Abstract
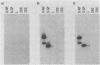
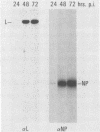
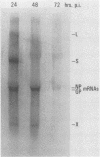
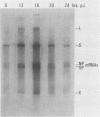
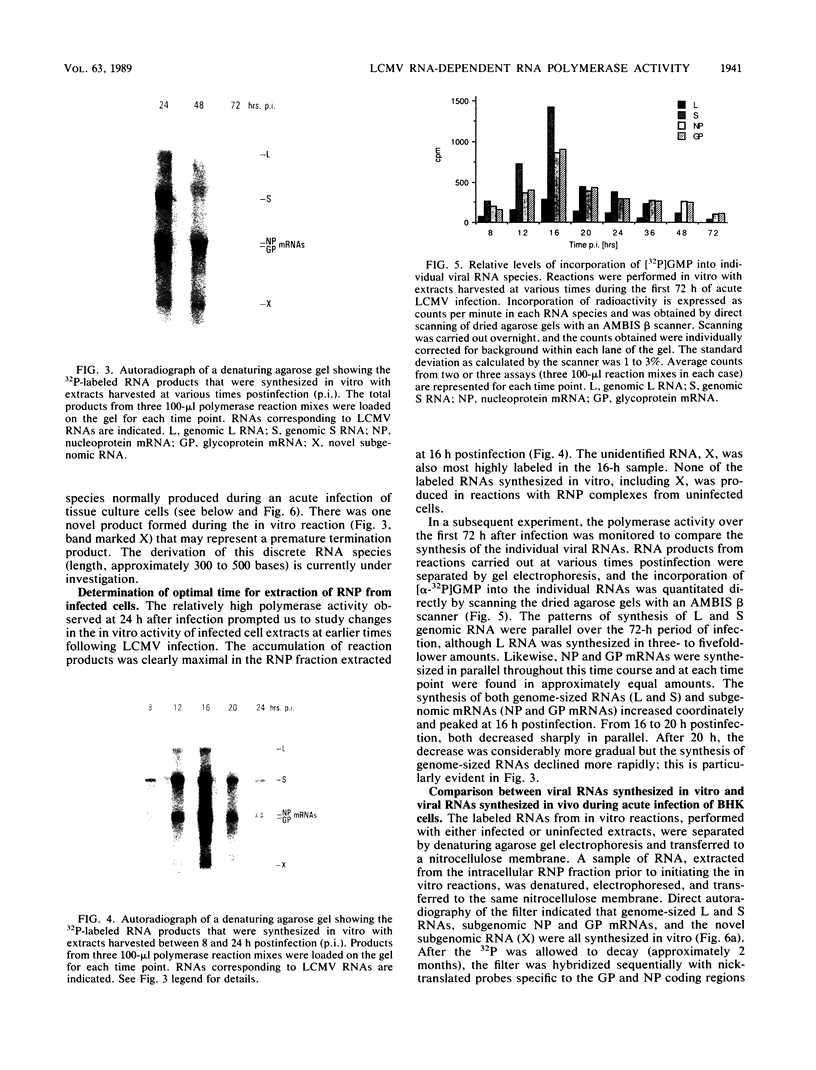
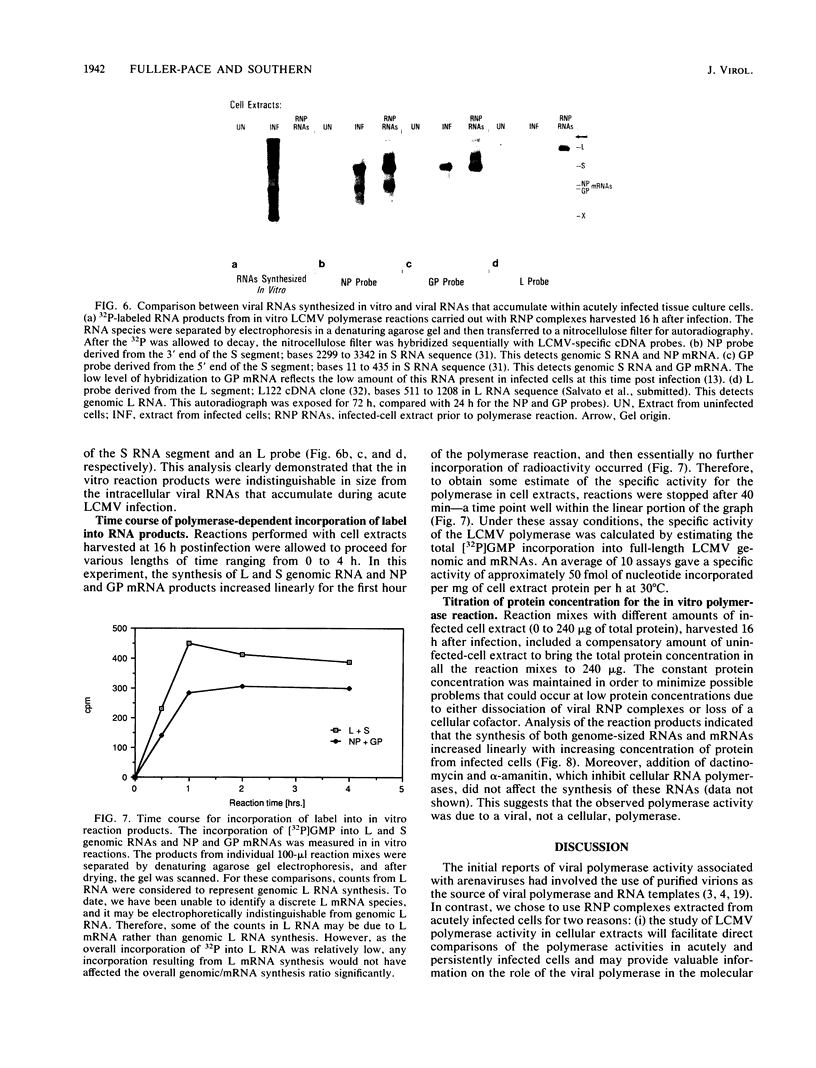
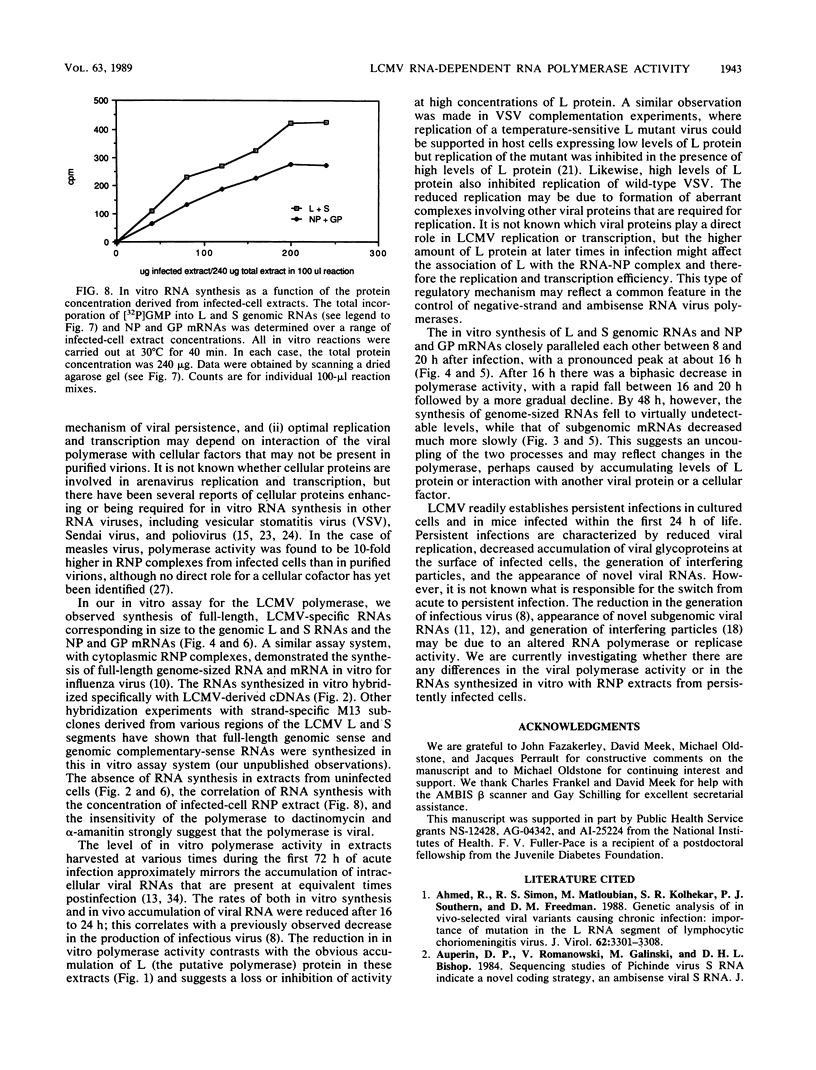
We have developed an in vitro assay for the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase with ribonucleoprotein complexes extracted from acutely infected tissue culture cells. The RNA products synthesized in vitro corresponded in size to the full-length genomic L and S RNAs and subgenomic NP and GP mRNAs normally produced in vivo during acute LCMV infection. In a temporal analysis spanning the first 72 h of acute infection, the in vitro polymerase activity of ribonucleoprotein complexes was maximal at 16 h and declined significantly at later times. In contrast, the intracellular levels of the viral L protein (the putative polymerase protein) appeared to be maximal at 48 to 72 h postinfection. Our results suggest that the accumulation of L protein correlates with reduced viral replication and transcription at later times in acute infection and may be involved in the transition from acute to persistent LCMV infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Simon R. S., Matloubian M., Kolhekar S. R., Southern P. J., Freedman D. M. Genetic analysis of in vivo-selected viral variants causing chronic infection: importance of mutation in the L RNA segment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3301–3308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3301-3308.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boersma D. P., Compans R. W. Synthesis of Tacaribe virus polypeptides in an in vitro coupled transcription and translation system. Virus Res. 1985 Apr;2(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M., Zeller W., Rohdewohld H., Lehmann-Grube F. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. IX. Properties of the nucleocapsid. Virology. 1986 May;151(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Elder J. H., Oldstone M. B. Protein structure of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: identification of the virus structural and cell associated polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Protein structure of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: evidence for a cell-associated precursor of the virion glycopeptides. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Southern P. J., Parekh B. S., Wooddell M. K., Oldstone M. B. Site-specific antibodies define a cleavage site conserved among arenavirus GP-C glycoproteins. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):982–985. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.982-985.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Bishop D. H. Biochemistry of arenaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:153–175. