Abstract
Visna virus is a lentivirus which causes a slow progressive disease involving the immune system and the central nervous system. To determine the role of the viral long terminal repeat (LTR) in targeting the virus to specific host cells and tissues, transgenic mice were constructed which contained the visna virus LTR directing expression of the bacterial gene encoding chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). Analysis of the transgenic mouse tissues for CAT activity revealed that the viral LTR was responsible, in part, for the tropism of visna virus for macrophages and the central nervous system. Expression of the LTR required the macrophage to be in an activated state both in vivo and in vitro. Thioglycolate activation of peritoneal macrophages in vivo and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate treatment in vitro induced expression of the visna virus LTR. Lymphocytes from the spleens of the transgenic mice expressed CAT activity, suggesting that visna virus was able to replicate in lymphocytes, as did human immunodeficiency virus and simian immunodeficiency virus. These studies demonstrated that the lentivirus LTR was responsible, in part, for cell and tissue tropism in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cork L. C., Hadlow W. J., Crawford T. B., Gorham J. R., Piper R. C. Infectious leukoencephalomyelitis of young goats. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):134–141. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragunow M., Robertson H. A. Kindling stimulation induces c-fos protein(s) in granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):441–442. doi: 10.1038/329441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Josephs S. F., Curran T. The Fos complex and Fos-related antigens recognize sequence elements that contain AP-1 binding sites. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1150–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.2964084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Kennedy P. G., Ghotbi Z., Clements J. E., Stanley J., Pezeshkpour G. Tropism of sheep lentiviruses for monocytes: susceptibility to infection and virus gene expression increase during maturation of monocytes to macrophages. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):67–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.67-74.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Narayan O., Molineaux S., Clements J. E., Ghotbi Z. Slow, persistent replication of lentiviruses: role of tissue macrophages and macrophage precursors in bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7086–7090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Braun M. J., Clements J. E., Pyper J. M., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Gilden R. V. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III shares sequence homology with a family of pathogenic lentiviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Ruddle F. H. Gene transfer into mouse embryos: production of transgenic mice by pronuclear injection. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:411–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudnadóttir M. Visna-maedi in sheep. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):336–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. Pathogenesis of lentivirus infections. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):130–136. doi: 10.1038/322130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. The slow infection caused by visna virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;72:101–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66289-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. L., Clements J. E., Narayan O. cis- and trans-acting transcriptional regulation of visna virus. Science. 1985 Aug 2;229(4712):482–485. doi: 10.1126/science.2990051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. L., Pyper J. M., Clements J. E. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional activity of the caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):385–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.385-393.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Riedel N., Viglianti G. A., Hirsch V., Mullins J. I. Cloning of HTLV-4 and its relation to simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):610–613. doi: 10.1038/326610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Cohen D. R., Hempstead J. L., Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):192–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3037702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Müller D., Guilbert L. Differential expression of c-fos in hematopoietic cells: correlation with differentiation of monomyelocytic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1887–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Griffin D. E., Silverstein A. M. Slow virus infection: replication and mechanisms of persistence of visna virus in sheep. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):800–806. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Sheffer D., Griffin D. E., Clements J. E. Activation of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus expression during maturation of monocytes to macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.67-73.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar S. M., Sharp F. R., Curran T. Expression of c-fos protein in brain: metabolic mapping at the cellular level. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1328–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.3131879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Chess L., Fahey J. L., Fauci A. S., Lachmann P. J., L'Age-Stehr J., Ngu J., Pinching A. J., Rosen F. S., Spira T. J. AIDS--an immunologic reevaluation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1286–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
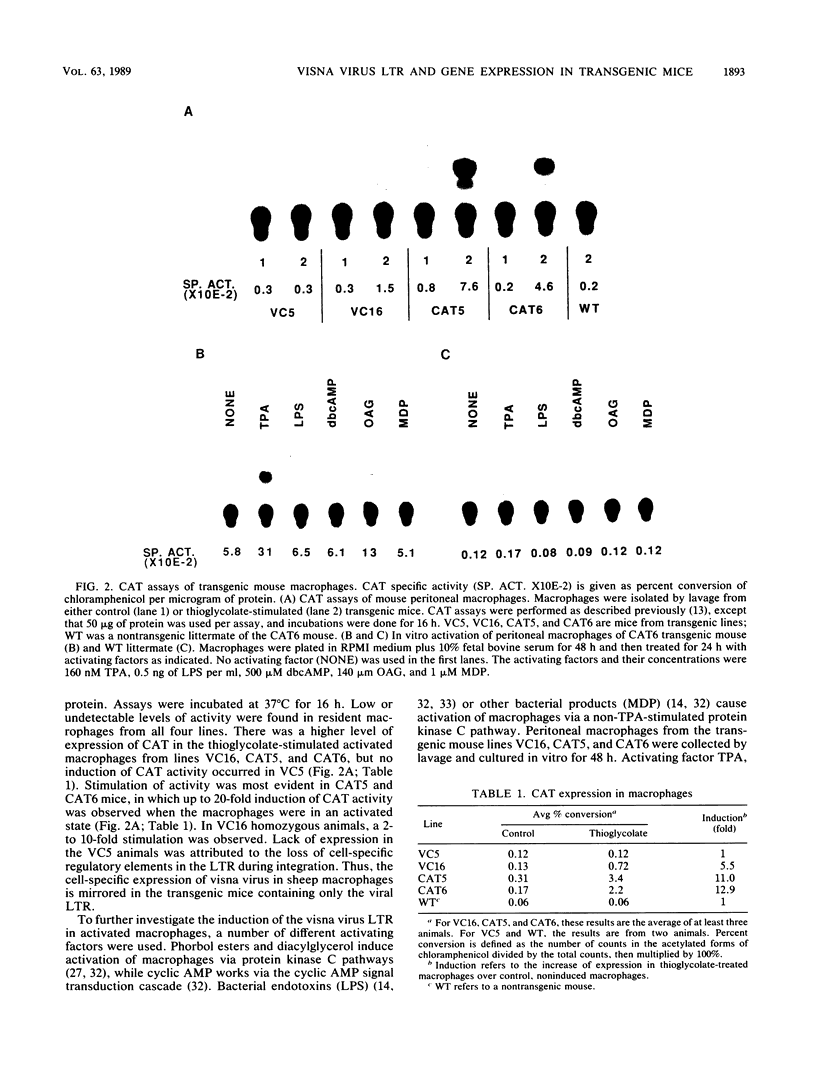
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Blair D. G., Showalter S. D., Scangos G. A. Analysis of a transgenic mouse containing simian virus 40 and v-myc sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):642–648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORMAR H. The growth cycle of visna virus in monolayer cultures of sheep cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:273–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Phagocytosis and inflammatory stimuli induce GM-CSF mRNA in macrophages through posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., 3rd, Liu D. Y. Mononuclear phagocyte activation: activation-associated antigens. Fed Proc. 1986 Nov;45(12):2829–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman P. D., Raetz C. R. The activation of protein kinase C by biologically active lipid moieties of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10048–10052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]