Abstract
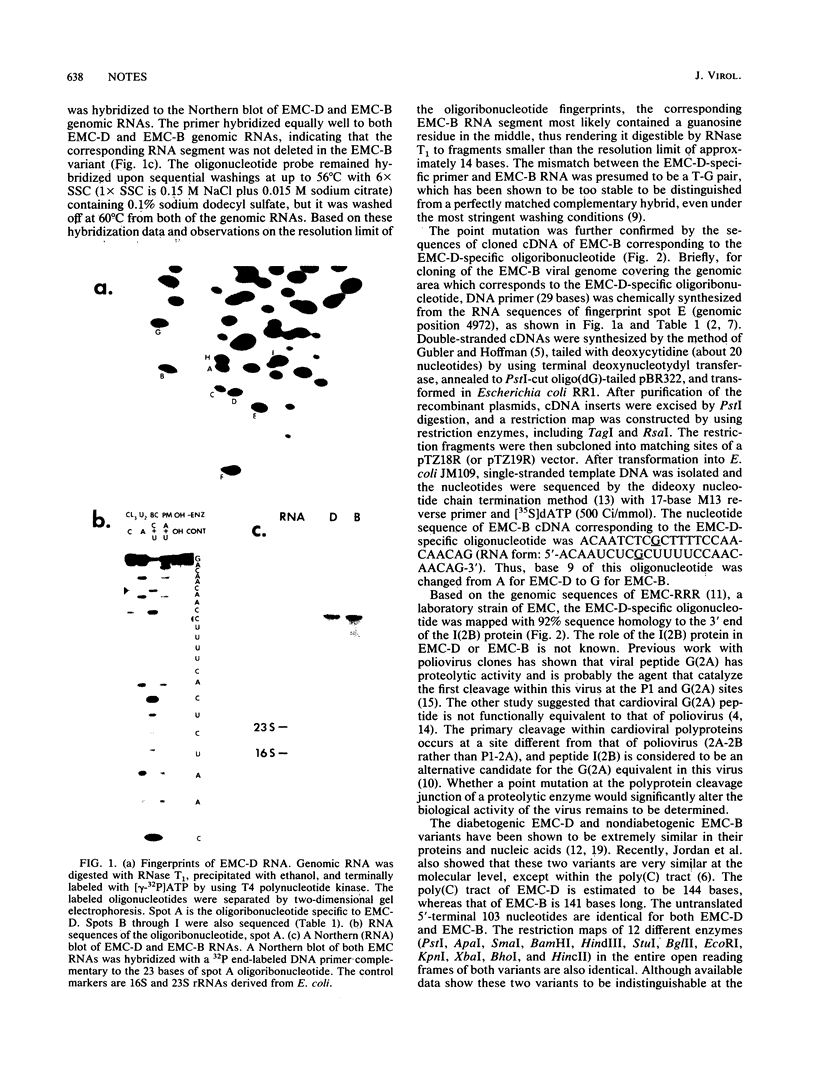
The diabetogenic D variant of encephalomyocarditis virus (EMC-D) was previously shown to be different from the nondiabetogenic B variant of encephalomyocarditis virus (EMC-B) by a single spot in an oligonucleotide fingerprint after RNase T1 digestion of their genomic RNAs. An oligoribonucleotide was missing from EMC-B but was present in EMC-D. The oligoribonucleotide specific to EMC-D was isolated from a two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel and sequenced as 5'-ACAAUCUCACUUUUCCAACAACAG-3'. Molecular hybridizations of EMC-D and EMC-B genomic RNAs with a DNA primer complementary to the EMC-D-specific oligoribonucleotide revealed that the absence of a corresponding spot in EMC-B was due to a point mutation rather than a deletion. By sequencing a cloned cDNA of EMC-B corresponding to the EMC-D-specific oligoribonucleotide, the point mutation was identified as a G for EMC-B and an A for EMC-D transversion at base 9 of the oligonucleotide. Comparative sequence analysis of eight randomly picked RNA segments around the EMC-D-specific oligoribonucleotide revealed that there were no base changes between EMC-D and EMC-B. It is concluded that the diabetogenic EMC-D viral genome differs from the nondiabetogenic EMC-B viral genome by at least a point mutation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boguski M. S., Hieter P. A., Levy C. C. Identification of a cytidine-specific ribonuclease from chicken liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2160–2163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruthers M. H. Gene synthesis machines: DNA chemistry and its uses. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):281–285. doi: 10.1126/science.3863253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Baxt B. Translation of foot-and-mouth disease virion RNA and processing of the primary cleavage products in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan G. W., Cohen S. H., Dandekar S., VandenBrink K. M. The genomic RNA of diabetogenic encephalomyocarditis virus: characterization and molecular cloning. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsinger R. L., Lunsford W. B. Synthesis of thymidine oligonucleotides by phosphite triester intermediates. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Jun 9;98(12):3655–3661. doi: 10.1021/ja00428a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozari G., Rahbar S., Wallace R. B. Discrimination among the transcripts of the allelic human beta-globin genes beta A, beta S and beta C using oligodeoxynucleotide hybridization probes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C. Picornaviral processing: some new ideas. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Mar;33(3):191–198. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray U. R., Aulakh G. S., Schubert M., McClintock P. R., Yoon J. W., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus. XXV. Difference in the RNA fingerprints of diabetogenic and non-diabetogenic variants of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):947–950. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., McClintock P. R., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus. XVIII. Inhibition by a nondiabetogenic variant of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):878–892. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes in mice. Metabolism. 1983 Jul;32(7 Suppl 1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(83)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus: VIII. Passage of encephalomyocarditis virus and severity of diabetes in susceptible and resistant strains of mice. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):225–232. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]