Abstract
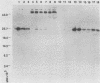
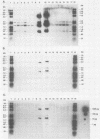
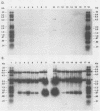
Replication-defective vectors derived from reticuloendotheliosis virus were used to transduce exogenous genes into early somatic stem cells of the chicken embryo. One of these vectors transduced and expressed the chicken growth hormone coding sequence. The helper cell line, C3, was used to generate stocks of vector containing about 10(4) transducing units per ml. Injection of 5- to 20-microliters volumes of vector directly beneath the blastoderm of unincubated chicken embryos led to infection of somatic stem cells. Infected embryos and adults contained unrearranged integrated proviral DNAs. Embryos expressed the transduced chicken growth hormone gene and contained high levels of serum growth hormone. Blood, brain, muscle, testis, and semen contained from individuals injected as embryos contained vector DNA. Replication-defective vectors of the reticuloendotheliosis virus transduced exogenous genes into chicken embryonic stem cells in vivo.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosselman R. A., Hsu R. Y., Bruszewski J., Hu S., Martin F., Nicolson M. Replication-defective chimeric helper proviruses and factors affecting generation of competent virus: expression of Moloney murine leukemia virus structural genes via the metallothionein promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1797–1806. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. Retrovirus vectors and their applications in neurobiology. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Mak T. W., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Characterization of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T DNA and isolation of a novel variant of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T by molecular cloning. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):800–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.800-811.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decuypere E., Scanes C. G. Variation in the release of thyroxine, triiodothyronine and growth hormone in response to thyrotrophin releasing hormone during development of the domestic fowl. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Feb;102(2):220–223. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyal-Giladi H., Kochav S. From cleavage to primitive streak formation: a complementary normal table and a new look at the first stages of the development of the chick. I. General morphology. Dev Biol. 1976 Apr;49(2):321–337. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyal-Giladi H., Kochav S., Menashi M. K. On the origin of primordial germ cells in the chick embryo. Differentiation. 1976 Mar 16;6(1):13–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1976.tb01462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyal-Giladi H., Spratt N. T., Jr The embryo-forming potencies of the young chick blastoderm. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1965 Jun;13(3):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyal-Giladi H. The gradual establishment of cell commitments during the early stages of chick development. Cell Differ. 1984 Oct;14(4):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Davison T. F., Chadwick A. Ontogeny of growth hormone and prolactin secretion in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1979 Nov;39(3):270–273. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(79)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Bruszewski J., Nicolson M., Tseng J., Hsu R. Y., Bosselman R. Generation of competent virus in the REV helper cell line C3. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):446–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90484-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Kosik E., Fadly A. M., Salter D. W., Crittenden L. B. Design of retroviral vectors for the insertion of foreign deoxyribonucleic acid sequences into the avian germ line. Poult Sci. 1986 Aug;65(8):1459–1467. doi: 10.3382/ps.0651459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Józsa R., Scanes C. G., Vigh S., Mess B. Functional differentiation of the embryonic chicken pituitary gland studied by immunohistological approach. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1979 Oct;39(2):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(79)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochav S., Ginsburg M., Eyal-Giladi H. From cleavage to primitive streak formation: a complementary normal table and a new look at the first stages of the development of the chick. II. Microscopic anatomy and cell population dynamics. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):296–308. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitrani E., Eyal-Giladi H. Cells from early chick embryos in culture. Differentiation. 1982;21(1):56–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noori-Daloii M. R., Swift R. A., Kung H. J., Crittenden L. B., Witter R. L. Specific integration of REV proviruses in avian bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):574–576. doi: 10.1038/294574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. M. A complete culture system for the chick embryo. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):70–72. doi: 10.1038/331070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. W., Smith E. J., Hughes S. H., Wright S. E., Crittenden L. B. Transgenic chickens: insertion of retroviral genes into the chicken germ line. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. W., Smith E. J., Hughes S. H., Wright S. E., Fadly A. M., Witter R. L., Crittenden L. B. Gene insertion into the chicken germ line by retroviruses. Poult Sci. 1986 Aug;65(8):1445–1458. doi: 10.3382/ps.0651445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanes C. G., Lauterio T. J. Growth hormone: its physiology and control. J Exp Zool. 1984 Dec;232(3):443–452. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402320310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Hughes S. H. Splicing of intervening sequences introduced into an infectious retroviral vector. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):547–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Boone T. C., Murdock D., Langley K., Wypych J., Fenton D., Johnson S., Lai P. H., Everett R., Hsu R. Y. Application of recombinant DNA technologies to studies on chicken growth hormone. J Exp Zool. 1984 Dec;232(3):465–473. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402320313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Development of avian sarcoma and leukosis virus-based vector-packaging cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1008–1015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1008-1015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift R. A., Boerkoel C., Ridgway A., Fujita D. J., Dodgson J. B., Kung H. J. B-lymphoma induction by reticuloendotheliosis virus: characterization of a mutated chicken syncytial virus provirus involved in c-myc activation. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2084–2090. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2084-2090.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Construction of a helper cell line for avian reticuloendotheliosis virus cloning vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L., Johnson D. C. Epidemiology of reticuloendotheliosis virus in broiler breeder flocks. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1140–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L., Smith E. J., Crittenden L. B. Tolerance, viral shedding, and neoplasia in chickens infected with non-defective reticuloendotheliosis viruses. Avian Dis. 1981 Apr-Jun;25(2):374–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]