Abstract
To investigate phylogenetic relationships among plasmons in Triticum and Aegilops, PCR–single-strand conformational polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) analyses were made of 14.0-kb chloroplast (ct) and 13.7-kb mitochondrial (mt)DNA regions that were isolated from 46 alloplasmic wheat lines and one euplasmic line. These plasmons represent 31 species of the two genera. The ct and mtDNA regions included 10 and 9 structural genes, respectively. A total of 177 bands were detected, of which 40.6% were variable. The proportion of variable bands in ctDNA (51.1%) was higher than that of mtDNA (28.9%). The phylogenetic trees of plasmons, derived by two different models, indicate a common picture of plasmon divergence in the two genera and suggest three major groups of plasmons (Einkorn, Triticum, and Aegilops). Because of uniparental plasmon transmission, the maternal parents of all but one polyploid species were identified. Only one Aegilops species, Ae. speltoides, was included in the Triticum group, suggesting that this species is the plasmon and B and G genome donor of all polyploid wheats. ctDNA variations were more intimately correlated with vegetative characters, whereas mtDNA variations were more closely correlated with reproductive characters. Plasmon divergence among the diploids of the two genera largely paralleled genome divergence. The relative times of origin of the polyploid species were inferred from genetic distances from their putative maternal parents.
Keywords: organellar genomes, evolution
Genetic diversity among plasmons within two genera, Triticum and Aegilops, was first reported by Kihara (1). On producing alloplasmic lines of common wheat (2n = 6x = 42, nuclear genome AABBDD), and then tracking plasmon-specific phenotypic variations, we were able to classify the plasmons of Triticum and Aegilops species into 16 types (2). The next logical step was to identify molecular variation of their organellar DNAs. First, the discovery of RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) variation among ct and mtDNAs was reported (3). Second, physical maps of common wheat ctDNA were constructed by using three restriction enzymes (4). The ctDNA maps were refined by using 13 restriction enzymes, after which we discovered that the chloroplast genomes of 33 Triticum and Aegilops species fell into 16 types (5). Eventually, RFLP analyses of mtDNAs from 17 species allowed us to distinguish their mitochondrial genomes from each other (6). Even though sequencing analyses are not as thorough as the RFLP analyses, the sequence of one chloroplast gene (rbcL, for the Rubisco large subunit) from seven Triticum and Aegilops species indicated that Ae. speltoides is the donor of both the plasmon and B genome of common wheat (7).
Although RFLP and sequencing analyses have been employed, sequencing lags behind. RFLP analyses are relatively easy but are insensitive to fine-structure variation. Sequencing is the ultimate way to detect variation, but it is cumbersome when applied to large numbers of species and DNA regions. This paper reports a new technique, PCR–single-strand conformational polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) analysis, which overcomes the weaknesses of past methods. PCR-SSCP analyses consist of PCR amplification, restriction enzyme digestion, and electrophoresis on nondenaturing acrylamide gels (8). DNA variation is detected as the difference in migration distances of single-stranded PCR products arising from changes in primary and secondary structures. PCR-SSCP is sensitive to about 80% of all DNA variations, including single nucleotide substitutions, and, importantly, it permits handling of large numbers of samples (9).
The objectives of this study were twofold. The first was to further clarify the phylogenetic relationships among Triticum and Aegilops species by way of both chloroplast (ct) and mitochondrial (mt)DNA variation. The second was to correlate DNA variation within organellar genomes to phenotypic variation among the alloplasmic wheats with the same nuclear genotype.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Materials.
Forty-six alloplasmic lines of common wheat with plasmons from 31 Triticum and Aegilops species, plus one euplasmic line, were used (Table 1). These include all species of the genera except for Triticum urartu and T. boeoticum. Among the alloplasmic lines, 36 had the nuclear genome of T. aestivum cv. Chinese Spring, and the other 10 had the nuclear genome of T. aestivum cv. Jones Fife, T. compactum, T. spelta, or T. macha, all of which are common wheats. All of the alloplasmic lines were backcrossed with their nucleus donors 4 to 19 times.
Table 1.
