Abstract
The gene encoding the major capsid protein of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) was identified, sequenced, and transcriptionally mapped. The location of the gene was determined by immunological screening of an expression library of AcMNPV open reading frame-beta-galactosidase fusions with an antibody raised to virus structural proteins. The DNA sequence of the corresponding region, which mapped within 56.6 and 58.0 map units on the AcMNPV genome, revealed a 1,040-base-pair open reading frame capable of encoding a 39-kilodalton polypeptide. The identity of the polypeptide was determined by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis of purified empty capsids with an antibody raised to the capsid-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. The identity of the peptide encoded by the gene was confirmed by immunoprecipitation of an in vitro translation product with RNA selected by hybridization to DNA sequences from the coding region of the gene. Transcripts of the capsid gene were analyzed by Northern (RNA) blots and mapped by nuclease protection and primer extension analysis. The capsid gene is transcribed maximally at 12 and 24 h postinfection but not in the presence of cycloheximide, a protein synthesis inhibitor, or aphidicolin, a viral DNA synthesis inhibitor, and is therefore classified as a late gene. The gene is transcribed in a counterclockwise direction with respect to the circular map. There are three transcriptional start sites, all containing the AGTAAG consensus sequence found at the start site of all late AcMNPV genes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adang M. J., Miller L. K. Molecular cloning of DNA complementary to mRNA of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: location and gene products of RNA transcripts found late in infection. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):782–793. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.782-793.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Quant-Russell R. L., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional mapping, and temporal expression of the gene encoding p39, a major structural protein of the multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Orgyia pseudotsugata. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):354–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Siegman L. J., Bellamy A. R., Ikegami N., Shatkin A. J., Furuichi Y. Comparative sequence analysis of rotavirus genomic segment 6--the gene specifying viral subgroups 1 and 2. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.97-101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. Expression of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome in insect cells: homologous viral and heterologous vertebrate genes--the baculovirus vector system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:51–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Siegmann B. Expression of early viral gene products in adenovirus type 12-infected and -transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):99–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Divergent transcription of early 35- and 94-kilodalton protein genes encoded by the HindIII K genome fragment of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2264–2272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2264-2272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. The regulation of baculovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs L. Y., Woods M. S., Weaver R. F. Viral Transcription During Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Infection: a Novel RNA Polymerase Induced in Infected Spodoptera frugiperda Cells. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):641–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.641-646.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. H., Miller L. K. Isolation of genotypic variants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):754–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.754-767.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Haarr L., Preston C. M. Processing of herpes simplex virus proteins and evidence that translation of thymidine kinase mRNA is initiated at three separate AUG codons. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):434–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.434-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Baculoviruses as gene expression vectors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:177–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Eight base pairs encompassing the transcriptional start point are the major determinant for baculovirus polyhedrin gene expression. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. C., Miller L. K. Baculovirus transcription in the presence of inhibitors and in nonpermissive Drosophila cells. Virus Res. 1986 Nov;6(2):155–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Application of a novel radioimmunoassay to identify baculovirus structural proteins that share interspecies antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):125–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.125-137.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Vlak J. M., Summers M. D. In Vitro Translation of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Early and Late mRNAs. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):199–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.199-208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
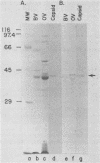
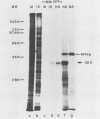
- Summers M. D., Smith G. E. Baculovirus structural polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
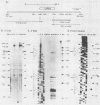
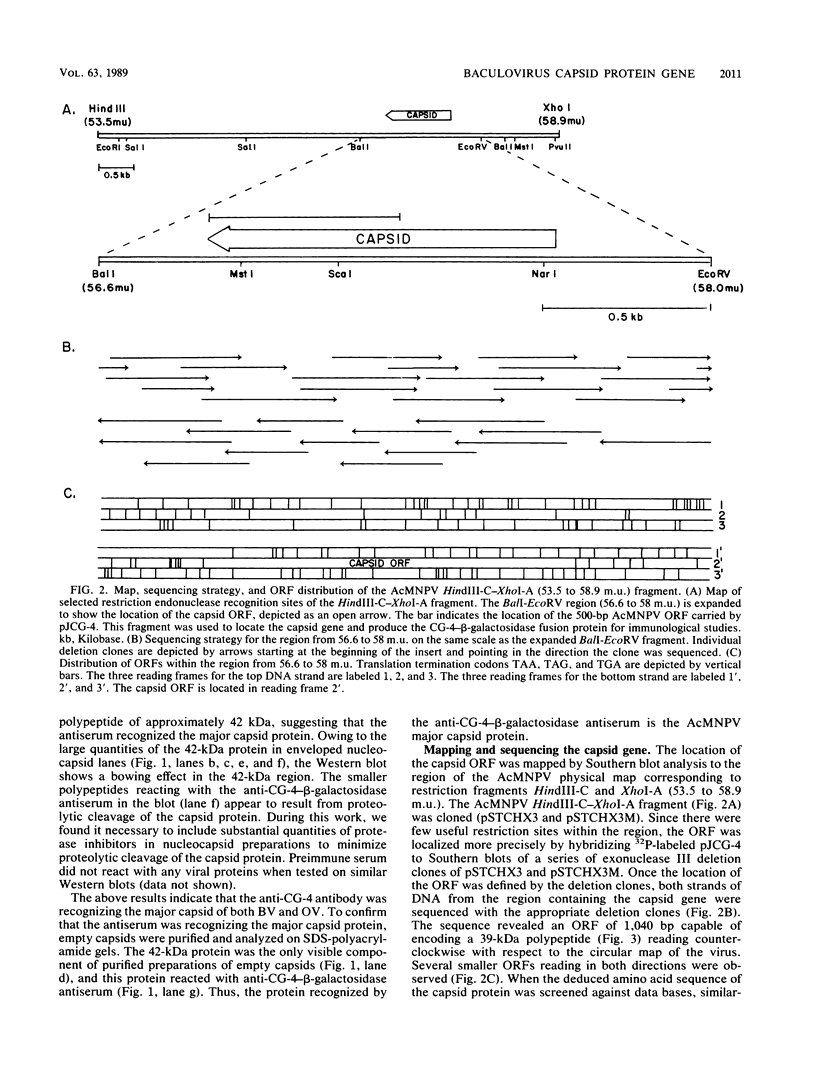
- Tweeten K. A., Bulla L. A., Consigli R. A. Characterization of an extremely basic protein derived from granulosis virus nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):866–876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.866-876.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Salstrom J. S., Watson R. J. An immunologically active chimaeric protein containing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):72–74. doi: 10.1038/302072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Mainprize T. H., Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Location, transcription, and sequence of a baculovirus gene encoding a small arginine-rich polypeptide. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.661-666.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]