Abstract
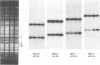
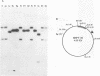
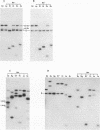
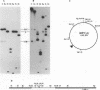
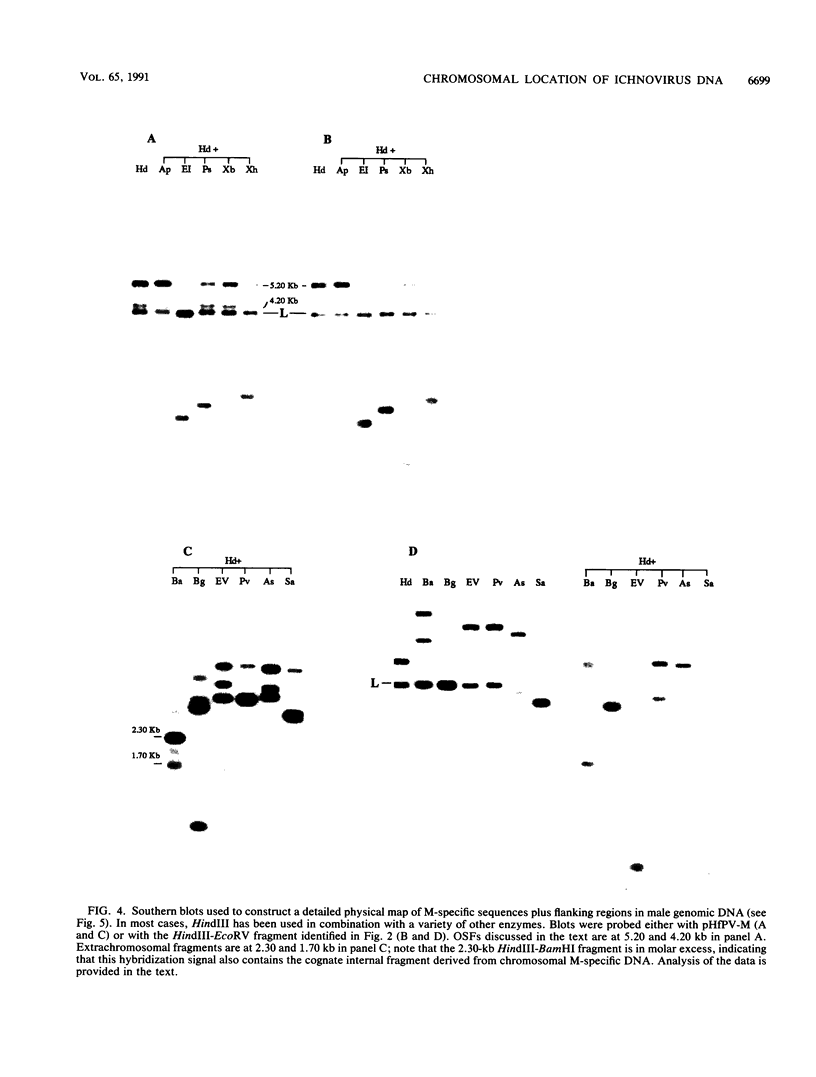
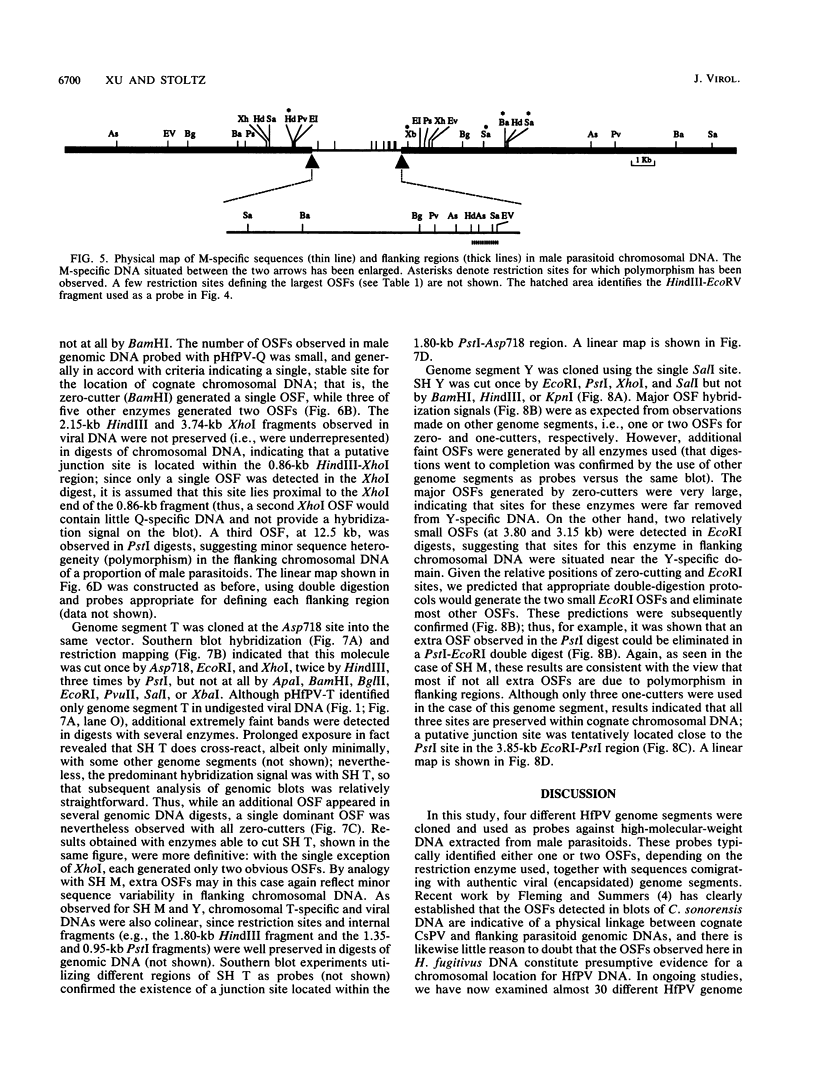
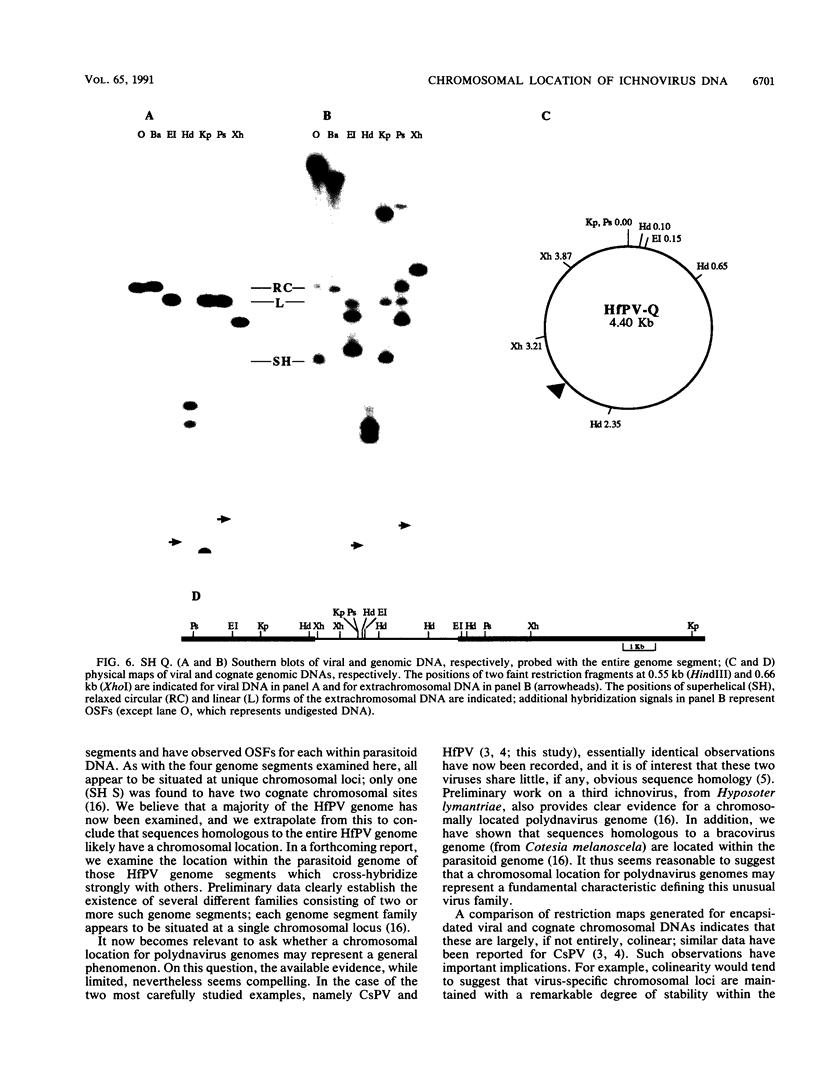
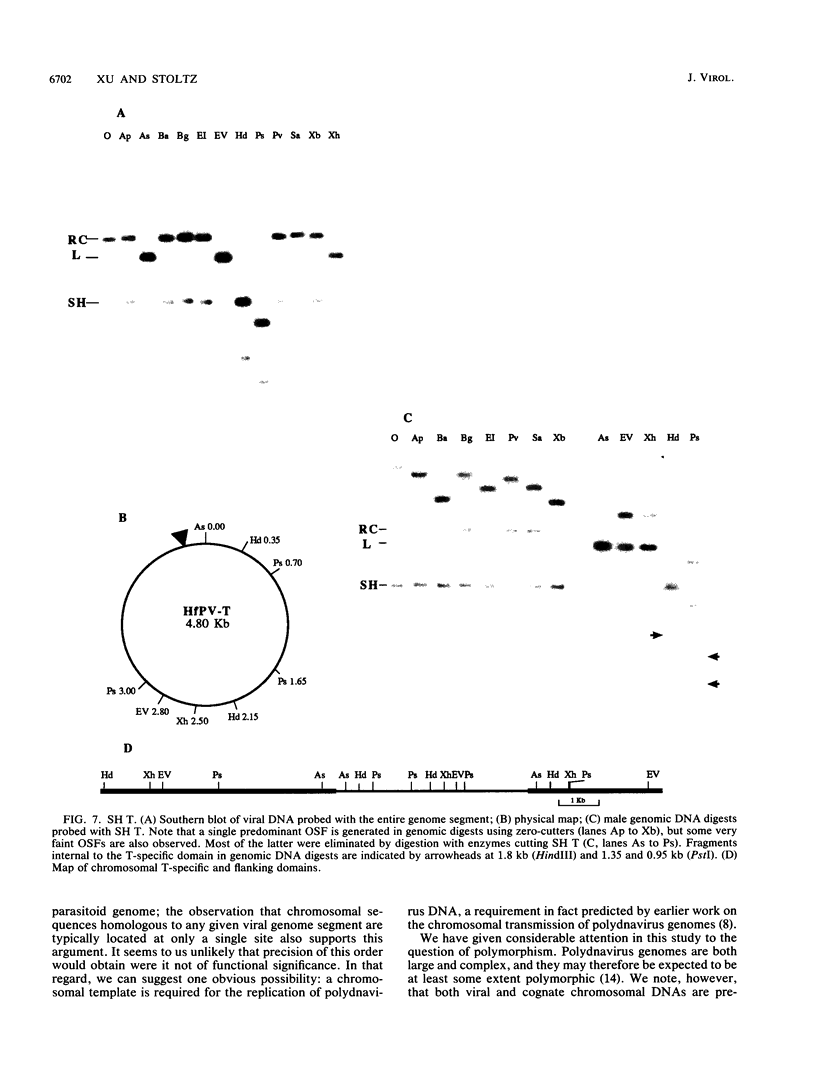
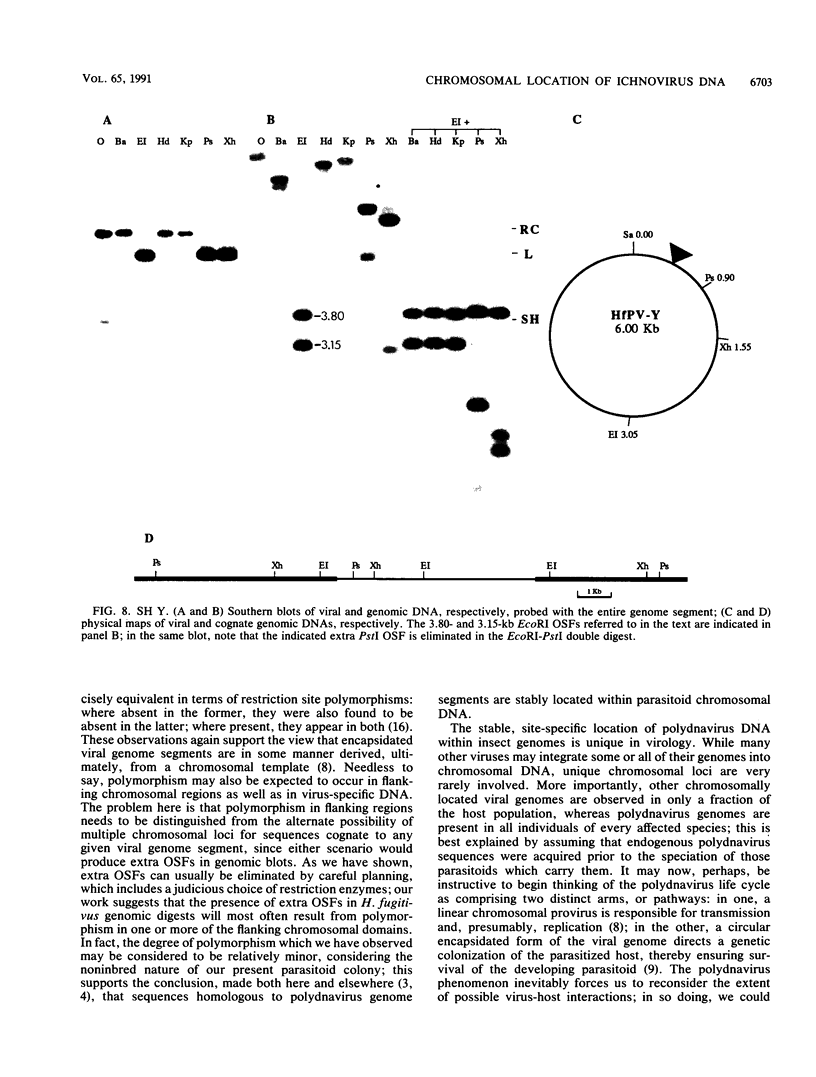
Evidence is presented in support of a chromosomal location for sequences homologous to polydnavirus DNA in the ichneumonid parasitoid Hyposoter fugitivus. In this study, four different viral genome segments were cloned and used as probes against genomic DNA extracted from male parasitoids and digested with a variety of restriction enzymes. Each probe typically identified a single off-size fragment (OSF) in the case