The genetic constitution of the 46 alloplasmic and 1 euplasmic (control) line used for SSCP analysis
| Plasmon donor to the alloplasmic
|
Alloplasmic line
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species and subspecies, variety, or cultivar | Ploidy | Genome constitution | Code no. | Nuclear genotype | Plasmon type | Backcross generation |
| Genus Triticum group Einkorn | ||||||
| T. monococcum | 2X | A | 16 | CS | A2 | 9 |
| Genus Triticum group Emmer | ||||||
| T. dicoccoides var. spont. | 4X | AB | 21 | CS | B | 7 |
| T. dicoccum cv. Vernal | 4X | AB | 22 | CS | B | 7 |
| Genus Triticum group Common | ||||||
| T. aestivum (control) | 6X | ABD | 52 | CS | B | — |
| T. aestivum | 6X | ABD | 11 | CS | B | 8 |
| T. aestivum ssp. tibet. | 6X | ABD | 58 | CS | B | 6 |
| Genus Triticum group Timopheevi | ||||||
| T. araraticum | 4X | AG | 23 | Splt | G | 9 |
| T. araraticum | 4X | AG | 24 | CS | G | 12 |
| T. timopheevi | 4X | AG | 25 | Splt | G | 12 |
| T. zhukovskyi | 6X | AAG | 51 | Splt | G | 7 |
| Genus Aegilops section Amblyopyrum | ||||||
| Ae. mutica | 2X | T | 13 | CS | T | 7 |
| Ae. mutica | 2X | T | 14 | CS | T2 | 12 |
| Genus Aegilops section Comopyrum | ||||||
| Ae. comosa | 2X | M | 05 | CS | M | 7 |
| Ae. heldreichii | 2X | M | 06 | CS | Mh | 14 |
| Ae. uniaristata | 2X | N | 07 | CS | N | 7 |
| Genus Aegilops section Cylindropyrum | ||||||
| Ae. caudata var. poly. | 2X | C | 02 | Cmp | C | 19 |
| Ae. caudata | 2X | C | 27 | CS | C | 10 |
| Ae. cylindrica | 4X | CD | 28 | CS | D | 7 |
| Genus Aegilops section Polyeides | ||||||
| Ae. umbellulata | 2X | U | 03 | JF | U | 8 |
| Ae. triuncialis | 4X | UC | 26 | CS | U | 10 |
| Ae. triuncialis | 4X | UC | 38 | Cmp | C2 | 14 |
| Ae. biuncialis | 4X | UM | 29 | CS | U | 7 |
| Ae. biuncialis | 4X | UM | 37 | CS | U | 9 |
| Ae. columnaris | 4X | UM | 30 | CS | U2 | 12 |
| Ae. ovata | 4X | UM | 31 | CS | M0 | 15 |
| Ae. triaristata 4X | 4X | UM | 32 | Cmp | U | 5 |
| Ae. triaristata 6X | 6X | UMN | 54 | CS | U | 5 |
| Ae. triaristata 6X | 6X | UMN | 57 | CS | U | 5 |
| Ae. kotschyi | 4X | US | 33 | CS | Sv | 8 |
| Ae. kotschyi | 4X | US | 39 | Cmp | Sv | 4 |
| Ae. variabilis | 4X | US | 34 | CS | Sv | 7 |
| Genus Aegilops section Sitopsis | ||||||
| Ae. speltoides var. auch. | 2X | S | 09 | Mch | G2 | 8 |
| Ae. speltoides var. auch. | 2X | S | 17 | CS | S | 8 |
| Ae. speltoides var. ligust. | 2X | S | 08 | CS | S | 8 |
| Ae. speltoides var. ligust. | 2X | S | 15 | Splt | G | 7 |
| Ae. bicornis | 2X | Sb | 12 | CS | Sb | 7 |
| Ae. longissima | 2X | Sl | 20 | CS | Sl2 | 4 |
| Ae. sharonensis | 2X | Sl | 10 | CS | Sl | 10 |
| Ae. searsii | 2X | Ss | 18 | CS | Sv | 6 |
| Genus Aegilops section Vertebrata | ||||||
| Ae. squarrosa | 2X | D | 04 | CS | D | 7 |
| Ae. squarrosa | 2X | D | 19 | CS | D | 9 |
| Ae. ventricosa | 4X | DN | 36 | CS | D | 7 |
| Ae. crassa 4X | 4X | DM | 35 | CS | D2 | 7 |
| Ae. crassa 6X | 6X | DDM | 55 | CS | D2 | 8 |
| Ae. juvenalis | 6X | DMN | 53 | CS | D2 | 7 |
| Ae. vavilovii | 6X | DMS | 56 | CS | D2 | 7 |
Nuclear genotype: CS and JF, T. aestivum cv. Chinese Spring and cv. Jones Fife; Cmp, T. compactum; Splt, T. spelta; and Mch, T. macha; all Common wheats. Genome constitution (haploid) and plasmon type after Kimber and Tsunewaki (1988). Modified genomes are underlined.
ct and mtDNA Regions Investigated.
Nucleotide sequences were obtained from the GenBank database. Seven regions of ctDNA and nine regions of mtDNA were chosen at random. Their total lengths were 14.0 and 13.7 kb, respectively. The ctDNA regions included the 3′ flanking region of the Rubisco large subunit gene (rbcL) (10) and 10 structural genes: encoding ATP synthase, α, β, and ɛ subunits (atpA, atpB, and atpE) (11), ATP synthase, CF0 subunit III and CF0 subunit I (atpH and atpF) (12), the 47-kDa chlorophyll a-binding protein, the 10-kDa phosphoprotein of photosystem II, photosystem II polypeptide of 43 aa, apocytochrome b-563, and the 15-kDa polypeptide of the cytochrome b–f complex (psbB, psbN, psbH, petB, and petD) (13). The mtDNA regions include nine structural genes: encoding the cytochrome oxidase subunit I, II, and III (cox1, cox2, and cox3) (14–16), the ATP synthase α subunit (atpA) (17), NADH dehydrogenase subunit I (nad1-a, nad1-b, and nad1-e) (18), cytochrome b (cob) (19), and ORF25 (orf25) (20). All of the primers used for PCR amplification were designed upon the sequences published in the above-mentioned articles.
