Abstract
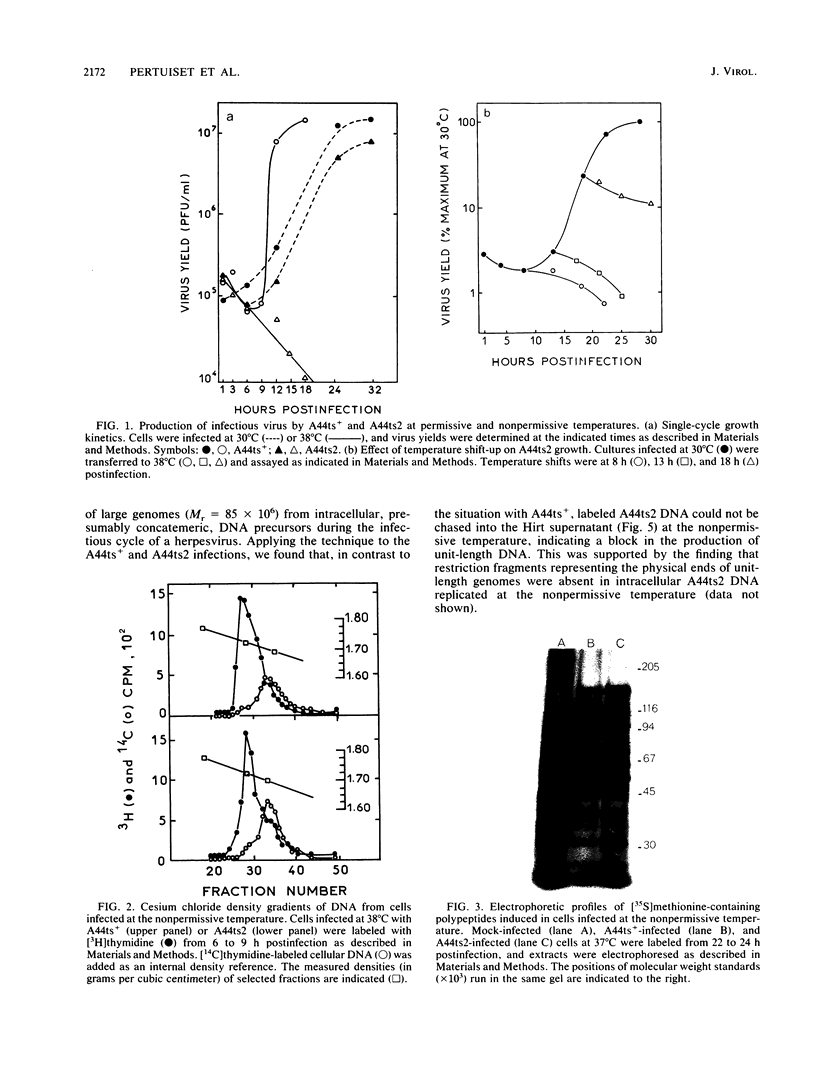
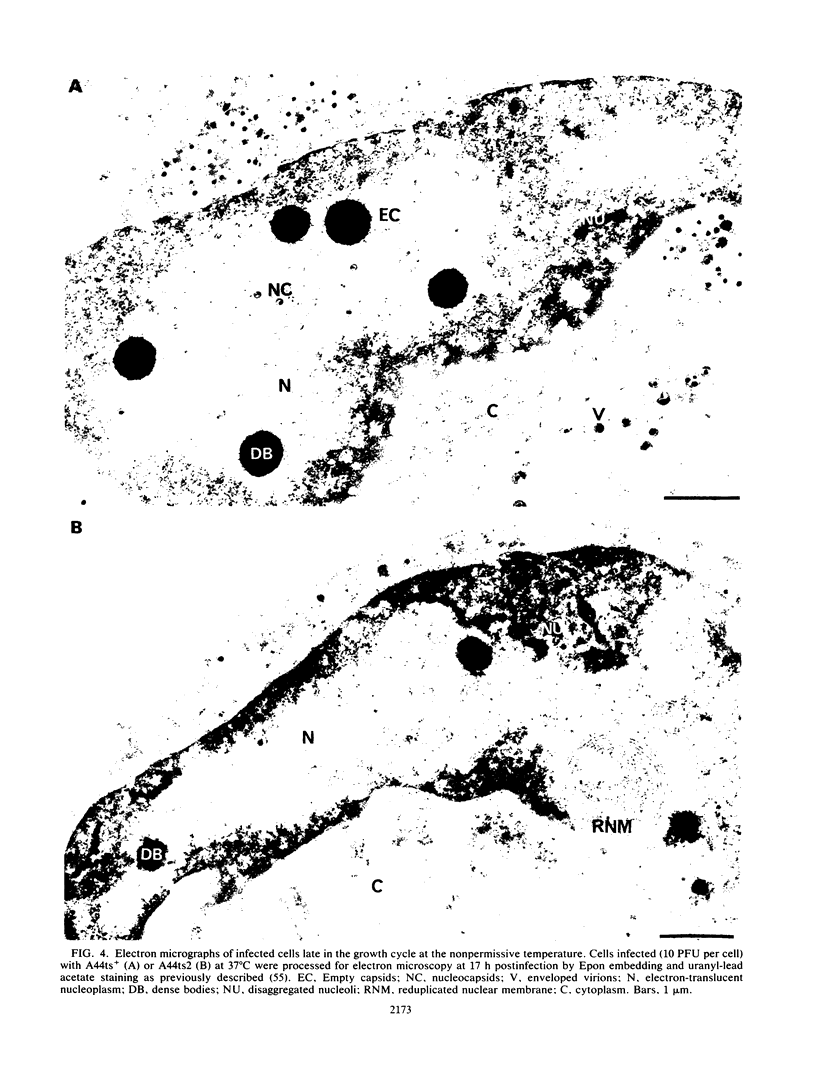
In this report, we describe some phenotypic properties of a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex type 1 (HSV-1) and present data concerning the physical location and nucleotide sequence of the genomic region harboring the mutation. The effect of shifts from the permissive to the nonpermissive temperature on infectious virus production by the mutant A44ts2 indicated that the mutated function is necessary throughout, or late in, the growth cycle. At the nonpermissive temperature, no major differences were detected in viral DNA or protein synthesis with respect to the parent A44ts+. On the other hand, electron microscopy of mutant-infected cells revealed that neither viral capsids nor capsid-related structures were assembled at the nonpermissive temperature. Additional analyses employing the Hirt extraction procedure showed that A44ts2 is also unable to mature replicated viral DNA into unit-length molecules under nonpermissive conditions. The results of marker rescue experiments with intact A44ts2 DNA and cloned restriction fragments of A44ts+ placed the lesion in the coordinate interval 0.553 to 0.565 (1,837 base pairs in region UL) of the HSV-1 physical map. No function has previously been assigned to this region, although it is known to be transcribed into two 5' coterminal mRNAs which code in vitro for a 54,000-molecular-weight polypeptide (K. P. Anderson, R. J. Frink, G. B. Devi, B. H. Gaylord, R. H. Costa, and E. K. Wagner, J. Virol. 37:1011-1027, 1981). We sequenced the interval 0.551 to 0.565 and found an open reading frame (ORF) for a 50,175-molecular-weight polypeptide. The predicted product of this ORF exhibits strong homology with the product of varicella-zoster virus ORF20 and lower, but significant, homology with the product of Epstein-Barr virus BORF1. For the three viruses, the corresponding ORFs lie just upstream of the gene coding for the large subunit of viral ribonucleotide reductase. The ORF described here corresponds to the ORF designated UL38 in the recently published nucleotide sequence of the HSV-1 UL region (D. J. McGeoch, M. A. Dalrymple, A. J. Davison, A. Dolan, M. C. Frame, D. McNab, L. J. Perry, J. E. Scott, and P. Taylor, J. Gen. Virol. 69:1531-1574, 1988).