of enzymes not cutting viral genome segments, while two OSFs were generated by enzymes cutting at one and two sites. While extra OSFs were occasionally observed, these were invariably found to be due to the presence of polymorphic restriction sites in flanking chromosomal DNA. Analysis of these data suggests that a single, stable chromosomal locus exists for sequences homologous to each viral genome segment; the data also indicate that viral and cognate parasitoid genomic DNAs are largely if not entirely colinear.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edson K. M., Vinson S. B., Stoltz D. B., Summers M. D. Virus in a parasitoid wasp: suppression of the cellular immune response in the parasitoid's host. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):582–583. doi: 10.1126/science.7455695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. A., Summers M. D. Campoletis sonorensis Endoparasitic Wasps Contain Forms of C. sonorensis Virus DNA Suggestive of Integrated and Extrachromosomal Polydnavirus DNAs. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):552–562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.552-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B. Evidence for chromosomal transmission of polydnavirus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1051–1056. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Guzo D., Cook D. Studies on polydnavirus transmission. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Krell P., Summers M. D., Vinson S. B. Polydnaviridae - a proposed family of insect viruses with segmented, double-stranded, circular DNA genomes. Intervirology. 1984;21(1):1–4. doi: 10.1159/000149497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Vinson S. B. Viruses and parasitism in insects. Adv Virus Res. 1979;24:125–171. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Xu D. Polymorphism in polydnavirus genomes. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Aug;36(8):538–543. doi: 10.1139/m90-094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann D. A., Summers M. D. Physical Analysis of the Campoletis sonorensis Virus Multipartite Genome and Identification of a Family of Tandemly Repeated Elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2589–2598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2589-2598.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]