PCR-SSCP Analyses.
Total DNA from each line was extracted after Liu et al. (21). PCRs were conducted in 50-ml volumes by using a Thermal Cycler PJ2000 (Perkin–Elmer). The PCR procedure with [α-32P]dCTP was described previously (22). To amplify the nad1-b and nad1-e regions of mtDNA, the annealing temperature was changed to 55°C. The procedure for electrophoresis on nondenaturing acrylamide gels has been described (22).
Relationships among molecular and phenotypic variations.
To study the effects of molecular variation on each of the 22 phenotypic characters of alloplasmic wheats, ANOVA were conducted. The model of ANOVA was as follows for each of the variant bands:
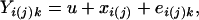 |
where Yi(j)k is the phenotypic value of a trait, u is the overall mean, xi(j) is the effect of molecular variation (band) of the jth line (if variant band is present, i = 1, and if absent, i = 0), and ei(j)k is the residual. Yi(j)k values were cited from G.-Z.W., Y. Matsuoka, and K.T. (unpublished data). The calculation was done with the general linear models procedure of Statistical Analysis System. A total of 1,584 ANOVAs were conducted, i.e., for all the combinations between the 72 variant bands and the 22 phenotypic traits observed.
RESULTS
Variations Detected by SSCP Analyses of ct and mtDNAs.
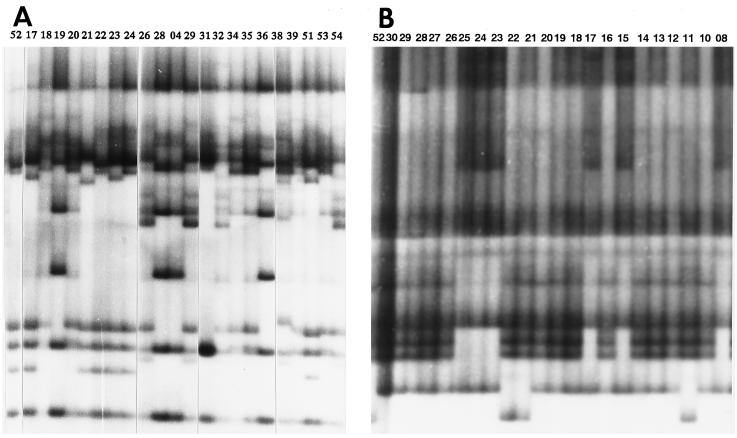
The variations detected by way of SSCP analyses are given in Table 2. In total, 177 bands were found within the organellar genomes, of which 72 were variable (40.7%) (Fig. 1). A total of 94 bands were detected in ctDNA, of which 48 (51.1%) were variable. The proportion of variable bands differed from region to region and was the highest in the 3′ flanking region of rbcL, in which 18 of 22 bands (81.8%) detected were variable. The high level of variation in this region was consistent with the high variation among nucleotide sequences in the same region (7, 10). On the other hand, no variation was detected in the psbB region.
Table 2.
Summary of SSCP detected in each region of the chloroplast and mitochondrial DNAs
| Region and gene | Length, kb | No. of bands | No. of SSCPs | % SSCPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroplast DNA region | ||||
| rbcL3′ flanking | 1.4 | 22 | 18 | 81.8 |
| rbcL5′, atpB, atpE | 2.8 | 13 | 8 | 61.5 |
| atpH, atpF | 1.7 | 13 | 10 | 76.9 |
| atpA | 2.0 | 14 | 3 | 21.4 |
| psbB | 2.1 | 7 | 0 | 0.0 |
| psbN, psbH, petB | 2.0 | 10 | 4 | 40.0 |
| petB, petD | 2.0 | 15 | 5 | 33.3 |
| Sum | 14.0 | 94 | 48 | 51.1 |
| Mitochondrial DNA region | ||||
| cox1 | 1.5 | 9 | 5 | 55.6 |
| cox2 | 1.9 | 13 | 6 | 46.2 |
| cox3 | 0.7 | 4 | 0 | 0.0 |
| atpA | 1.7 | 10 | 3 | 30.0 |
| cob | 0.6 | 2 | 0 | 0.0 |
| nad1-a | 1.1 | 4 | 0 | 0.0 |
| orf25 | 0.4 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 |
| nad1-e | 3.0 | 22 | 4 | 18.2 |
| nad1-b | 2.8 | 16 | 3 | 18.8 |
| Sum | 13.7 | 83 | 24 | 28.9 |
Figure 1.
PCR-SSCP autoradiogram. (A) The atpH-atpF region of ctDNA, and (B) the cox2 region of mtDNA, digested with HinfI. The code number of each line (top of the margin) is given in Table 1.
In mtDNA, 83 bands were detected, of which 24 were variable (28.9%). The proportion of variable bands also varied among regions. In the cox1 and cox2 regions, a high proportion of bands (55.6 and 46.2%, respectively) was variable, whereas no variation was detected in the cox3, cob, and nad1-a regions.
Genetic Distances Among Plasmons.