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. J., Southern P. J. Deleted viral RNAs and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus persistence in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):1893–1902. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. J., Southern P. J. Molecular analysis of viral RNAs in mice persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1251–1257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1251-1257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller-Pace F. V., Southern P. J. Temporal analysis of transcription and replication during acute infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnish D. G., Dimock K., Bishop D. H., Rawls W. E. Gene mapping in Pichinde virus: assignment of viral polypeptides to genomic L and S RNAs. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):638–641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.638-641.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill V. M., Harmon S. A., Summers D. F. Stimulation of vesicular stomatitis virus in vitro RNA synthesis by microtubule-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5410–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill V. M., Summers D. F. Synthesis of VSV RNPs in vitro by cellular VSV RNPs added to uninfected HeLa cell extracts: VSV protein requirements for replication in vitro. Virology. 1982 Dec;123(2):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F. Portraits of viruses: arenaviruses. Intervirology. 1984;22(3):121–145. doi: 10.1159/000149543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Leung M. F., Rawls W. E. Distinctive RNA transcriptase, polyadenylic acid polymerase, and polyuridylic acid polymerase activities associated with Pichinde virus. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):98–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.98-107.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier E., Harmison G. G., Schubert M. Homotypic and heterotypic exclusion of vesicular stomatitis virus replication by high levels of recombinant polymerase protein L. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3133–3142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3133-3142.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Gibbons G. F., Dasgupta A. The host protein required for in vitro replication of poliovirus is a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor-2. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Baker S. C., Lessard J. L. Tubulin: a factor necessary for the synthesis of both Sendai virus and vesicular stomatitis virus RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5405–5409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Salvato M., Tishon A., Lewicki H. Virus-lymphocyte interactions. III. Biologic parameters of a virus variant that fails to generate CTL and establishes persistent infection in immunocompetent hosts. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90565-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen I. R. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus RNAs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 24;234(47):112–114. doi: 10.1038/newbio234112a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J., Fujinami R. S. Characterization of in vitro transcription and transcriptional products of measles virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3381–3387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3381-3387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riviere Y., Ahmed R., Southern P. J., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Genetic mapping of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus pathogenicity: virulence in guinea pigs is associated with the L RNA segment. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):704–709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.704-709.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanowski V., Matsuura Y., Bishop D. H. Complete sequence of the S RNA of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (WE strain) compared to that of Pichinde arenavirus. Virus Res. 1985 Sep;3(2):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvato M., Shimomaye E., Southern P., Oldstone M. B. Virus-lymphocyte interactions. IV. Molecular characterization of LCMV Armstrong (CTL+) small genomic segment and that of its variant, Clone 13 (CTL-). Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):517–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90566-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M. K., Fuller-Pace F. V., Buchmeier M. J., Southern P. J. Analysis of the genomic L RNA segment from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):448–456. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Singh M. K., Riviere Y., Jacoby D. R., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Molecular characterization of the genomic S RNA segment from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90323-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vezza A. C., Clewley J. P., Gard G. P., Abraham N. Z., Compans R. W., Bishop D. H. Virion RNA species of the arenaviruses Pichinde, Tacaribe, and Tamiami. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):485–497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.485-497.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Río L., Martínez C., Domingo E., Ortín J. In vitro synthesis of full-length influenza virus complementary RNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):243–247. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]