar M., Orberg P. K., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 oriL is not required for virus replication or for the establishment and reactivation of latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3528–3535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3528-3535.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G. mRNA- and DNA-directed synthesis of herpes simplex virus-coded exonuclease in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):386–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.386-394.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
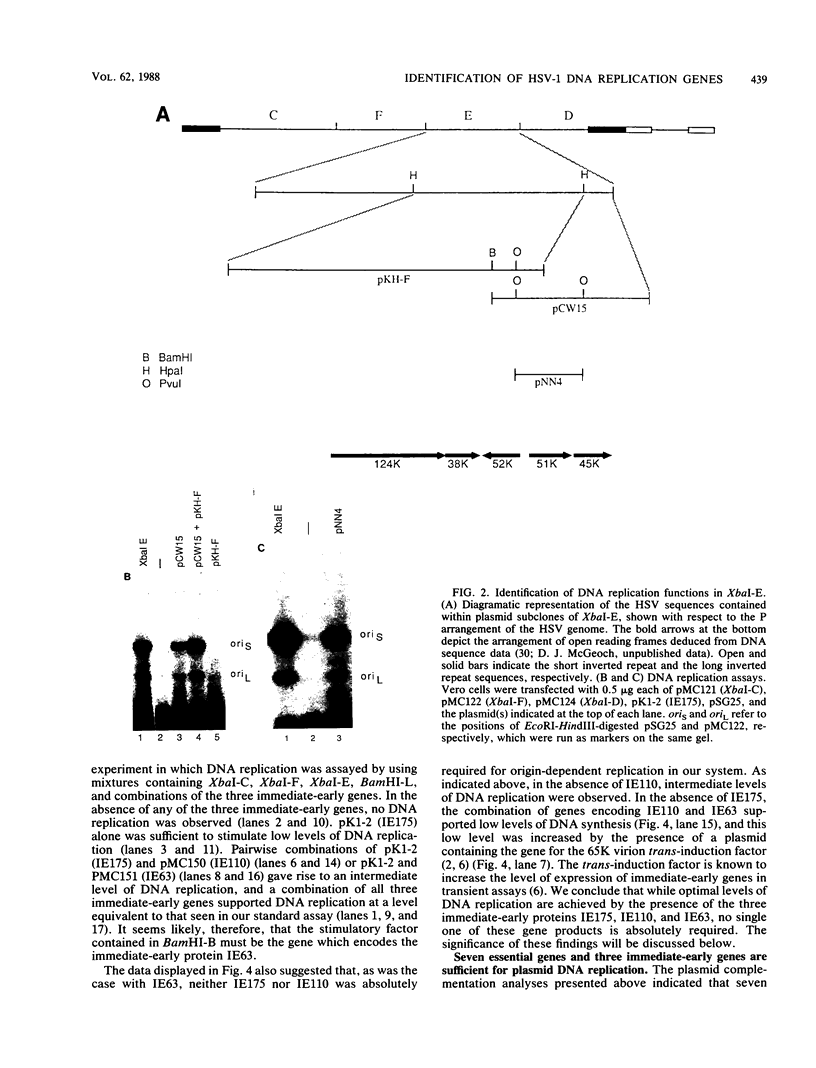
- Preston V. G., Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Timbury M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Recombinants between herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: analyses of genome structures and expression of immediate early polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):499–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.499-517.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Palfreyman J. W., Dutia B. M. Identification of a herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide which is a component of the virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1457–1466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
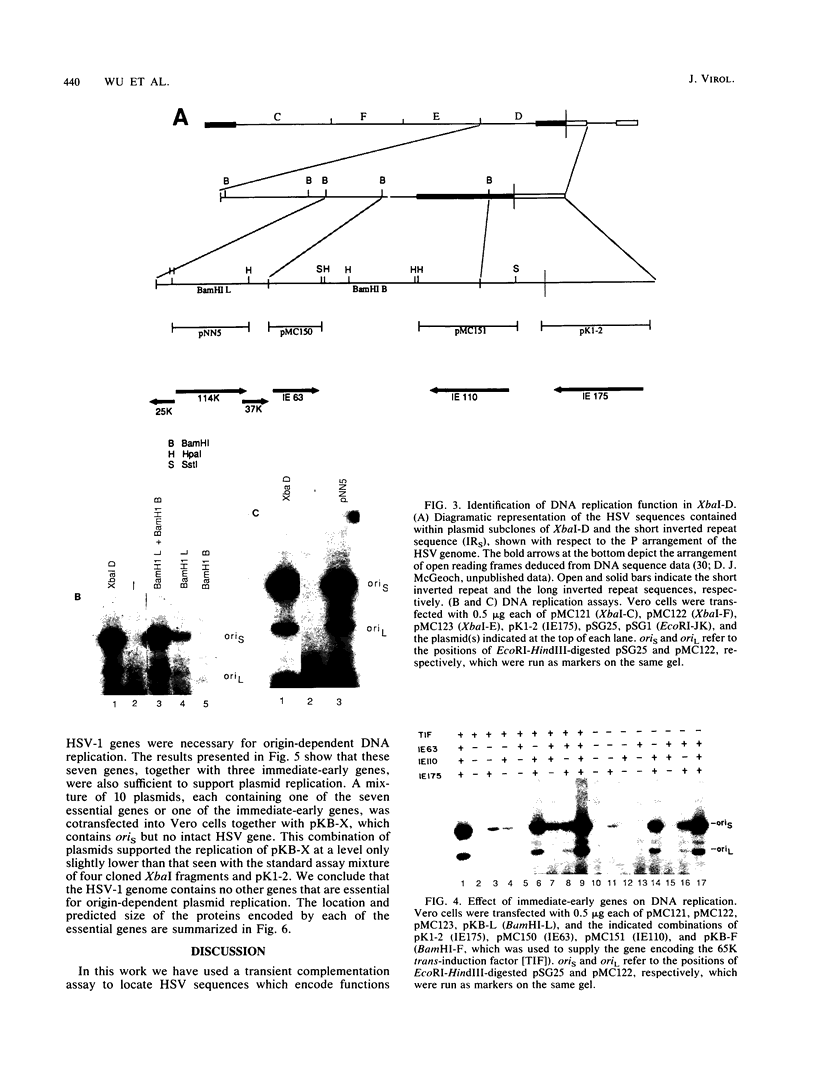
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding proteins induced by herpes simplex virus type 2 in HEp-2 cells. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):717–731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.717-731.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the genes for DNA polymerase and the major DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8143–8163. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Aschman D. P., Sacks W. R., Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV-1: the combined use of complementation and physical mapping for cistron assignment. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):290–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]