Abstract
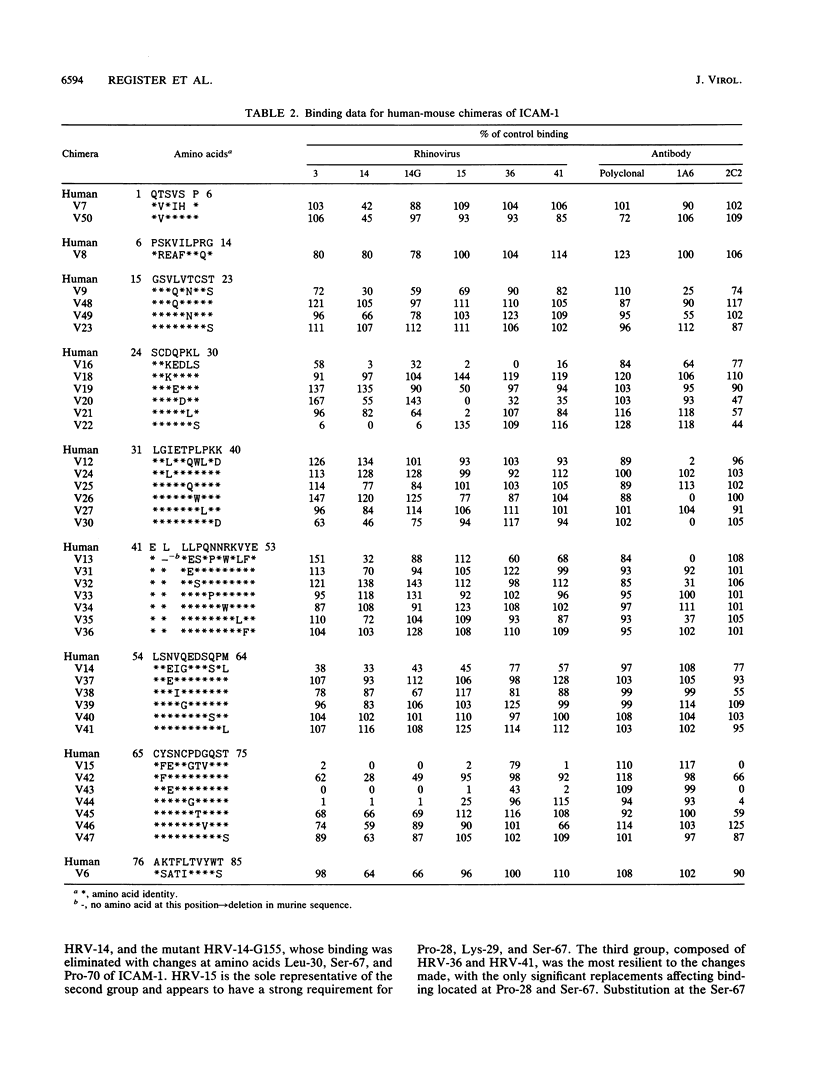
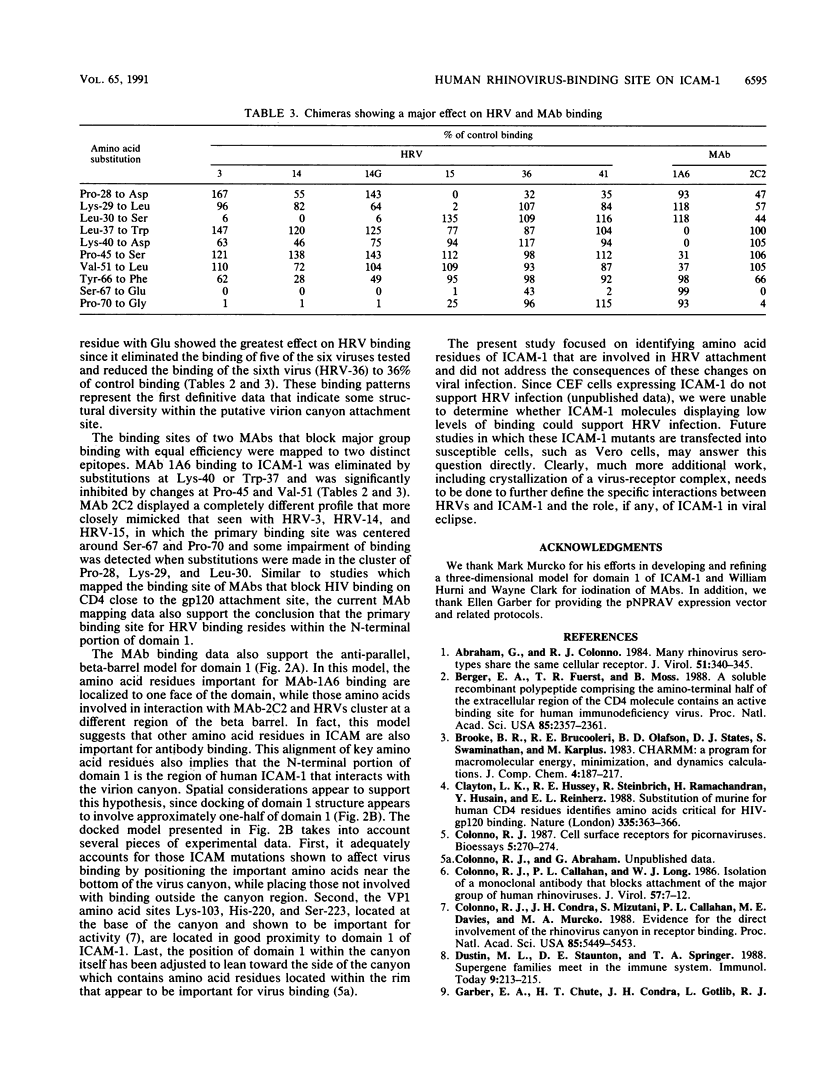
Human ICAM-1 is the cellular receptor for the major group of human rhinoviruses (HRVs). Previous studies have suggested that the N-terminal domain of ICAM-1 is critical for binding of the major group rhinoviruses. To further define the residues within domain 1 that are involved in virus binding, we constructed an extensive series of ICAM-1 cDNAs containing single and multiple amino acid residue substitutions. In each case, substitutions involved replacement of the human amino acids with those found in murine ICAM-1 to minimize conformational effects. To facilitate the mutagenesis process, a synthetic gene encompassing the first two domains of ICAM-1 was constructed which incorporated 27 additional restriction sites to allow mutagenesis by oligonucleotide replacement. Each of the new constructs was placed into a Rous sarcoma virus vector and expressed in primary chicken embryo fibroblast cells. Binding assays were performed with six major group HRVs, including one high-affinity binding mutant of HRV-14, and two monoclonal antibodies. Results indicated that different serotypes displayed a range of sensitivities to various amino acid substitutions. Amino acid residues of ICAM-1 showing the greatest effect on virus and antibody binding included Pro-28, Lys-29, Leu-30, Leu-37, Lys-40, Ser-67, and Pro-70.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. A soluble recombinant polypeptide comprising the amino-terminal half of the extracellular region of the CD4 molecule contains an active binding site for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2357–2361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L. K., Hussey R. E., Steinbrich R., Ramachandran H., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L. Substitution of murine for human CD4 residues identifies amino acids critical for HIV-gp120 binding. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):363–366. doi: 10.1038/335363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Callahan P. L., Long W. J. Isolation of a monoclonal antibody that blocks attachment of the major group of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.7-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J. Cell surface receptors for picornaviruses. Bioessays. 1986 Dec;5(6):270–274. doi: 10.1002/bies.950050609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Condra J. H., Mizutani S., Callahan P. L., Davies M. E., Murcko M. A. Evidence for the direct involvement of the rhinovirus canyon in receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. Supergene families meet in the immune system. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Chute H. T., Condra J. H., Gotlib L., Colonno R. J., Smith R. G. Avian cells expressing the murine Mx1 protein are resistant to influenza virus infection. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):754–762. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90088-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giranda V. L., Chapman M. S., Rossmann M. G. Modeling of the human intercellular adhesion molecule-1, the human rhinovirus major group receptor. Proteins. 1990;7(3):227–233. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horley K. J., Carpenito C., Baker B., Takei F. Molecular cloning of murine intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1). EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2889–2896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Rao P. E., Kong L. I., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Location and chemical synthesis of a binding site for HIV-1 on the CD4 protein. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1335–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.2453925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Warton M., Littman D. R. The envelope glycoprotein of the human immunodeficiency virus binds to the immunoglobulin-like domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):159–162. doi: 10.1038/334159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lineberger D. W., Graham D. J., Tomassini J. E., Colonno R. J. Antibodies that block rhinovirus attachment map to domain 1 of the major group receptor. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2582–2587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2582-2587.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makgoba M. W., Sanders M. E., Ginther Luce G. E., Gugel E. A., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A., Shaw S. Functional evidence that intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for LFA-1-dependent adhesion in T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):637–640. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. E., Kwong P. D., Truneh A., Porter T. G., Arthos J., Rosenberg M., Dai X. P., Xuong N. H., Axel R., Sweet R. W. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Makgoba M. W., Seed B. ICAM, an adhesion ligand of LFA-1, is homologous to the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):624–627. doi: 10.1038/331624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Erickson H. P., Springer T. A. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90805-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Marlin S. D., Stratowa C., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Primary structure of ICAM-1 demonstrates interaction between members of the immunoglobulin and integrin supergene families. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Colonno R. J. Isolation of a receptor protein involved in attachment of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.290-295.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Maxson T. R., Colonno R. J. Biochemical characterization of a glycoprotein required for rhinovirus attachment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1656–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uncapher C. R., DeWitt C. M., Colonno R. J. The major and minor group receptor families contain all but one human rhinovirus serotype. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):814–817. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90098-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Yan Y. W., Garrett T. P., Liu J. H., Rodgers D. W., Garlick R. L., Tarr G. E., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L., Harrison S. C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]