Abstract
The herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 and ICP0 polypeptides are immediate-early proteins that positively and negatively regulate expression of other viral genes in trans. ICP4 has recently been shown to bind DNA bearing the consensus sequence 5'-ATCGTCNNNN(T/C)CG(A/G)C-3', present upstream of a number of viral genes. To test the hypothesis that this DNA-binding activity is involved in ICP4-mediated gene regulation, site-specific mutagenesis was employed to mutate the version of this sequence in the promoter of the ICP0 gene. The mutation eliminated detectable binding of ICP4 to the promoter as measured in vitro by a gel electrophoresis band shift assay. The ability of the mutated ICP0 promoter to direct synthesis of a reporter gene was also investigated in a transient transfection assay. Whereas ICP4 was found to transactivate the wild-type ICP0 promoter two- to threefold, the mutated promoter was transactivated seven- to ninefold. In assays containing the ICP0 transactivator gene, ICP4 down regulated the wild-type promoter far more efficiently than the mutated promoter. Finally, both the wild-type and mutated ICP0 promoters exhibited a similar response to ICP4 in transfections that included a vector expressing the viral transactivator protein VP16. These experiments suggest that the sequence-specific DNA-binding activity of ICP4 is an essential element of its role as a negative regulator of gene expression.
Full text
PDF
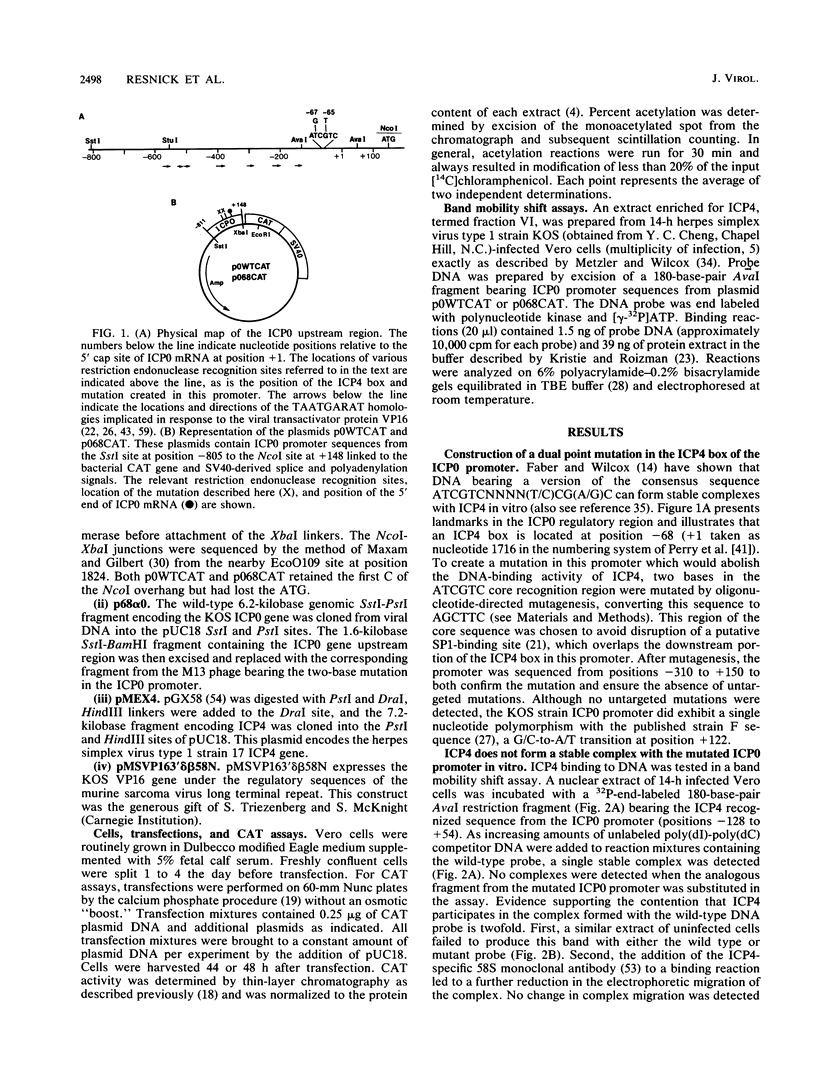


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block T., Jordan R. Herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha gene containing plasmids can inhibit expression regulated from an alpha promoter in CV-1 but not HeLa cells. Virus Res. 1988 Nov;11(4):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
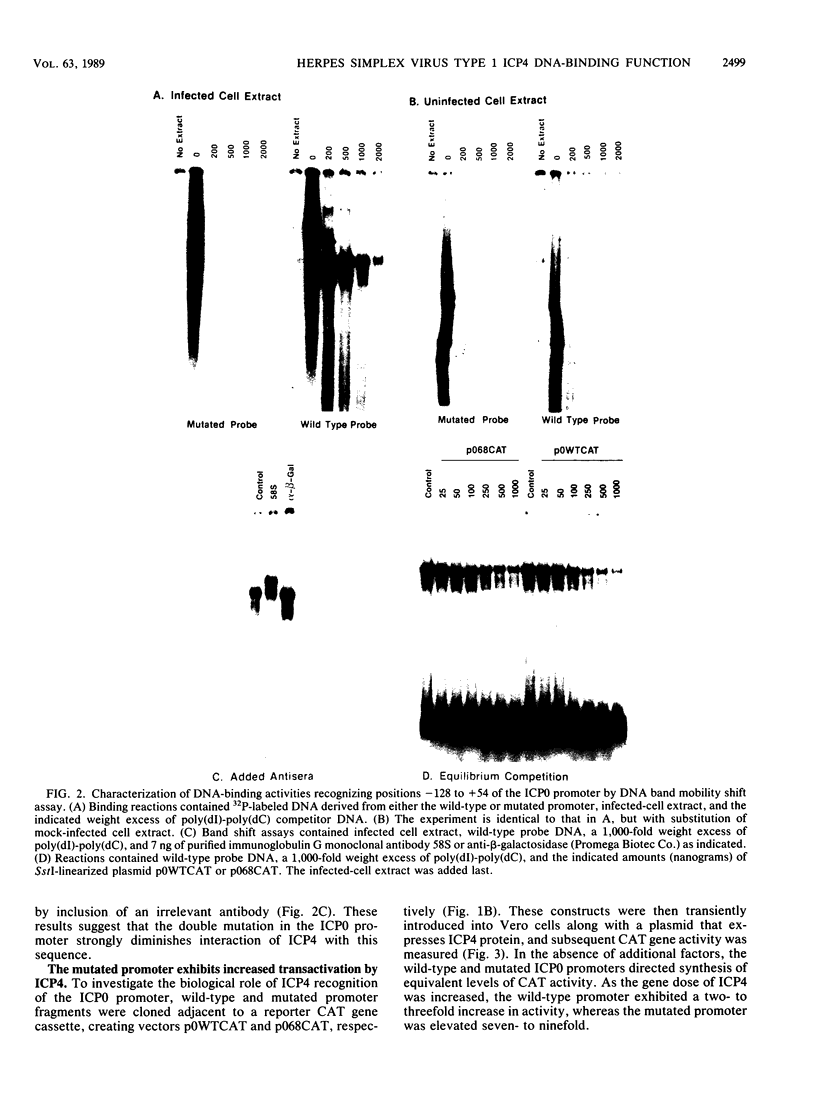
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Courtney M. A., Schaffer P. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants in herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 permissive for early gene expression. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):767–776. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.767-776.