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison C., Rixon F. J., Palfreyman J. W., O'Hara M., Preston V. G. Characterisation of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant which has a temperature-sensitive defect in penetration of cells and assembly of capsids. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):246–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Holland L. E., Gaylord B. H., Wagner E. K. Isolation and translation of mRNA encoded by a specific region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):749–759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.749-759.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Barr S., Timbury M. C. The fine structure of cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):103–119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Furlong D., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VIII. further characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in release of viral DNA and in other stages of the viral reproductive cycle. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):397–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.397-407.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Batterson W., Roizman B. Identification and genetic mapping of a herpes simplex virus capsid protein that binds DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):645–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.645-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral G. A., Schaffer P. A. Electron microscope studies of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):727–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.727-737.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrian J., Bucchini D., Sheldrick P. "Endless" viral DNA in cells infected with channel catfish virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.405-412.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Ponce de Leon M., Diggelmann H., Lawrence W. C., Vernon S. K., Eisenberg R. J. Structural analysis of the capsid polypeptides of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):521–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.521-531.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargan D., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Ultrastructural characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 (strain 17) temperature-sensitive mutants. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1311–1326. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., McGeoch D. J. Evolutionary comparisons of the S segments in the genomes of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):597–611. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. DNA sequence of the major capsid protein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2279–2286. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Taylor P. Genetic relations between varicella-zoster virus and Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1067–1079. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Casjens S. R. DNA packaging by the double-stranded DNA bacteriophages. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., Dutia B. M. The ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 involves minimally a complex of two polypeptides (136K and 38K). J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1581–1587. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Coward J. E., Rosenkranz H. S., Morgan C. Electron microscopic studies on assembly of herpes simplex virus upon removal of hydroxyurea block. J Gen Virol. 1975 Feb;26(2):171–181. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Draper K. G., Wagner E. K. Uninfected cell polymerase efficiently transcribes early but not late herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Barrell B. G., Farrell P. J. Coding content and expression of the EBV B95-8 genome in the region from base 62,248 to base 82,920. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):136–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Stockwell P., Ginsburg M., Barrell B. Homology between two EBV early genes and HSV ribonucleotide reductase and 38K genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5087–5099. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad W. B., Kanehisa M. I. Pattern recognition in nucleic acid sequences. I. A general method for finding local homologies and symmetries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):247–263. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. J., Jr, Zweig M., Stephenson J. R., Hampar B. Isolation of a nucleocapsid polypeptide of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 possessing immunologically type-specific and cross-reactive determinants. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):34–42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.34-42.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W. Herpes simplex and 'the herpes complex': diverse observations and a unifying hypothesis. The eighth Fleming lecture. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2077–2107. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Blankenship M. L., Ben-Porat T. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. V. Maturation of concatemeric DNA of pseudorabies virus to genome length is related to capsid formation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1151–1164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1151-1164.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Ihara S., Hampl H., Ben-Porat T. Pathway of assembly of herpesvirus capsids: an analysis using DNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):544–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaster S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. II. Characterization of the virion protein kinase and of the polypeptides phosphorylated in the virion. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):798–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.798-811.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J. DNA sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gene encoding glycoprotein gH, and identification of homologues in the genomes of varicella-zoster virus and Epstein-Barr virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4281–4292. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Brauer D. H. Complete DNA sequence of the short repeat region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1727–1745. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Moss H. W., McNab D., Frame M. C. DNA sequence and genetic content of the HindIII l region in the short unique component of the herpes simplex virus type 2 genome: identification of the gene encoding glycoprotein G, and evolutionary comparisons. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):19–38. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. The genome of herpes simplex virus: structure, replication and evolution. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:67–94. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. Organization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription unit encoding two early proteins with molecular weights of 140000 and 40000. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):997–1006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Post L. E., Roizman B. Molecular engineering of the herpes simplex virus genome: insertion of a second L-S junction into the genome causes additional genome inversions. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. IX. Apparent exclusion of some parental DNA arrangements in the generation of intertypic (HSV-1 X HSV-2) recombinants. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):231–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.231-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii S., Rosenkranz H. S., Morgan C., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. 3. Effect of hydroxyurea. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1163–1171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1163-1171.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Coates J. A., Rixon F. J. Identification and characterization of a herpes simplex virus gene product required for encapsidation of virus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1056–1064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1056-1064.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Palfreyman J. W., Dutia B. M. Identification of a herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide which is a component of the virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1457–1466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG M., KAPLAN A. S. The morphology of noninfective pseudorabies virus produced by cells treated with 5-fluorouracil. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Martin R. G. Genetic analysis of simian virus 40. I. Description of microtitration and replica-plating techniques for virus. Virology. 1970 Aug;41(4):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90439-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Brunschwig J. P., McCombs R. M., Benyesh-Melnick M. Electron microscopic studies of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):444–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Laithier M., Lando D., Ryhiner M. L. Infectious DNA from herpes simplex virus: infectivity of double-stranded and single-stranded molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3621–3625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman G., Bachenheimer S. L. Characterization of intranuclear capsids made by ts morphogenic mutants of HSV-1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman G., Bachenheimer S. L. DNA processing in temperature-sensitive morphogenic mutants of HSV-1. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Summers W. C. Structure and function of herpesvirus genomes. II. EcoRl, Sbal, and HindIII endonuclease cleavage sites on herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):581–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Carmichael E. P., Aschman D. P., Goldstein D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of mutants in four essential genes that map to the left half of HSV-1 UL DNA. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):198–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Davison A., Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C. Recombination in herpes simplex virus: mapping of mutations and analysis of intertypic recombinants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):827–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]