Abstract
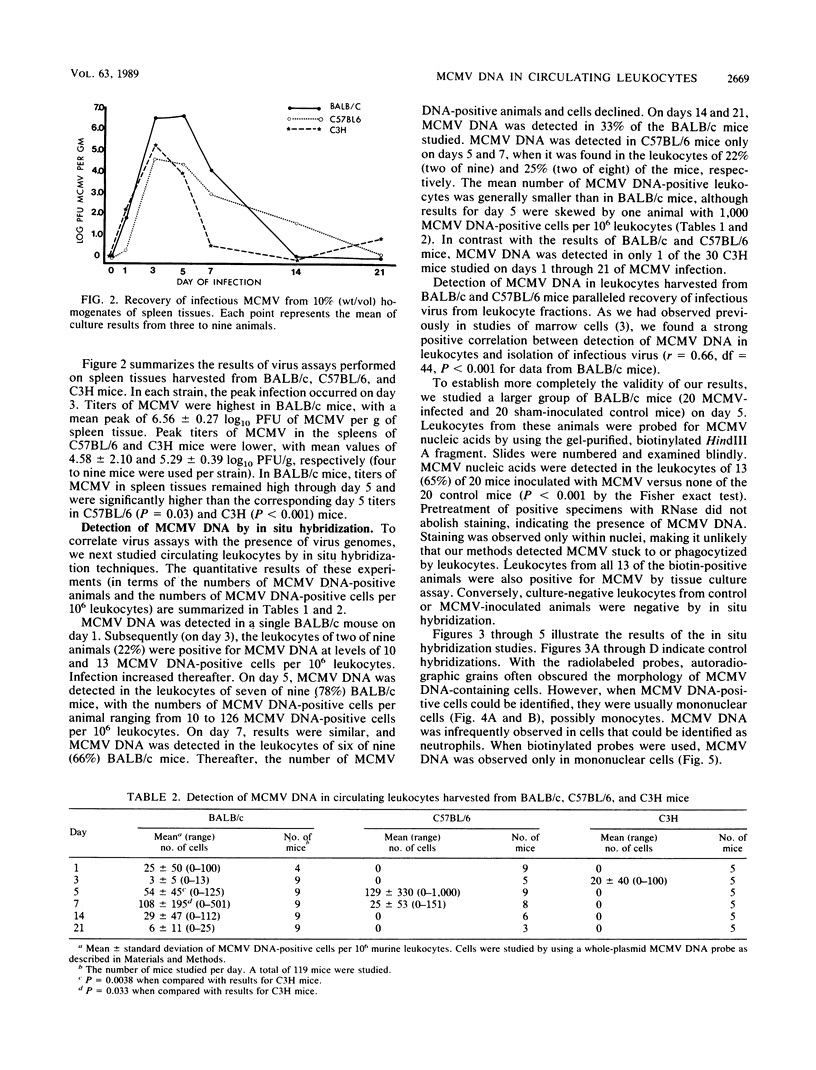
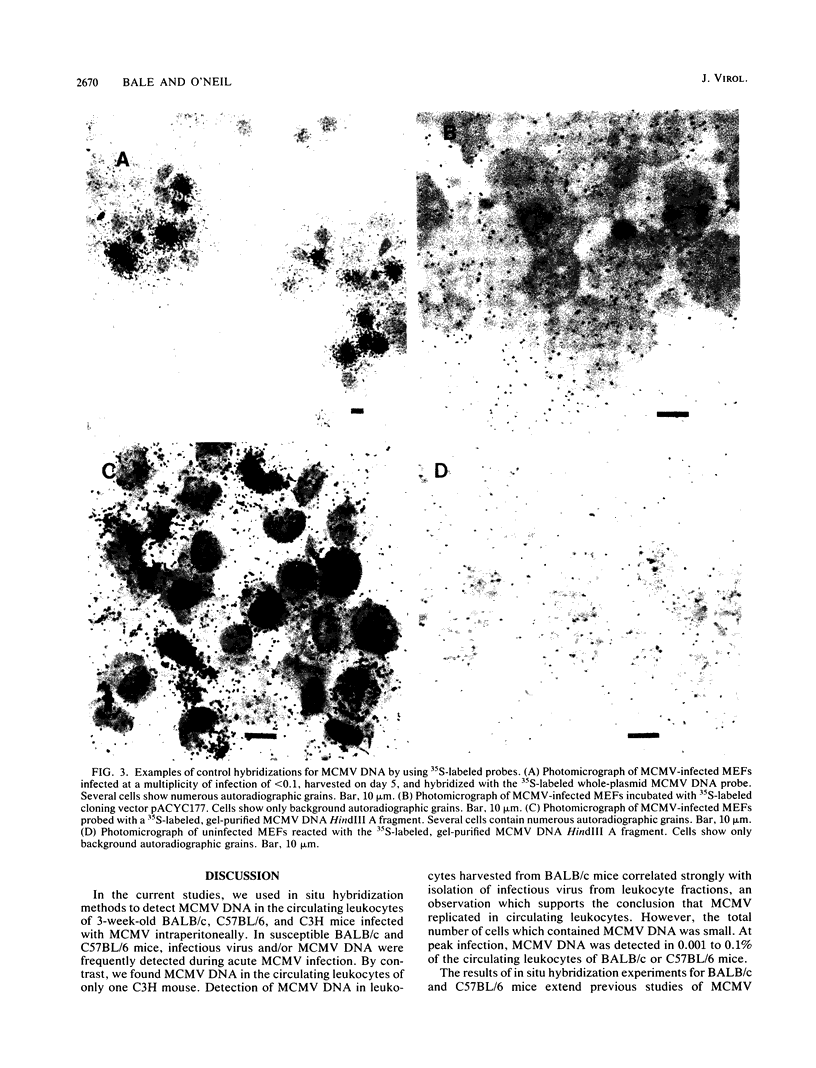
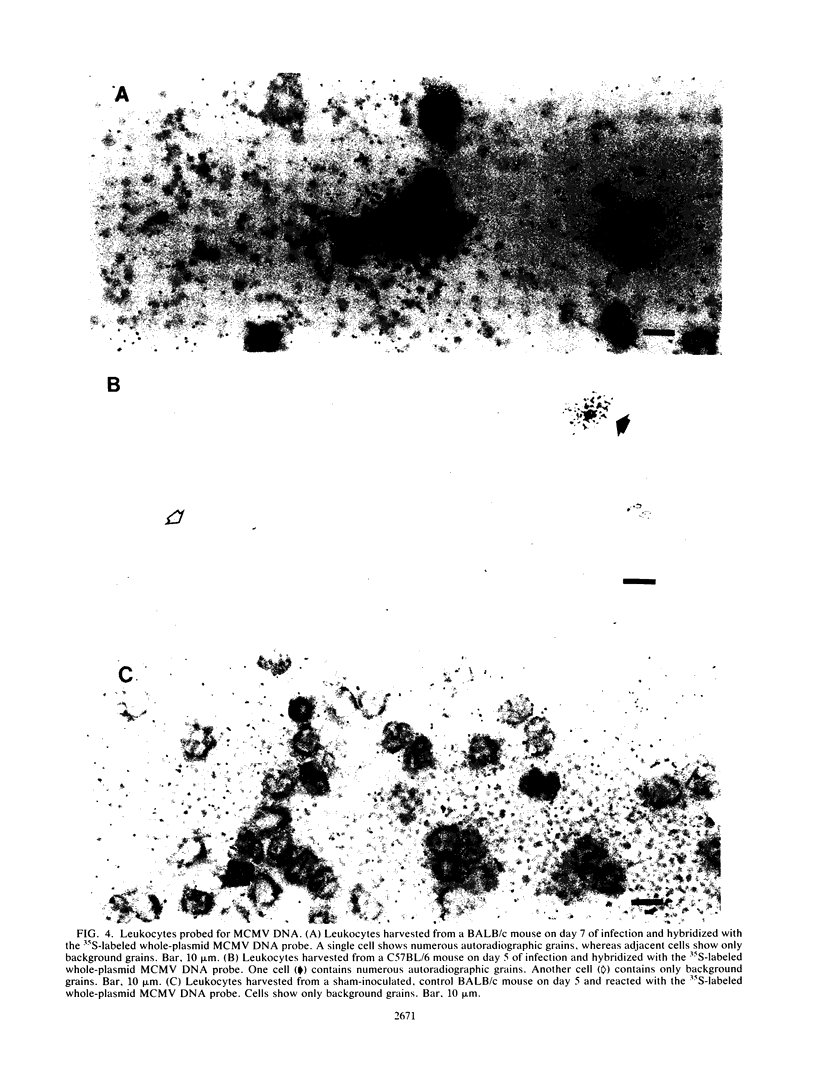
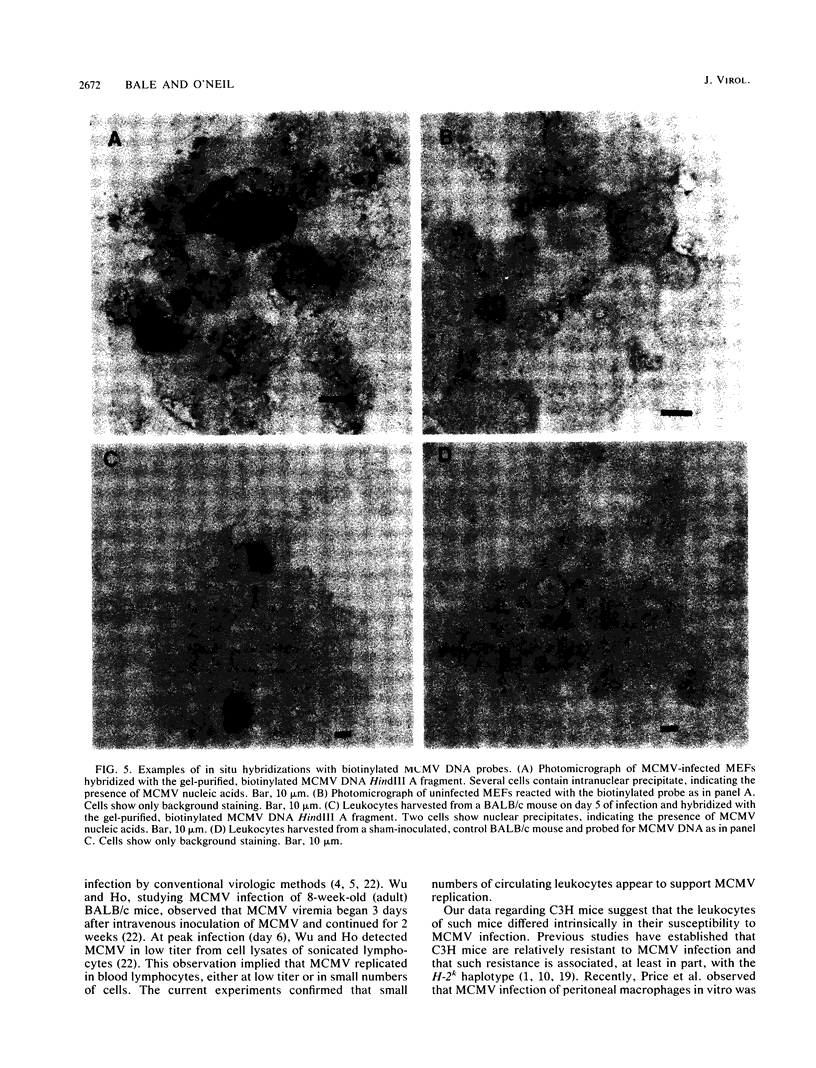
We used virus assay and in situ hybridization with a cloned fragment of the murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) genome to study MCMV infection of circulating leukocytes harvested from 3-week-old BALB/c, C57BL/6, and C3H mice infected with MCMV intraperitoneally. Infectious virus or MCMV DNA was detected in leukocytes on days 1 through 21 of infection in BALB/c mice and on days 3 through 7 in C57BL/6 mice. On days 5 and 7, MCMV DNA or infectious virus was detected in the leukocytes of 17 (94%) of 18 BALB/c mice and 10 (59%) of 17 C57BL/6 mice. In both strains infection peaked on days 5 and 7, when as many as 0.01 to 0.1% of the circulating leukocytes contained MCMV DNA. In C3H mice, however, infectious virus was rarely recovered from leukocyte fractions and MCMV DNA was detected in the circulating leukocytes of only one animal. Circulating leukocytes may have an important role in the dissemination of CMV infections in susceptible hosts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. E., Shellam G. R. Genetic control of murine cytomegalovirus infection: virus titres in resistant and susceptible strains of mice. Arch Virol. 1984;81(1-2):139–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01309303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale J. F., Jr, Kern E. R., Overall J. C., Jr, Baringer J. R. Impaired migratory and chemotactic activity of neutrophils during murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):518–525. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale J. F., Jr, O'Neil M. E., Giller R., Perlman S., Koszinowski U. Murine cytomegalovirus genomic material in marrow cells: relation to altered leukocyte counts during sublethal infection of mice. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):207–212. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Role of viremia in the suppression of T-cell function during murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):378–381. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.378-381.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. S., Lang D. J. Transmission and activation of cytomegalovirus with blood transfusion: a mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):841–845. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. S., Li J. K., Falletta J. M., Wagner J. L., Lang D. J. Murine cytomegalovirus infection: hematological, morphological, and functional study of lymphoid cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):239–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.239-249.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling A., Keil G. M., Knust E., Koszinowski U. H. Molecular cloning and physical mapping of murine cytomegalovirus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):421–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.421-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Chatterjee S. The role of lymphocytes in infections due to Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):300–301. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Payne J. E., Berne T. V., Moore T. C., Henle W., Montgomerie J. Z., Chatterjee S. N., Guze L. B. Epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infection after transplantation and immunosuppression. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):421–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Mackenzie J. S., Stanley N. F. Influence of H-2 and non-H-2 genes on resistance to murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):277–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.277-286.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. The lymphocyte in infections with Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):857–862. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B. The murine cytomegalovirus as a model for the study of viral pathogenesis and persistent infections. Arch Virol. 1979;62(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01314900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil G. M., Ebeling-Keil A., Koszinowski U. H. Temporal regulation of murine cytomegalovirus transcription and mapping of viral RNA synthesized at immediate early times after infection. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):784–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.784-795.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. C., Katzenstein D. A., Yu G. S., Jordan M. C. Cytomegalovirus viremia detected by molecular hybridization and electron microscopy. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Feb;100(2):222–225. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-2-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Spector D. H. Pathogenesis of acute murine cytomegalovirus infection in resistant and susceptible strains of mice. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):497–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.497-504.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Shahidi N. T. Thrombocytopenia in murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jan;81(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P., Winter J. G., Nikoletti S., Hudson J. B., Shellam G. R. Functional changes in murine macrophages infected with cytomegalovirus relate to H-2-determined sensitivity to infection. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3602–3606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3602-3606.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Manischewitz J. F. Genetically determined resistance to lethal murine cytomegalovirus infection is mediated by interferon-dependent and -independent restriction of virus replication. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1875–1881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1875-1881.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Black P. H., Hirsch M. S. Interaction of cytomegalovirus with leukocytes from patients with mononucleosis due to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):667–678. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral blood lymphocytes in a natural infection. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1048–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2997930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. C., Ho M. Characteristics of infection of B and T lymphocytes from mice after inoculation with cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):856–864. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.856-864.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Forman S. J., Gallagher M. T., Vanderwal-Urbina E., Blume K. G. Prolonged human cytomegalovirus viremia following bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1984 Mar;37(3):315–317. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198403000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]