The total number of bands detected in each line was about the same (ca. 135). The genetic distance between plasmons (d) was calculated as 1 (the proportion of shared bands) for each pair of lines based on variations of both ct and mtDNAs. Rather than presenting distances between each pair of lines, the average and standard error of genetic distances within and between plasmon types are shown in Table 3. There was a significant and positive correlation of genetic distance between chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes (r = 0.25, P < 0.0001). This result indicates that evolution of the two organellar genomes has been parallel only to a limited extent, even though they are inherited maternally as a set.
Table 3.
The average (below the stepwise line) and standard error (above the stepwise line) of genetic distance (×1,000) within and between plasmon types
| Plasmon type | no. | A2 | B | C | D | D2 | G | M | Mh | Mo | N | S | Sb | Sl | Sv | T | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | 1 | −|− | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | − | − | − | − | 0 | − | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| B | 5 | 93 | 13|4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| C | 3 | 80 | 88 | 17|2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| D | 4 | 55 | 73 | 64 | 11|2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| D2 | 4 | 63 | 64 | 44 | 47 | 4|2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| G | 6 | 97 | 61 | 89 | 71 | 75 | 5|1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| M | 1 | 67 | 63 | 62 | 42 | 28 | 65 | −|− | − | − | − | 0 | − | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Mh | 1 | 67 | 63 | 69 | 49 | 35 | 72 | 22 | −|− | − | − | 0 | − | 8 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Mo | 1 | 63 | 67 | 61 | 35 | 39 | 63 | 26 | 33 | −|− | − | 0 | − | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| N | 1 | 67 | 60 | 64 | 36 | 24 | 64 | 22 | 22 | 33 | −|− | 1 | − | 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| S | 2 | 97 | 63 | 96 | 79 | 85 | 18 | 74 | 81 | 71 | 74 | 0|− | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Sb | 1 | 82 | 98 | 91 | 74 | 57 | 102 | 52 | 52 | 63 | 51 | 111 | −|− | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| Sl | 2 | 78 | 90 | 82 | 62 | 53 | 93 | 52 | 48 | 59 | 33 | 103 | 26 | 15|− | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Sv | 4 | 74 | 84 | 78 | 57 | 52 | 86 | 47 | 47 | 58 | 36 | 95 | 23 | 12 | 7|2 | 1 | 1 |
| T | 2 | 78 | 64 | 62 | 47 | 24 | 75 | 26 | 33 | 37 | 26 | 85 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 7|− | 1 |
| U | 8 | 82 | 80 | 76 | 52 | 44 | 81 | 41 | 48 | 43 | 35 | 87 | 70 | 64 | 63 | 29 | 5|1 |
| Average | − | 76 | 74 | 74 | 56 | 49 | 74 | 46 | 49 | 50 | 43 | 81 | 67 | 61 | 58 | 50 | 60 |
Note that C2, G2, Sl2, and T2 subtypes are included in C, G, Sl, and T types, respectively. No. indicates the number of different plasmons investigated and classified as to plasmon type.
As expected, identical banding patterns (d = 0) were observed mainly among pairs of lines with the same or related plasmons, namely within each of B, D2, G, S, Sv, and U (U2 inclusively) plasmon types. However, some pairs of lines with the same plasmon type did not show identical banding patterns, although estimates of their genetic distances were 0.017 or smaller. This finding suggests a certain degree of within-plasmon-type variation.
Genetic distances between lines with different plasmons were larger than 0.033 in most cases (106 of 120 plasmon pairs compared), with a standard error of 0.008 at most, a clear indication of plasmon divergence within genera. The three largest distances (d = 0.111–0.102) were observed between S and G plasmons of Ae. speltoides and Timopheevi wheats, and Sb and Sl plasmons of Ae. bicornis, Ae. sharonensis, and Ae. longissima (interestingly, all of these Aegilops species belong to the Sitopsis section).
Phylogenetic Trees Drawn from Plasmons of Triticum and Aegilops.
