Abstract
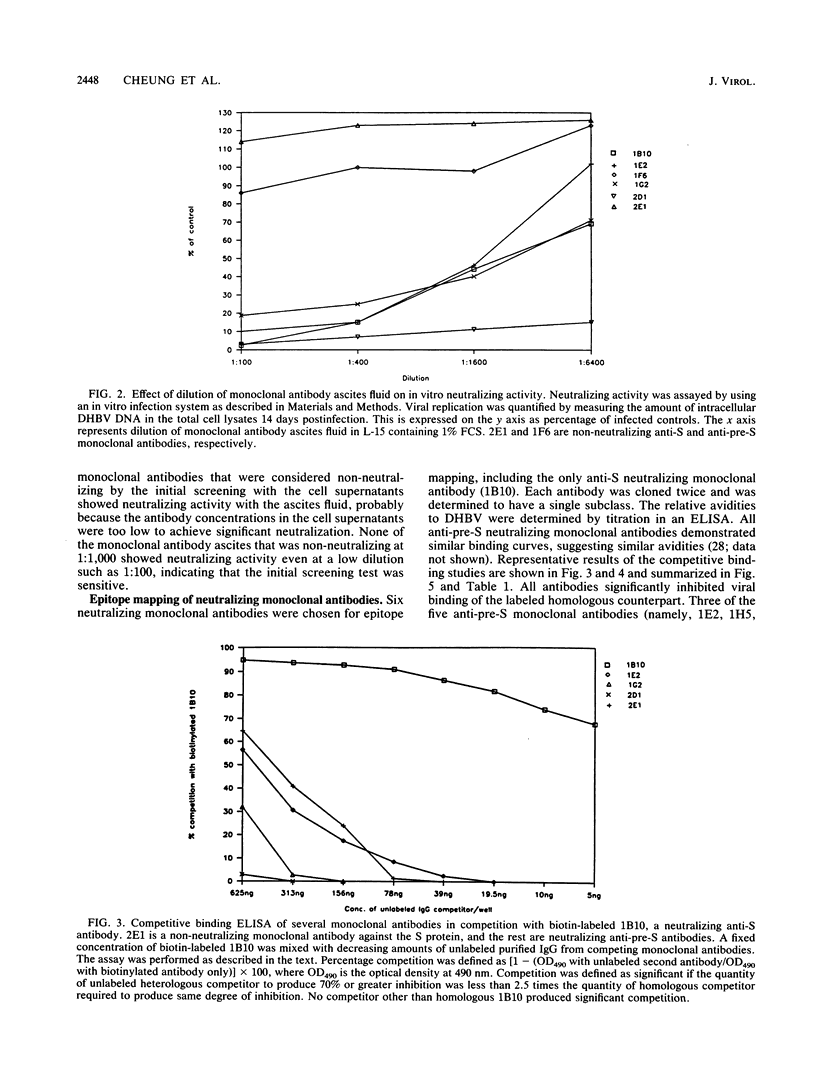
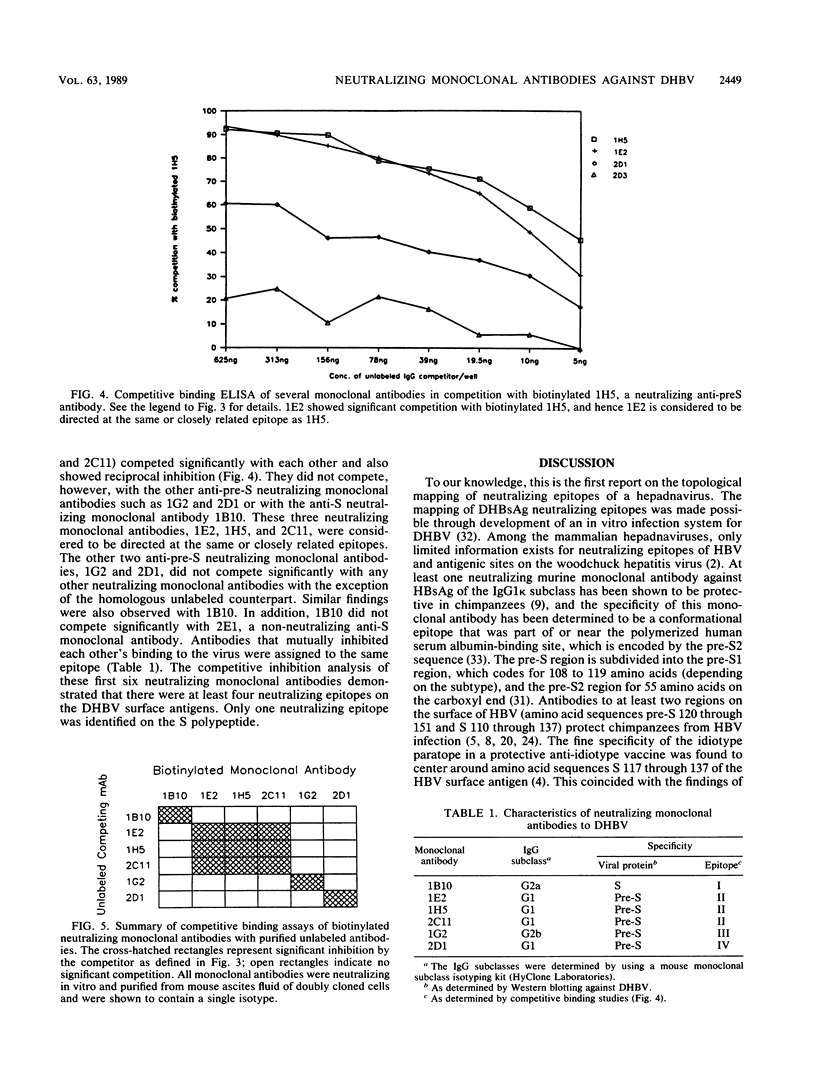
In this article we report the first topological mapping of neutralizing epitopes of a hepadnavirus. Duck hepatitis B virus is the only hepadnavirus that can replicate and spread from cell to cell in tissue culture. As a result, it is possible to study hepadnaviral neutralization in vitro with this system. To accomplish this goal, we produced a library of monoclonal antibodies against duck hepatitis B virus and identified 12 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies by using an in vitro neutralization assay. The characteristics of six of the neutralizing monoclonal antibodies were further studied by epitope mapping. From the results of competitive binding studies, three distinct neutralizing epitopes were identified on the pre-S polypeptides and one was identified on the S polypeptide. Our findings suggest that antibodies to both the pre-S and S gene products of duck hepatitis B virus can neutralize viral infection in vitro. The pre-S gene product is at least as important as the S gene product in eliciting neutralizing antibodies.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. Semin Liver Dis. 1984 May;4(2):113–121. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote P. J., Jr, Gerin J. L. Nonoverlapping antigenic sites of woodchuck hepatitis virus surface antigen and their cross-reactivity with ground squirrel hepatitis virus and hepatitis B virus surface antigens. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.15-23.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Mechanisms of neutralization of animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jun;65(Pt 6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-6-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Sanchez Y., Ionescu-Matiu I., Sparrow J. T., Six H. R., Peterson D. L., Hollinger F. B., Melnick J. L. Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen after a single inoculation of uncoupled synthetic HBsAg peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):158–160. doi: 10.1038/295158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Alexander H., Shih J. W., Purcell R. H., Dapolito G., Engle R., Green N., Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A. Chemically synthesized peptides of hepatitis B surface antigen duplicate the d/y specificities and induce subtype-specific antibodies in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J., van Wyke K., Midthun K., Walsh M., McAuliffe V., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Hoshino Y. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed at two surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.267-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. R. The biology of hepadnaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1215–1235. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Takai E., Ohnuma H., Kitajima K., Tsuda F., Machida A., Mishiro S., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A synthetic peptide vaccine involving the product of the pre-S(2) region of hepatitis B virus DNA: protective efficacy in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9174–9178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwarson S., Tabor E., Thomas H. C., Goodall A., Waters J., Snoy P., Shih J. W., Gerety R. J. Neutralization of hepatitis B virus infectivity by a murine monoclonal antibody: an experimental study in the chimpanzee. J Med Virol. 1985 May;16(1):89–96. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Eichberg J. W., Lanford R. E., Dreesman G. R. Anti-idiotypic antibody vaccine for type B viral hepatitis in chimpanzees. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):220–223. doi: 10.1126/science.3952505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Cullen J. M., Azcárraga R. R., Van Davelaar M. J., Robinson W. S. Experimental transmission of duck hepatitis B virus to Pekin ducks and to domestic geese. