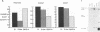Abstract
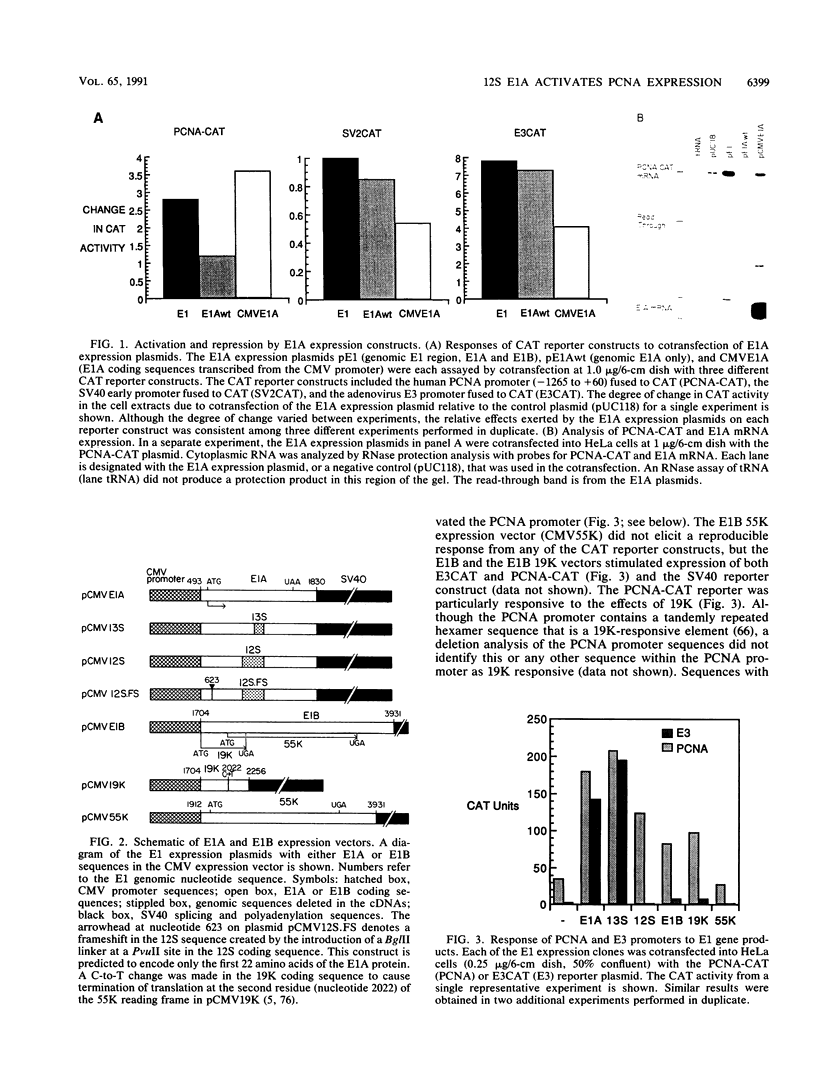
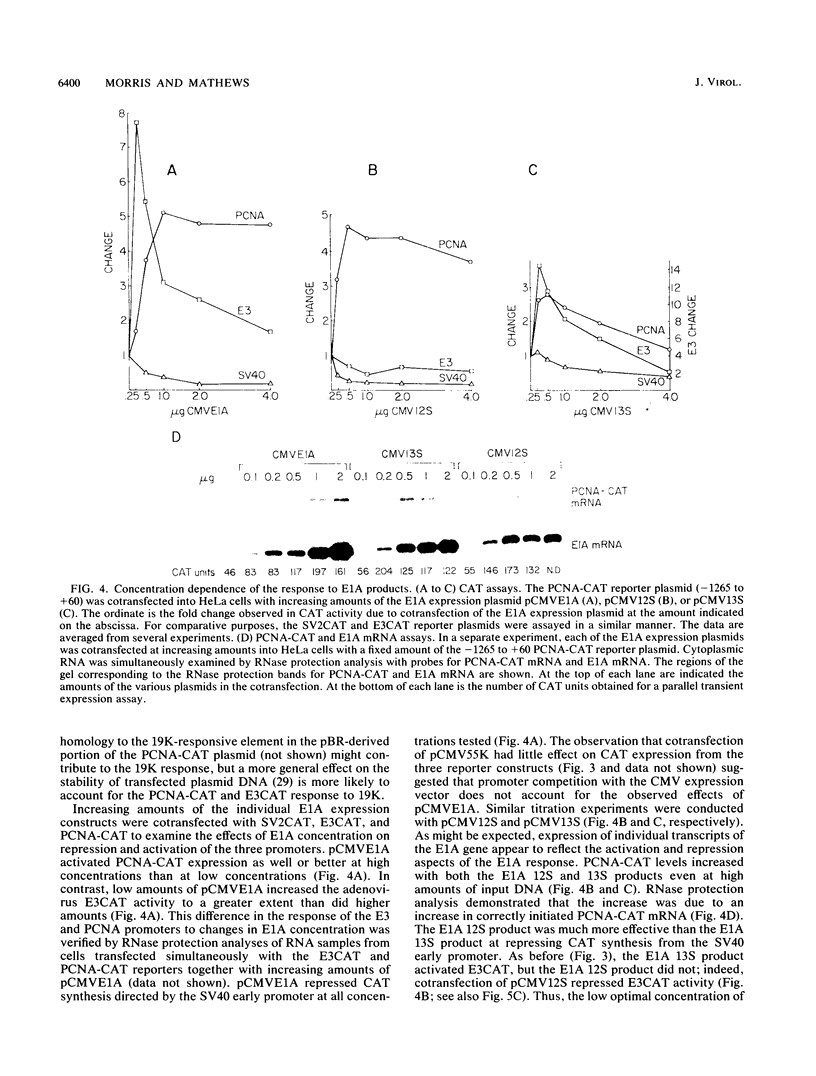
The transforming region of adenovirus (E1) stimulates expression of a reporter construct linked to the promoter for the human proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene in a cotransfection assay (G. F. Morris and M. B. Mathews, J. Biol. Chem. 264:13856-13864, 1989). The major products of the E1 region were assessed individually for their contribution to transactivation of the PCNA promoter. The E1A 13S and 12S products and the E1B 19-kDa product elevated expression from the PCNA promoter, whereas the E1B 55-kDa product did not. Induction of the PCNA promoter by E1A differed from transcriptional activation of the adenovirus E3 promoter in that the PCNA promoter is activated by the E1A 12S product whereas the E3 promoter is repressed; furthermore, the PCNA promoter is activated upon E1A overexpression, whereas the E3 promoter responds less well to high amounts of E1A. A site for the activating transcription factor ATF located approximately 50 nucleotides upstream from the transcription initiation site in the PCNA promoter mediates a positive response to the E1A 12S and 13S products.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G. R., Babiss L. E. The efficiency of adenovirus transformation of rodent cells is inversely related to the rate of viral E1A gene expression. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3427–3436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3427-3436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus proteins from both E1B reading frames are required for transformation of rodent cells by viral infection and DNA transfection. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90441-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer G. A., Burgers P. M. Molecular cloning, structure and expression of the yeast proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):261–265. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Jones N. C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Fey S. J., Bellatin J., Larsen P. M., Arevalo J., Celis J. E. Identification of a nuclear and of a cytoplasmic polypeptide whose relative proportions are sensitive to changes in the rate of cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Dec;136(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet L. J., Berk A. J. Concentration dependence of transcriptional transactivation in inducible E1A-containing human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4799–4807. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. D., Ottavio L., Travali S., Lipson K. E., Baserga R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3289–3296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dery C. V., Herrmann C. H., Mathews M. B. Response of individual adenovirus promoters to the products of the E1A gene. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D., Moran E. Synthesis of p34, the mammalian homolog of the yeast cdc2+/CDC28 protein kinase, is stimulated during adenovirus-induced proliferation of primary baby rat kidney cells. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):553–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock M. L., Lewis J. B. Genetic dissection of the transactivating domain of the E1a 289R protein of adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1495–1504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1495-1504.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J., Shenk T. Adenovirus E1A protein paradigm viral transactivator. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:141–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Franza B. R., Jr The REF52 protein database. Methods of database construction and analysis using the QUEST system and characterizations of protein patterns from proliferating and quiescent REF52 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5283–5298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Franza B. R., Jr Transformation-sensitive and growth-related changes of protein synthesis in REF52 cells. A two-dimensional gel analysis of SV40-, adenovirus-, and Kirsten murine sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells using the REF52 protein database. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5299–5312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Ricciardi R. P. Detailed kinetics of adenovirus type-5 steady-state transcripts during early infection. Virus Res. 1988 Jan;9(1):73–91. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Gies D., McCray G., Huang M. The human cytomegalovirus major immediate early promoter can be trans-activated by adenovirus early proteins. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Engel D. A., Shenk T. An adenovirus early region 4 gene product is required for induction of the infection-specific form of cellular E2F activity. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1062–1074. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Association of adenovirus early-region 1A proteins with cellular polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1579–1589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. An enhancer element is located 340 base pairs upstream from the adenovirus-2 E1A capsite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8747–8760. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C. H., Dery C. V., Mathews M. B. Transactivation of host and viral genes by the adenovirus E1B 19K tumor antigen. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C. H., Mathews M. B. The adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein stimulates gene expression by increasing DNA levels. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5412–5423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitt M. M., Graham F. L. Adenovirus E1A under the control of heterologous promoters: wide variation in E1A expression levels has little effect on virus replication. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):667–678. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90134-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Egan C., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Retinoblastoma growth suppressor and a 300-kDa protein appear to regulate cellular DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5883–5887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Hearing P. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes two gene products with redundant effects in lytic infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2605–2615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2605-2615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Gatti C., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10175–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., deRiel J. K., Mercer W. E., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Inhibition of cellular proliferation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to PCNA cyclin. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1544–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2897717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Evelegh C. M., Cunniff N. F., Bayley S. T. Sequences in E1A proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):120–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochemsen A. G., Peltenburg L. T., te Pas M. F., de Wit C. M., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Activation of adenovirus 5 E1A transcription by region E1B in transformed primary rat cells. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3399–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Lillie J. W., Daouk G. H., Green M. R., Kingston R., Schimmel P. Induction of a cellular enzyme for energy metabolism by transforming domains of adenovirus E1a. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1476–1483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabayashi I., Chiu R., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. E1A dependent up-regulation of c-jun/AP-1 activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):649–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. C., Marraccino R. L., Keng P. C., Bambara R. A., Lord E. M., Chou W. G., Zain S. B. Requirement for proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression during stages of the Chinese hamster ovary cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2967–2974. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. J., Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Evidence for interaction of different eukaryotic transcriptional activators with distinct cellular targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):147–152. doi: 10.1038/346147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Moriuchi T., Koji T., Nakane P. K. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for rat proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):637–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Lin D., Appella E., Ullrich S. J. Growth suppression induced by wild-type p53 protein is accompanied by selective down-regulation of proliferating-cell nuclear antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1958–1962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
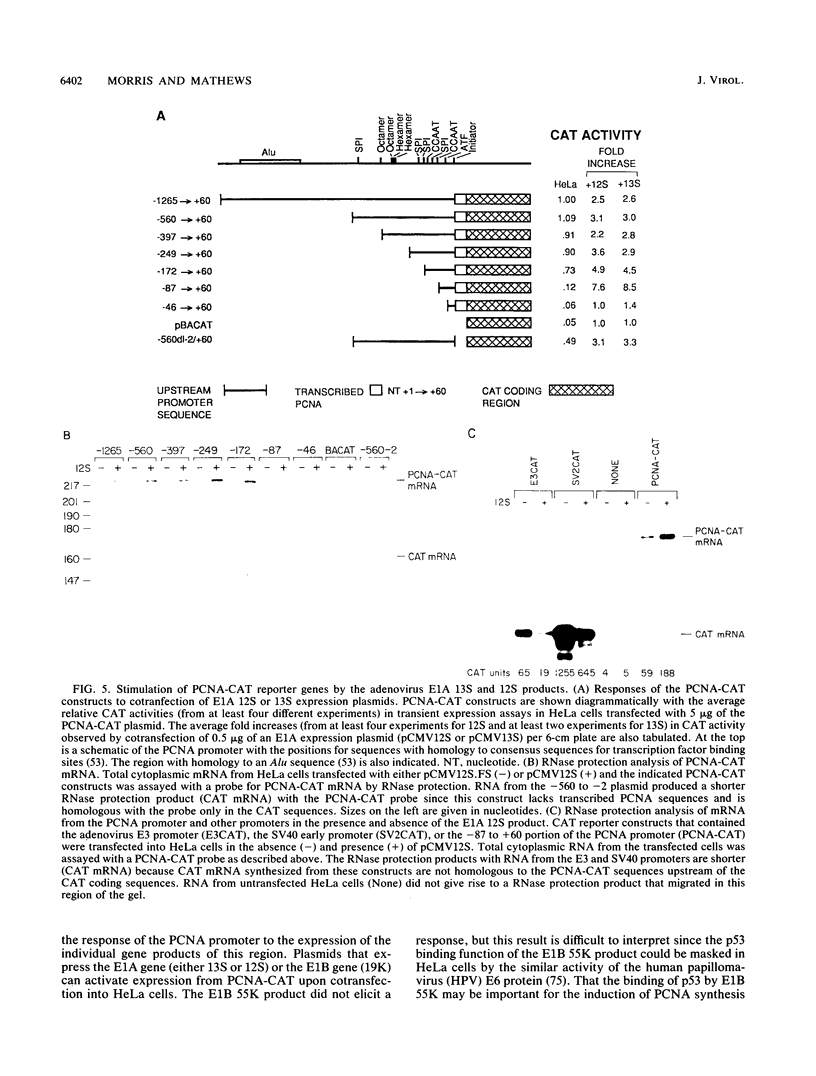
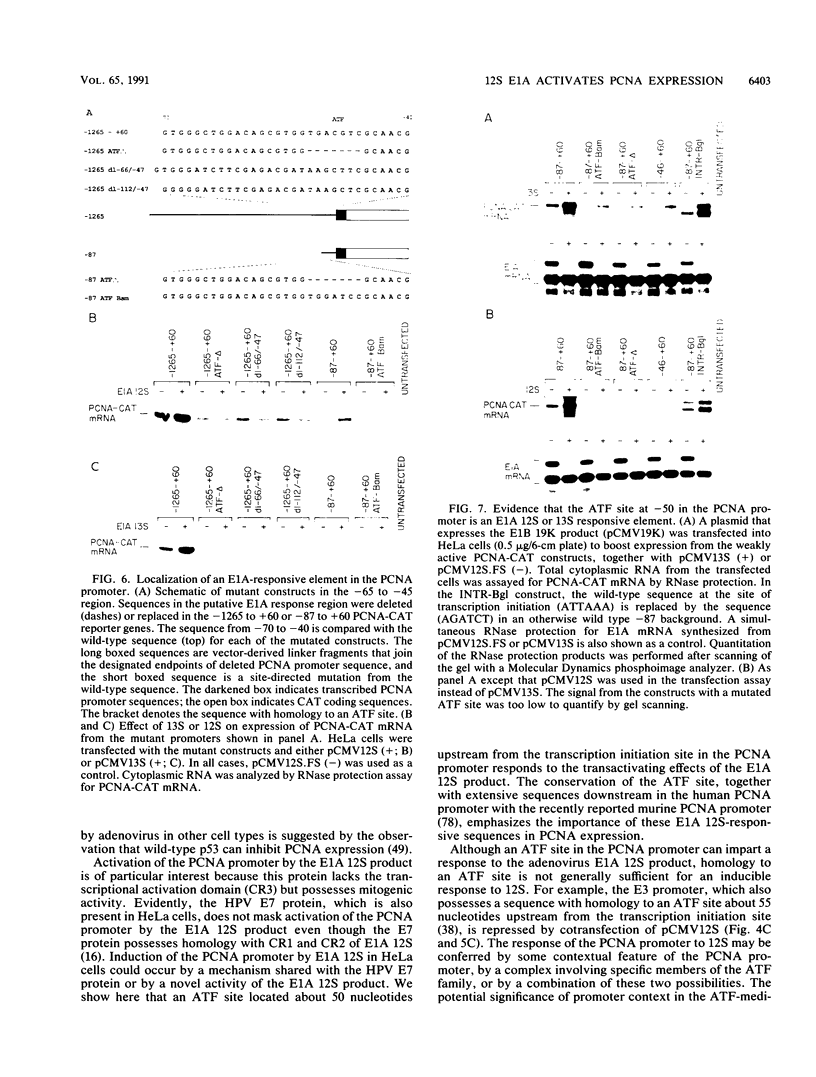
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter and its response to adenovirus early region 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16116–16125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13856–13864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Roberts M. P., Engel D. A., Doerfler W., Shenk T. Induction of transcription factor AP-1 by adenovirus E1A protein and cAMP. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1991–2002. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanisms of viral-mediated trans-activation of transcription. Adv Virus Res. 1989;37:35–83. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks C. L., Spector D. J. cis-dominant defect in activation of adenovirus type 5 E1b early RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2780–2787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2780-2787.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Fromental C., Chambon P. General repression of enhanson activity by the adenovirus-2 E1A proteins. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):137–150. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Transforming collaborations between ras and nuclear oncogenes. Cancer Cells. 1990 Aug-Sep;2(8-9):258–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senear A. W., Lewis J. B. Morphological transformation of established rodent cell lines by high-level expression of the adenovirus type 2 E1a gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1253–1260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Kato H., Kawai S. Tandemly repeated hexamer sequences within the beta interferon promoter can function as an inducible regulatory element in activation by the adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3063–3068. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3063-3068.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Kitchener K., Kao H. T., Hickey E., Weber L., Voellmy R., Heintz N., Nevins J. R. Selective induction of human heat shock gene transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene products, including the 12S E1A product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2884–2890. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Castillo C., So A. G., Downey K. M. An auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase-delta from fetal calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12310–12316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Factor substitution in a human HSP70 gene promoter: TATA-dependent and TATA-independent interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Role of adenovirus E1B proteins in transformation: altered organization of intermediate filaments in transformed cells that express the 19-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):120–130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widen S. G., Kedar P., Wilson S. H. Human beta-polymerase gene. Structure of the 5'-flanking region and active promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16992–16998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y., Hirose F., Matsuoka S., Moriuchi T., Shiroishi T., Moriwaki K., Matsukage A. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of mouse gene and pseudogenes for proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2403–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Branton P. E. Detection of cellular proteins associated with human adenovirus type 5 early region 1A polypeptides. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Venkatesh L., Kuppuswamy M., Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus transforming 19-kD T antigen has an enhancer-dependent trans-activation function and relieves enhancer repression mediated by viral and cellular genes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):645–658. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R., Foulkes N., Mulder M., Kruijer W., Sassone-Corsi P. Positive regulation of jun/AP-1 by E1A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):192–201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Meijer I., Stein B., Smits A. M., Herrlich P., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Differential effects of the adenovirus E1A oncogene on members of the AP-1 transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5857–5864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]