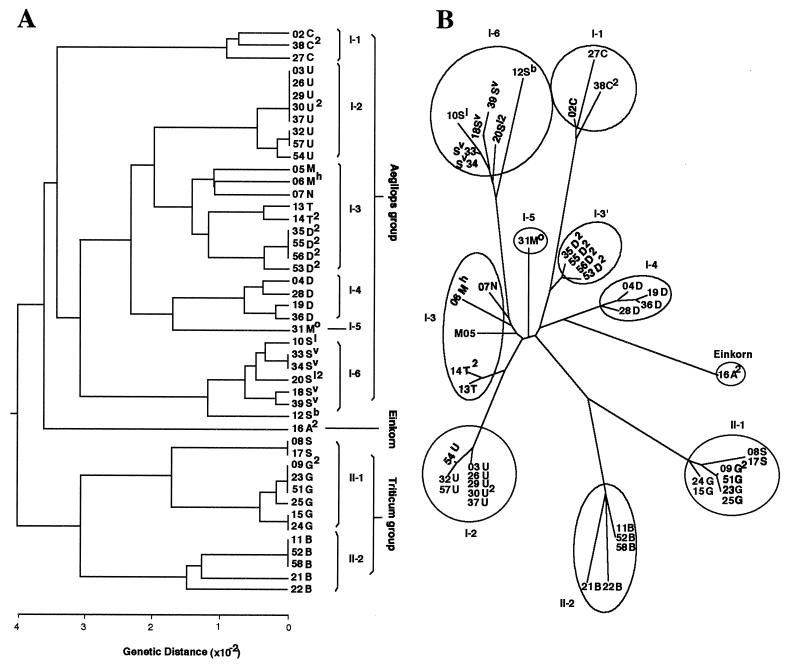
Fig. 2 illustrates the phylogenetic trees constructed by unweighted pair-group method using arithmetic averages (UPGMA) (23) and neighbor-joining (NJ) methods (24). The two trees are essentially identical. Their common features are as follows. First, the plasmons of the two genera fall into three groups (called Aegilops, Einkorn, and Triticum, for convenience). Einkorn is closer to Aegilops than to Triticum in both trees. Second, the Triticum group includes all polyploid wheats and one diploid Aegilops species, Ae. speltoides, carrying the S nuclear genome. This result strongly supports the idea that Ae. speltoides is the plasmon and B and G genome donor of all polyploid wheats (5, 25, 26). Third, the B, G, and S type plasmons of Triticum group fall into two subgroups (II-1 and -2 in Fig. 2). Fourth, the Aegilops group has six subgroups (I-1 to -6 in Fig. 2) that correspond closely to the separate sections.
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic trees for 46 Triticum and Aegilops plasmons based on SSCP variations detected in seven chloroplast and nine mitochondrial DNA regions. (A) A UPGMA tree based on genetic distances. (B) An NJ tree.
Molecular Variation and Phenotypic Traits.
The 179 ANOVAs (11.3%) revealed a significant relationship between molecular and phenotypic variation at the 1% or lower level of probability (we call these “highly significant”). In Tables 4 and 5 only the highly significant correlations are shown. Of 1,056 ctDNA SSCP × trait combinations, 14.8% were highly significant, whereas only 4.4% of mtDNA SSCP × trait combinations were highly significant. Molecular variations within ctDNAs affect phenotypic traits to a much greater extent than do variations in mtDNAs.
Table 4.
Summary of ANOVA on the effect of SSCP variations detected in chloroplast DNA on 22 phenotypic traits in alloplasmic lines
| Trait | Chloroplast gene and SSCP number
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rbcL3′
|
rbcL5′-atpB-atpE
|
atpH-atpF
|
atpA
|
psbN,H,D
|
petB,D
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 33 | 34 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 48 | |
| WV | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||
| GV | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||||||||
| HD | *** | ** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ** | ** | |||||||||||||
| PH | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | ||||||||||||
| EN | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||
| DM | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ** | ||||||||
| CL | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | ||||||||||||
| CD | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ** | ||||||||||||||
| IL1 | *** | *** | ** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||
| IL2 | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ** | ||||||||||||||
| IL3 | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||
| IL4 | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||
| IL5 | ** | ** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||||||||
| EL | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||||||||
| AL | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||
| NS | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||||||
| SFF | ** | *** | *** | ** | ||||||||||||||||||
| PF | *** | |||||||||||||||||||||
| CF | *** | |||||||||||||||||||||
| SFG | ** | *** | ** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||
| HF | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| TF | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The SSCP number was assigned to the variable band detected in this experiment. Only the bands that showed significant F values at the 1% or lower level of probability in ANOVA are shown. Traits are abbreviated as follows: WV, winter variegation; GV, growth vigor; HD, heading date; PH, plant height; EN, ear number per plant; DM, dry matter weight; CL, culm length; CD, culm diameter; IL1–5, 1st–5th internode length; EL, ear length; AL, awn length; NS, number of spikelets per ear; SFF, selfed seed fertility in field; PF, pollen fertility; CF, crossed seed fertility; SFG, selfed seed fertility in greenhouse; HF, haploid frequency; TF, twins frequency.
Table 5.
Summary of ANOVA on the effect of SSCP variations detected in mitochondrial DNA on various phenotypic traits in alloplasmic wheat lines
| Trait | Mitochondrial gene and SSCP number
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
cox1
|
cox2
|
nad1-b
|
nad1-e
|
|||||
| 52 | 53 | 58 | 59 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 72 | |
| HD | ** | |||||||
| PH | *** | |||||||
| EN | ** | |||||||
| DM | ** | ** | *** | |||||
| CL | *** | |||||||
| IL1 | *** | |||||||
| IL2 | ** | |||||||
| IL3 | ** | |||||||
| IL5 | *** | |||||||
| AL | *** | |||||||
| SFF | *** | *** | *** | |||||
| PF | ** | ** | ** | |||||
| SFG | *** | *** | *** | |||||
| TF | ** | *** | ||||||
Refer to the footnotes of Table 4 for the symbols and abbreviations.
Of the 22 phenotypic traits shown in Table 4, the top 16 are vegetative and the bottom 6 are reproductive. A partitioning of two phenotypic categories with molecular variation reveals an interesting feature of the two organellar genomes; namely, chloroplast genomes play a more important role in the vegetative phase of the life cycle, and mitochondrial genomes, in the reproductive phase. The highly significant correlations were detected in 18.5% of the ctDNA SSCP × vegetative trait combinations and only 4.9% of the ctDNA SSCP × reproductive trait combinations. The analogous correlations with mtDNA SSCP were 3.1 and 7.6%, respectively.