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):724–731. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Knight S. S., Feitelson M. A., Oshiro L. S., Robinson W. S. Major polypeptide of duck hepatitis B surface antigen particles. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):534–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.534-541.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Chisari F. V., Kent S. B., Thorton G. B. Immune response to the pre-S(1) region of the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): a pre-S(1)-specific T cell response can bypass nonresponsiveness to the pre-S(2) and S regions of HBsAg. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Thornton G. B., Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Michel M. L., Tiollais P., Chisari F. V. Enhanced immunogenicity of the pre-S region of hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1195–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.2408336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. Application of recombinant DNA techniques in the development of viral vaccines. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):164–174. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Parker K., Prince A. M., Strick N., Brotman B., Sproul P. Antibodies to a synthetic peptide from the preS 120-145 region of the hepatitis B virus envelope are virus neutralizing. Vaccine. 1986 Mar;4(1):35–37. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(86)80001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K., Courouce A. M., Riottot M. M., Petit M. A., Budkowska A., Girard M., Pillot J. Antibodies to synthetic peptides from the pre-S1 and pre-S2 regions of one subtype of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope protein recognize all HBV subtypes. Mol Immunol. 1987 Sep;24(9):975–980. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Sninsky J. J., Summers J. W., Schaeffer E. Characterization of a pre-S polypeptide on the surfaces of infectious avian hepadnavirus particles. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1384-1390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Prospects for second and third generation hepatitis B vaccines. Hepatology. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):159–163. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Marion P. L., Miller R. H. The hepadna viruses of animals. Semin Liver Dis. 1984 Nov;4(4):347–360. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Kuhn C., Guhr B., Mattaliano R. J., Schaller H. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the duck hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2280–2285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2280-2285.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. R., Nowinski R. C. Topological mapping of murine leukemia virus proteins by competition-binding assays with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):370–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90528-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart R. T., Samloff I. M. Stable antibody-producing murine hybridomas. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1228–1230. doi: 10.1126/science.6402815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. A., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. Relationship between poliovirus neutralization and aggregation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.479-485.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters J., Pignatelli M., Galpin S., Ishihara K., Thomas H. C. Virus-neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis B virus: the nature of an immunogenic epitope on the S gene peptide. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2467–2473. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman A. J. The development of novel hepatitis B vaccines. Bull World Health Organ. 1987;65(3):265–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]