Abstract
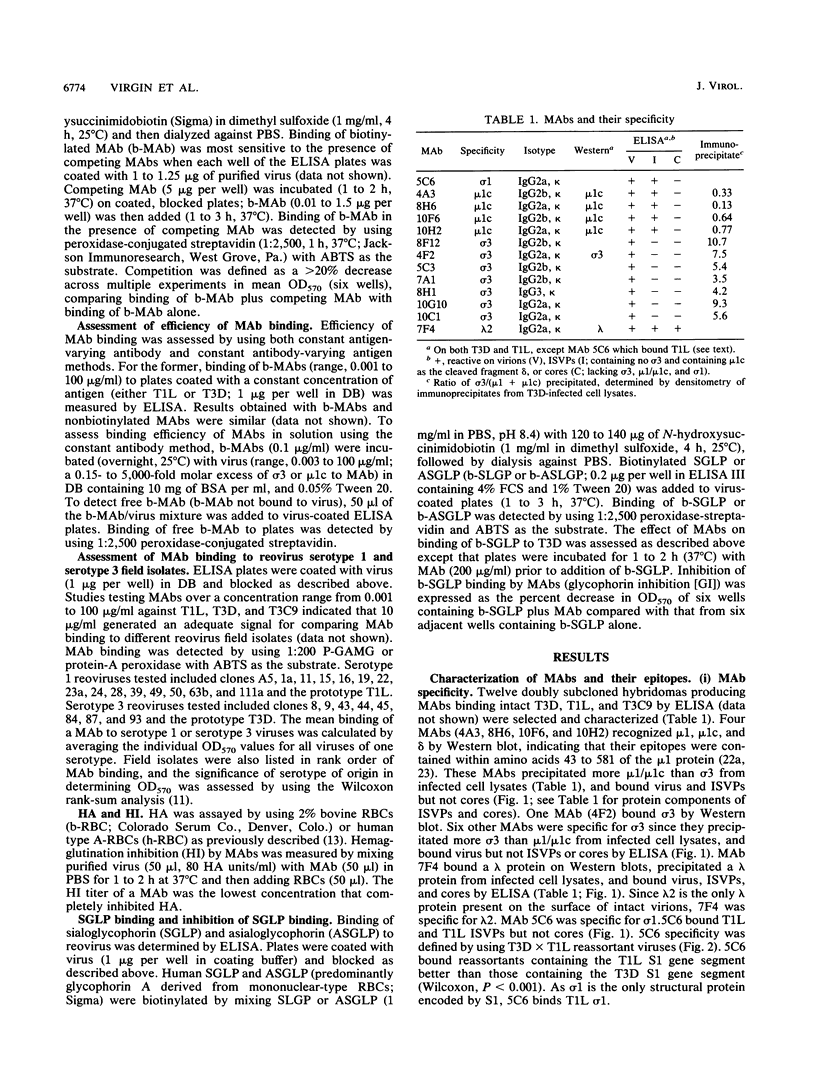