DISCUSSION
Genetic Divergence Among Plasmons and Nuclear Genomes Within Diploid Species.
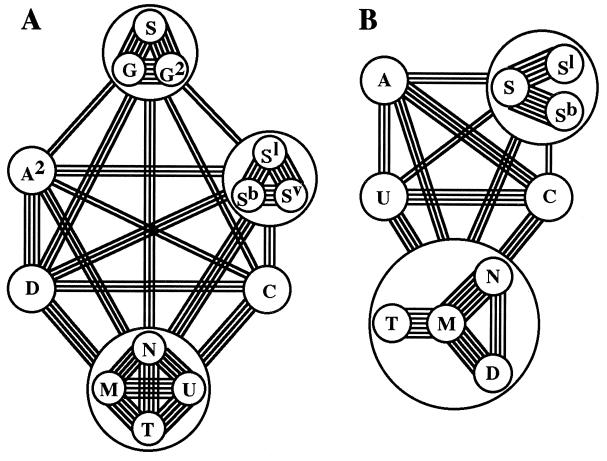
Estimates of genetic distance among plasmons of the diploids reveal genetic relationships among those plasmons (Fig. 3A). These data support our previous conclusion (2), namely that plasmons of the diploids have diverged into 13 types plus 4 subtypes. Genetic relationships among the nuclear genomes of these species have been assayed by previous workers (27, 28) by way of chromosome-pairing affinity (Fig. 3B).
Figure 3.
Plasmon and genome divergence at the diploid level in Triticum and Aegilops. (A) Plasmon relationships revealed by the present study. Number of lines connecting each pair (or group) of plasmons corresponds to their genetic distance (d) as follows: double, triple, quadruple, quintuple, and sextuple lines indicate d = 0.08–0.10, 0.06–0.08, 0.04–0.06, 0.02–0.04, and less than 0.02, respectively. Of 13 types and 4 subtypes of plasmon identified among the diploids, A type and three subtypes, C2, Sl2, and T2, are not shown in this figure, because A type was not studied, and the three subtypes are included in the respective main types, C, Sl, and T. (B) Genomic relationships. The number of lines connecting each pair of genomes corresponds to the modal number of bivalent chromosomes observed among the respective genomes (31, 32).
Comparisons between nuclear and cytoplasmic genomes show a general tendency toward parallel divergence, with three exceptions. First, the S, G, and G2 plasmons of Ae. speltoides differ greatly from the plasmons of Ae. bicornis (Sb), Ae. sharonensis (Sl), Ae. longissima (Sl2), and Ae. searsii (Sv) (Fig. 3A). This result is compatible with the relatively long genetic distances between those species (22, 29). On the contrary, all of those Sitopsis species showed close nuclear genome homology (Fig. 3B). One explanation for this discrepancy is that Ae. speltoides, studied by Kihara, was a high-pairing type, carrying a suppressor for the Ph gene that inhibits pairing between the homoeologous chromosomes (30). The real genome homology between Ae. speltoides and other Sitopsis species is much lower than that described by Kihara (28). Second, the genetic relationships between the U genome of Ae. umbellulata and the C, M, N, T, and D genomes of Ae. caudata, Ae. comosa, Ae. uniaristata, Ae. mutica, and Ae. squarrosa are only moderately close, whereas the plasmon of Ae. umbellulata is closely related to the plasmons of Ae. comosa, Ae. heldreichii, Ae. uniaristata, and Ae. mutica. Third, the D genome of Ae. squarrosa is closely related to the genomes of Ae. comosa, Ae. uniaristata, and Ae. mutica, whereas its D plasmon is more distantly related to the plasmons of the other diploids.
Polyploid Evolution.
From genetic distance, we have predicted aspects of the evolution of polyploids. We assume that genetic distance is indicative of the time of divergence and that rates of attaining polymorphism are the same for species of similar ploidy; if our assumption is correct, then the genetic distance between a putative maternal parent and its polyploid descendant reflects the time between polyploid formation and the present.
First, the ancestral, female parent of the Emmer and Timopheevi wheats was Ae. speltoides (refs. 6 and 25 and this work). The average distance between Emmer and Ae. speltoides was 0.067, whereas that between Timopheevi and Ae. speltoides was 0.012. These distances indicate that Timopheevi is of a more recent origin than Emmer. In turn, they imply diphyletic origin of Emmer and Timopheevi wheats. This conclusion is supported by cytological studies (31) and by RFLP analyses of chloroplast and nuclear DNAs (25, 32, 33). It is from the tetraploid wheats as female parent that Common wheat and T. zhukovski arose. The average distance between Emmer and Common wheats was 0.016, whereas that between Timopheevi and T. zhukovski was 0.004, suggesting that Common wheat appeared at about the same time as Timopheevi, and that T. zhukovski arose quite recently.