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical and functional domains of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):732–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.732-743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed mutational analysis of Vmw110, a trans-acting transcriptional activator encoded by herpes simplex virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2069–2076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The products of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate early genes 1, 2 and 3 can activate HSV-1 gene expression in trans. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2507–2513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Co-ordinate regulation of herpes simplex virus gene expression is mediated by the functional interaction of two immediate early gene products. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
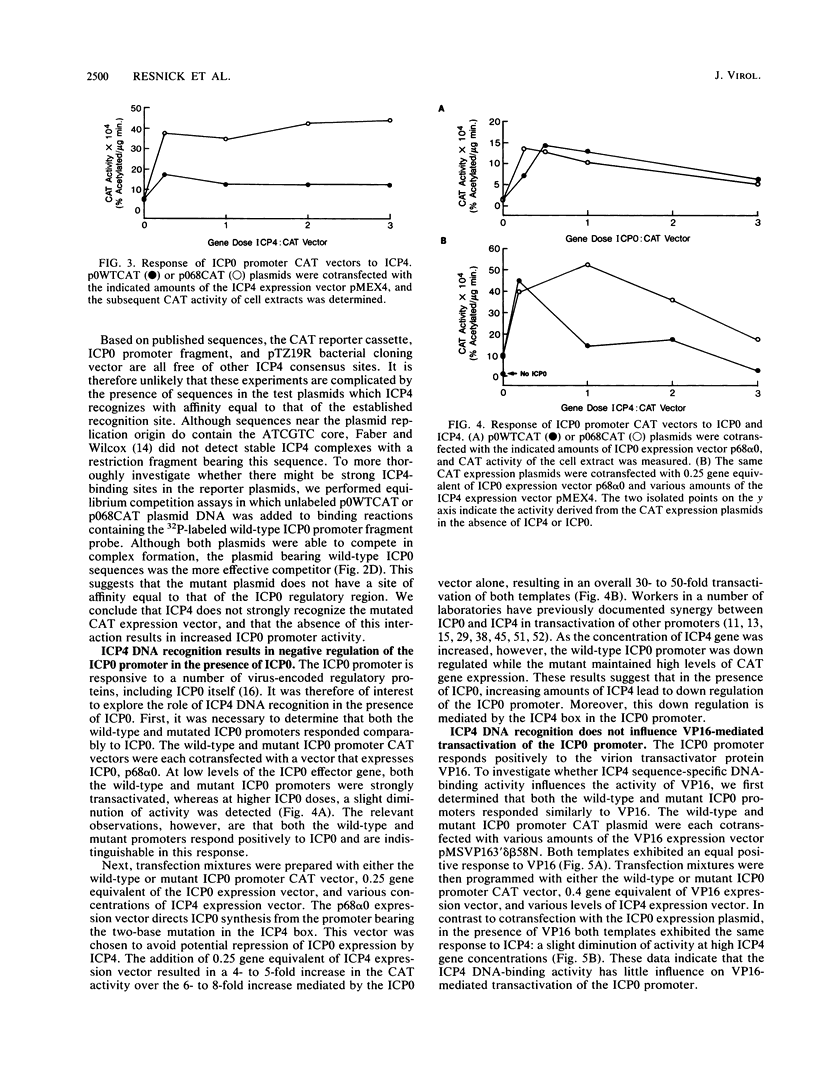
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Transcriptional control of herpesvirus gene expression: gene functions required for positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Sp1 binds to promoter sequences and activates herpes simplex virus 'immediate-early' gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):179–182. doi: 10.1038/317179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Silver S., Hubenthal-Voss J., McKnight J. L., Roizman B. Regulation of herpes simplex virus 1 genes: alpha gene sequence requirements for transient induction of indicator genes regulated by beta or late (gamma 2) promoters. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler D. W., Wilcox K. W. Isolation of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 as a homodimeric complex. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):329–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.329-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Spector D., Mavromara-Nazos P., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. The DNA-binding properties of the major regulatory protein alpha 4 of herpes simplex viruses. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1531–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2832940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T. Binding of the herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene product ICP4 to its own transcription start site. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):858–865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.858-865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Rice S. A., Knipe D. M., Baltimore D. Alternative mechanisms for activation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.2830675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Everett R. D. The regions of the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein Vmw175 required for site specific DNA binding closely correspond to those involved in transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11005–11025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Gene-specific transactivation by herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3814–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3814-3823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., Boundy A., O'Hare P., Pizzorno M. C., Ciufo D. M., Hayward G. S. Direct correlation between a negative autoregulatory response element at the cap site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE175 (alpha 4) promoter and a specific binding site for the IE175 (ICP4) protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4307–4320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4307-4320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder C. H., DeZazzo J., Knopf K. W., Kaerner H. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. A herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant with a deletion in the polypeptide-coding sequences of the ICP4 gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1589–1593. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder D. G., Pizer L. I. Role for DNA-protein interaction in activation of the herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D gene. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4661–4672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4661-4672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Rixon F. J., Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Immediate-early mRNA-2 of herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 is unspliced: conserved sequences around the 5' and 3' termini correspond to transcription regulatory signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6271–6287. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]