Abstract
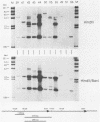
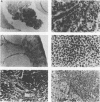
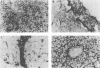
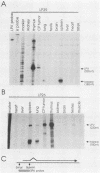
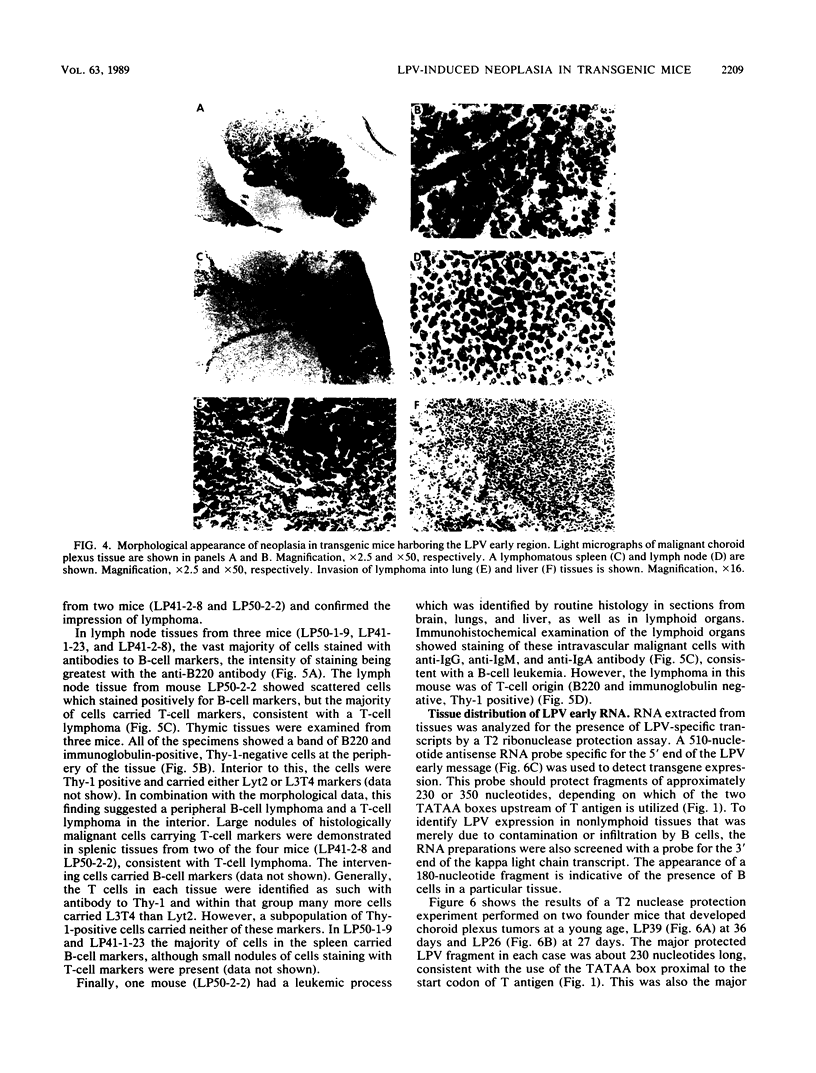
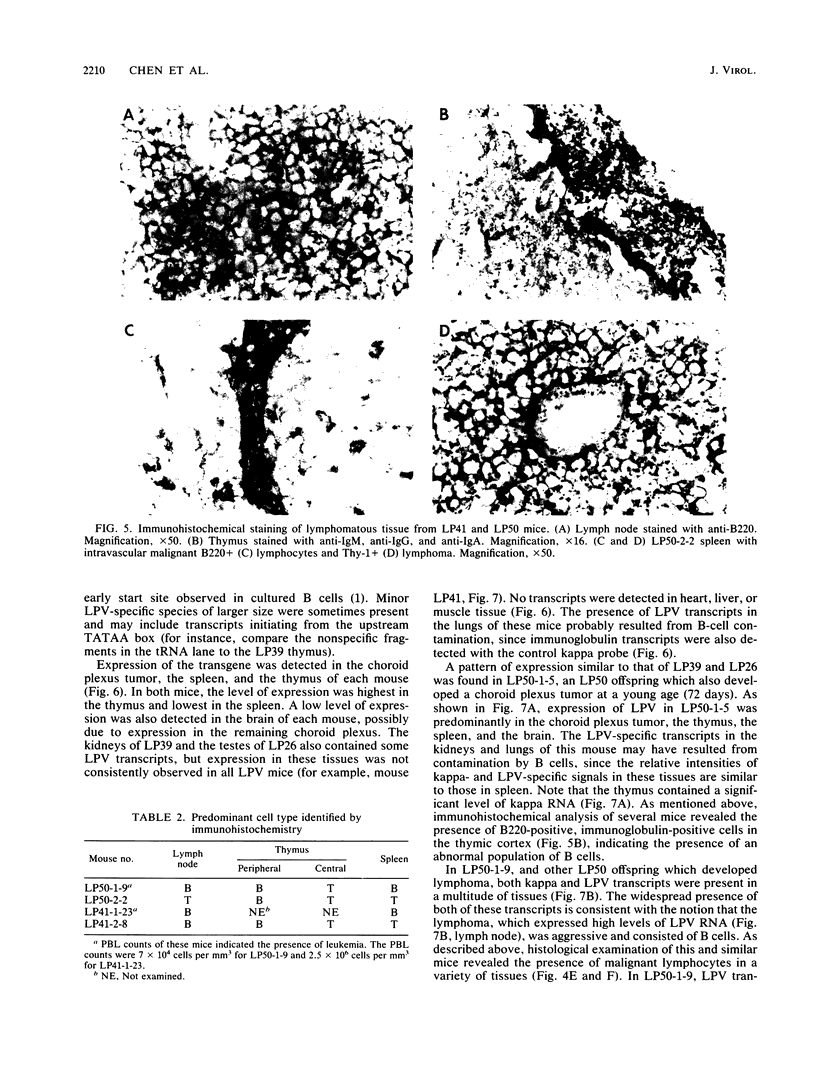
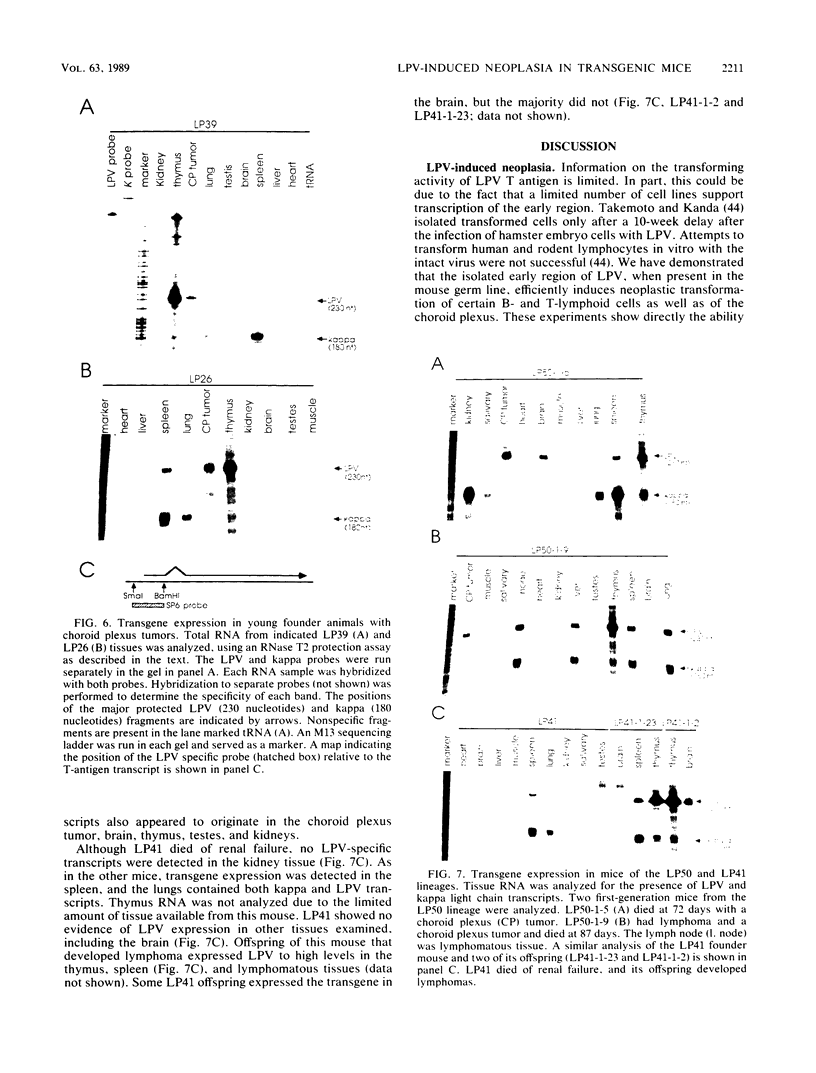
Transgenic mice have been generated which carry the early region of lymphotropic papovavirus (LPV). Eight of eleven founder animals died before 3 months of age after developing one or both of two distinct proliferative disorders. Of the three surviving animals, two are known to have rearranged or partial copies of the LPV genes. The majority of the founder animals (six) developed debilitating choroid plexus tumors by 26 to 42 days. Although this is the same tumor type induced by the simian virus 40 T-antigen gene, those induced by LPV appeared at a much younger age. The LPV early region was expressed in the brain tumors of these mice, as well as in the thymus and spleen. Expression in the latter two tissues reflects the cell-type specificity of the LPV enhancer demonstrated in cultured cells (i.e., lymphoid cells). Two founder animals (LP41 and LP50) gave rise to lines of mice that routinely develop lymphoproliferative disorders. LP50 and its LPV-positive offspring developed aggressive lymphomas and choroid plexus tumors. The transgenic offspring of LP41 also developed lymphomas. High levels of LPV RNA were expressed in the lymphomas of these mice as well as in the spleens and thymuses. The origin of the lymphomas from B- and T-cell lineages suggests that the LPV early genes are expressed in and can transform both of these cell types in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Manor H. Transcription map of the African green monkey lymphotropic papovavirus. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. M., Harris A. W., Pinkert C. A., Corcoran L. M., Alexander W. S., Cory S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):533–538. doi: 10.1038/318533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Müller-Lantzsch N., zur Hausen H. B-lymphotropic papovavirus and possibility of infections in humans. J Med Virol. 1981;6(4):301–308. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Vogl W., Gissman L., zur Hausen H. Propagation of B-lymphotropic papovavirus (LPV) in human B-lymphoma cells and characterization of its DNA. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Messing A., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinsky J., Goodenow M. M., Jackson M., Lilly F., Leinwand L., Childs G. Comparison of endogenous murine leukemia virus proviral organization and RNA expression in 3-methylcholanthrene-induced and spontaneous thymic lymphomas in RF and AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):94–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.94-99.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. B220: a B cell-specific member of th T200 glycoprotein family. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):681–683. doi: 10.1038/289681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G. C., Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Melief C. J., Berns A. J. Tumor progression in murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas: monitoring clonal selections with viral and cellular probes. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):230–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.230-241.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta U. B., Lilly F. Chemically induced murine T lymphomas: continued rearrangement within the T-cell receptor beta-chain gene during serial passage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3193–3197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Quan Z. S., Wall K. A., Pierres A., Quintáns J., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Fitch F. W. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2445–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J. Atrial natriuretic factor-SV40 T antigen transgenes produce tumors and cardiac arrhythmias in mice. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.2964082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuno A., Kanda T., Yoshiike K. Monkey B-lymphotropic papovavirus genome: the entire DNA sequence and variable regions. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1986 Aug;39(4):151–161. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.39.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Transgenic animals. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1468–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.3287623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Mutation in the VP-1 gene is responsible for the extended host range of a monkey B-lymphotropic papovavirus mutant capable of growing in T-lymphoblastoid cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):531–534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.531-534.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Takemoto K. K. Monkey B-lymphotropic papovavirus mutant capable of replicating in T-lymphoblastoid cells. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):96–100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.96-100.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon K. A., Chepelinsky A. B., Khillan J. S., Overbeek P. A., Piatigorsky J., Westphal H. Oncogenesis of the lens in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1622–1628. doi: 10.1126/science.3029873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Pawlita M., Gruss P. A viral enhancer element specifically active in human haematopoietic cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):597–600. doi: 10.1038/315597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Hammer R. E., Messing A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Pancreatic neoplasia induced by SV40 T-antigen expression in acinar cells of transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):188–193. doi: 10.1126/science.2821617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Messing A., Brinster R. L. SV40 enhancer and large-T antigen are instrumental in development of choroid plexus tumours in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):457–460. doi: 10.1038/316457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlita M., Clad A., zur Hausen H. Complete DNA sequence of lymphotropic papovavirus: prototype of a new species of the polyomavirus genus. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):196–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlita M., Mosthaf L., Clad A., Gruss P. Genome structure and host range restriction of the lymphotropic papovavirus (LPV): identification of a viral lymphocyte specific enhancer element. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;113:26–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69860-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Wong C., Butel J. S. Tumorigenesis in transgenic mice by a nuclear transport-defective SV40 large T-antigen gene. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. K., Hoekzema G. S., Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Jay G. Multiple endocrine neoplasia induced by the promiscuous expression of a viral oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3135–3139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlokat U., Bohmann D., Schöler H., Gruss P. Nuclear factors binding specific sequences within the immunoglobulin enhancer interact differentially with other enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3251–3258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinn E., Muller W., Pattengale P., Tepler I., Wallace R., Leder P. Coexpression of MMTV/v-Ha-ras and MMTV/c-myc genes in transgenic mice: synergistic action of oncogenes in vivo. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Blair D. G., Showalter S. D., Scangos G. A. Analysis of a transgenic mouse containing simian virus 40 and v-myc sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):642–648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Khoury G., Jay G., Howley P. M., Scangos G. A. Early regions of JC virus and BK virus induce distinct and tissue-specific tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda Y., Aizawa S., Hirai S., Inoue T., Furuta Y., Suzuki M., Hirohashi S., Ikawa Y. Driven by the same Ig enhancer and SV40 T promoter ras induced lung adenomatous tumors, myc induced pre-B cell lymphomas and SV40 large T gene a variety of tumors in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4055–4065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Furuno A., Kato K., Yoshiike K. Biological and biochemical studies of African green monkey lymphotropic papovavirus. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):502–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.502-509.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Kanda T. Lymphotropic papovavirus transformation of hamster embryo cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.100-105.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Finlay C., Miller D., Marks J., Lozano G., Levine A. J. Relationship between simian virus 40 large tumor antigen expression and tumor formation in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2029–2032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2029-2032.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T., Finlay C., Levine A. J. A comparison of several lines of transgenic mice containing the SV40 early genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:671–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Gissmann L. Lymphotropic papovaviruses isolated from African green monkey and human cells. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979 Aug;167(3):137–153. doi: 10.1007/BF02121180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]