The present study supports the dimaternal origin of Ae. triuncialis from reciprocal crosses between Ae. umbellulata and Ae. caudata (34). The plasmons of these species point to zero genetic distance between Ae. triuncialis [line 26] and Ae. umbellulata, and a large distance (average 0.074) between it and Ae. caudata. On the other hand, Ae. triuncialis [38] is a short distance (average 0.019) from Ae. caudata and a much larger distance (0.081) from Ae. umbellulata. If intraspecific variation of Ae. caudata is subtracted from the distance between Ae. triuncialis [38] and Ae. caudata, the distance between them is small, suggesting that both types of Ae. triuncialis arose recently and at about the same time.
Four tetraploid species, Ae. biuncialis, Ae. columnaris, Ae. triaristata, and Ae. triuncialis [26], arose from Ae. umbellulata as mother (2). The distance between Ae. triaristata and Ae. umbellulata is 0.011 but is zero between the other three tetraploids and Ae. umbellulata. This result suggests that Ae. triaristata is the oldest of the four tetraploids.
Ae. squarrosa is the maternal parent of three tetraploids, Ae. cylindrica, Ae. crassa, and Ae. ventricosa (2). The average distances between pairs of these tetraploids and Ae. squarrosa are 0.015, 0.050, and 0.006, respectively. Indeed, the distances between pairs of these tetraploids are relatively large (0.015–0.052), which suggests that these tetraploids originated at three different times from Ae. squarrosa as mother (triphyletic origin) in the order Ae. crassa, Ae. cylindrica, and Ae. ventricosa. The tetraploid form of Ae. crassa is the maternal parent of three hexaploids, Ae. juvenalis, Ae. vavilovii, and Ae. crassa (2). The genetic distances (0.007, 0.000, and 0.000, respectively) suggest that Ae. juvenalis originated a little earlier than the other two species.
Two tetraploids, Ae. kotschyi and Ae. variabilis, arose from Ae. searsii as mother (35). The genetic distances between it and two tetraploids are moderate (0.008 and 0.011) and between the two tetraploids is small (0.005). Apparently, Ae. kotschyi and Ae. variabilis had a monophyletic origin.
Finally, the origin of Ae. ovata is not clear; several diploid species show similar and moderate genetic distances from this species (i.e., Ae. umbellulata, Ae. comosa, Ae. heldreichii, Ae. uniaristata, Ae. mutica, and Ae. squarrosa show genetic distances of 0.032, 0.026, 0.033, 0.033, 0.037, and 0.032, from Ae. ovata). We suggest Ae. mutica to be the putative female parent (2). In any case, this tetraploid appears to be fairly old.
In summary, Emmer wheat is the oldest tetraploid, followed by Ae. crassa and Ae. ovata. All other tetraploids originated relatively recently. As to hexaploids, T. aestivum is the oldest, but it arose at about the same time as Timopheevi wheat.
The correctness of those estimates depends on two assumptions: genetic distance between two species is proportional to the time of their divergence, and rates of attaining the same magnitude of polymorphism are the same among species of similar ploidy. First, PCR–RFLP analyses (data not shown) suggest that the molecular variations detected by this method are a mix of nucleotide mutations and insertion/deletions. Generally, nucleotide mutation rates are thought to be constant through time (36), whereas the rates of insertion/deletions are found to be constant within different lineages of primates, but lower than that of nucleotide substitutions (37). Therefore, we assume a constant rate of insertion/deletions in Triticum and Aegilops. If correct, the genetic distances found in our study satisfy the first assumption. Although the level of polymorphism has been analyzed so far only for a few Triticum and Aegilops species, all of the estimates of intraspecific variation in organellar DNAs of T. dicoccoides, T. araraticum (25), Ae. speltoides (33), and Ae. mutica (22) are low. From this we suggest that a violation of the second assumption does not influence our argument greatly.
Association Between Phenotypic and Molecular Variation.
The investigation of organellar DNA variation with respect to phenotypic variation is both new and important. In this study, ANOVA was used to study correlations between phenotypic variation in alloplasmic wheats and molecular variation in their ct and mtDNAs. Surprisingly, significant correlations were detected in many combinations between organellar DNA and phenotypic variations. It is unlikely that all molecular variations are direct causes of phenotypic variations. Because each plasmon has evolved more or less independently from the others, a certain number of unique mutations must have accumulated within each plasmon. Such mutations, then, would be transferred to alloplasmic lines in complete linkage. If one of these mutations influences a certain phenotypic trait, then some of the linked mutations may show a “false” influence, of the same magnitude, on the trait. However, from these kinds of statistical analyses, it is not possible to pinpoint specific molecular events that affect specific phenotypic traits.
Within these limitations, we did detect some interesting relationships between phenotypic traits and organellar DNA variations. ctDNA mutations were more closely correlated with vegetative characters, whereas mtDNA mutations influenced reproductive characters more frequently. In chloroplast genomes, the variations within 10 bands in the rbcL-atpB-atpE region, and within a single band (no. 27) in the atpH-atpF region, showed strong correlations to almost all of the vegetative characters studied. On the other hand, variations in two bands (nos. 33 and 34) of the atpH-atpF region showed specific effects on male fertility. In the mitochondrial genome, band 70 in the nad1-e region showed specific effects on many vegetative characters. The cox2 region is unique in showing a strong influence on male fertility, and the cox1 region shows a strong influence on twin formation. Studying each of the B, D2, T, U, and U2 plasmon types, Ikeda et al.(38) showed that the activity of COXII is high in the B and D2 plasmons, intermediate in the T plasmon, and negligible in the U and U2 plasmons. The B and D2 plasmons show high (93 and 80%), the T plasmon shows moderate (44%), and the U and U2 plasmons show low male fertility (30 and 12%) in a wide range of common wheat genotypes (39). Together these data suggest that cox2 plays a key role in male fertility/sterility expression.
Acknowledgments
We thank Val W. Woodward, University of Minnesota, for his review of this article in preparation and for his suggestions for its improvement. We also thank T. Endo, S. Nasuda, Y. Matsuoka, and S. Takumi for their comments and suggestions, and Y. Yasui, T. Ohsako, and T. Sasanuma for their help during the course of these experiments and analyses. This is contribution no. 546 from the Laboratory of Plant Genetics, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, Japan.
ABBREVIATIONS
- RFLP
restriction fragment length polymorphism
- ctDNA
chloroplast DNA
- PCR-SSCP
PCR–single-strand conformational polymorphism
References
- 1.Kihara H. Cytologia. 1951;16:177–193. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tsunewaki K. In: Methods of Genome Analysis in Plants. Jauhar P P, editor. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1996. pp. 271–298. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vedel F, Quetier F, Dosba F, Doussinault G. Plant Sci Lett. 1978;13:97–102. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bowman C M, Koller B, Delius H, Dyer T A. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183:93–101. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ogihara Y, Tsunewaki K. Theor Appl Genet. 1988;76:321–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00265331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Terachi T, Tsunewaki K. Mol Biol Evol. 1992;9:917–931. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Terachi T, Ogihara Y, Tsunewaki K. Proc Int Wheat Genet Symp 7th. 1988;1:789–795. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Orita M, Iwahata H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cotton R G H. Mutat Res. 1993;285:125–144. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(93)90060-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ogihara Y, Terachi T, Sasakuma T. Genetics. 1991;129:873–884. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Howe C J, Fearnley I M, Walker J E, Dyer T A, Gray J C. Plant Mol Biol. 1985;4:333–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02418255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bird C R, Koller B, Auffret A D, Huttly A K, Howe C J, Dyer T A, Gray J C. EMBO J. 1985;4:1381–1388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hird S M, Webber A N, Wilson R J, Dyer T A, Gray J C. Curr Genet. 1991;19:199–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00336487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bonen L, Boer P H, McIntosh J E, Gray M W. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15:6734. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bonen L, Boer P H, Gray M W. EMBO J. 1984;3:2531–2536. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guarberto J M, Lamattina L, Bonnard G, Weil J H, Grienenberger J M. Nature (London) 1989;341:660–662. doi: 10.1038/341660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schulte E, Staubach S, Laser B, Kueck U. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:7531. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chapdelaine Y, Bonen L. Cell. 1991;65:465–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90464-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schuster W, Brennicke A. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;204:29–35. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bonen L, Bird S, Belanger I. Plant Mol Biol. 1990;15:793–795. doi: 10.1007/BF00016131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu Y-G, Mori N, Tsunewaki K. Jpn J Genet. 1990;65:367–380. doi: 10.1266/jjg.65.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ohsako T, Wang G-Z, Miyashita N T. Genes Genet Syst. 1996;71:281–292. doi: 10.1266/ggs.71.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sokal R R, Sneath P H A. Principles of Numerical Taxonomy. San Francisco: Freeman; 1963. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Saitou N, Nei M. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4:189–204. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mori N, Terachi T, Tsunewaki K. Proc Int Wheat Genet Symp 7th. 1988;1:109–114. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dvorak J, Zhang H-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:9640–9644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sears, E. R. (1941) Mo. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Bull. 336.
- 28.Kihara H. Wheat (in Japanese) Tokyo: Chuokoronsha; 1951. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sasanuma T, Miyashita N T, Tsunewaki K. Theor Appl Genet. 1996;92:928–934. doi: 10.1007/BF00224032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shands, H. & Kimber, G. (1973) Proc. Int. Wheat Genet. Symp. 4th 101–108.
- 31.Jiang J, Gill B S. Chromosome Res. 1994;2:59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01539455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mori N, Liu Y-G, Tsunewaki K. Theor Appl Genet. 1995;90:129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00221006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miyashita N T, Mori N, Tsunewaki K. Genetics. 1994;137:883–889. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Murai K, Tsunewaki K. Heredity. 1986;57:335–339. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Siregar U J, Ishii T, Tsunewaki K. Proc Int Wheat Genet Symp 7th. 1988;1:145–151. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kimura M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ. Press; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Saitou N, Ueda S. Mol Biol Evol. 1994;11:504–512. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ikeda T M, Shibasaka M, Tsunewaki K. Plant Cell Physiol. 1994;35:779–784. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tsunewaki K, Wang G-Z, Matsuoka Y. Genes Genet Syst. 1996;71:293–331. doi: 10.1266/ggs.71.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]