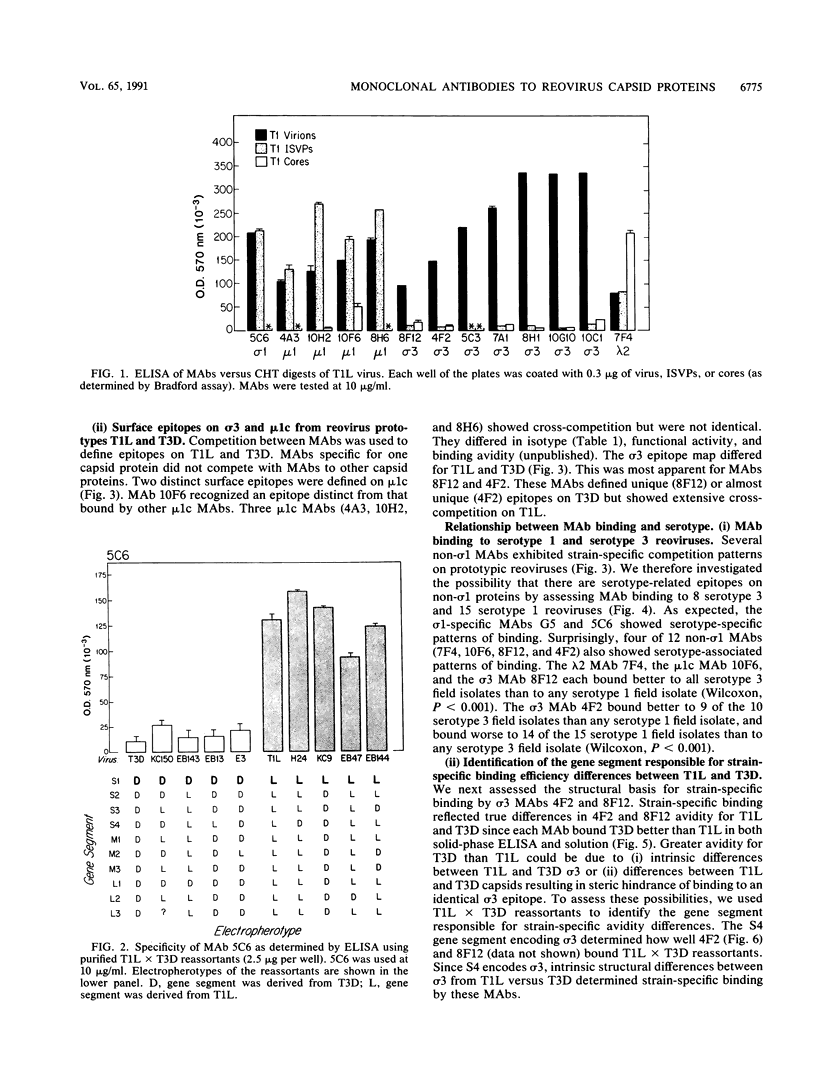
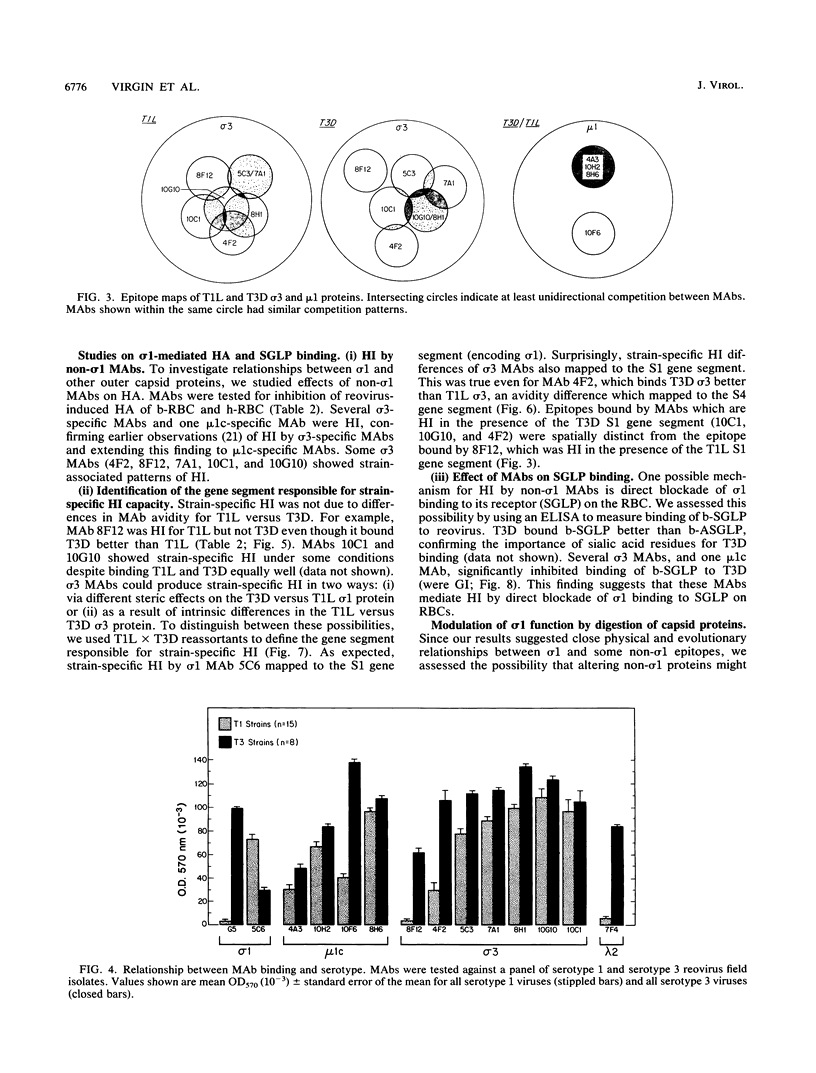
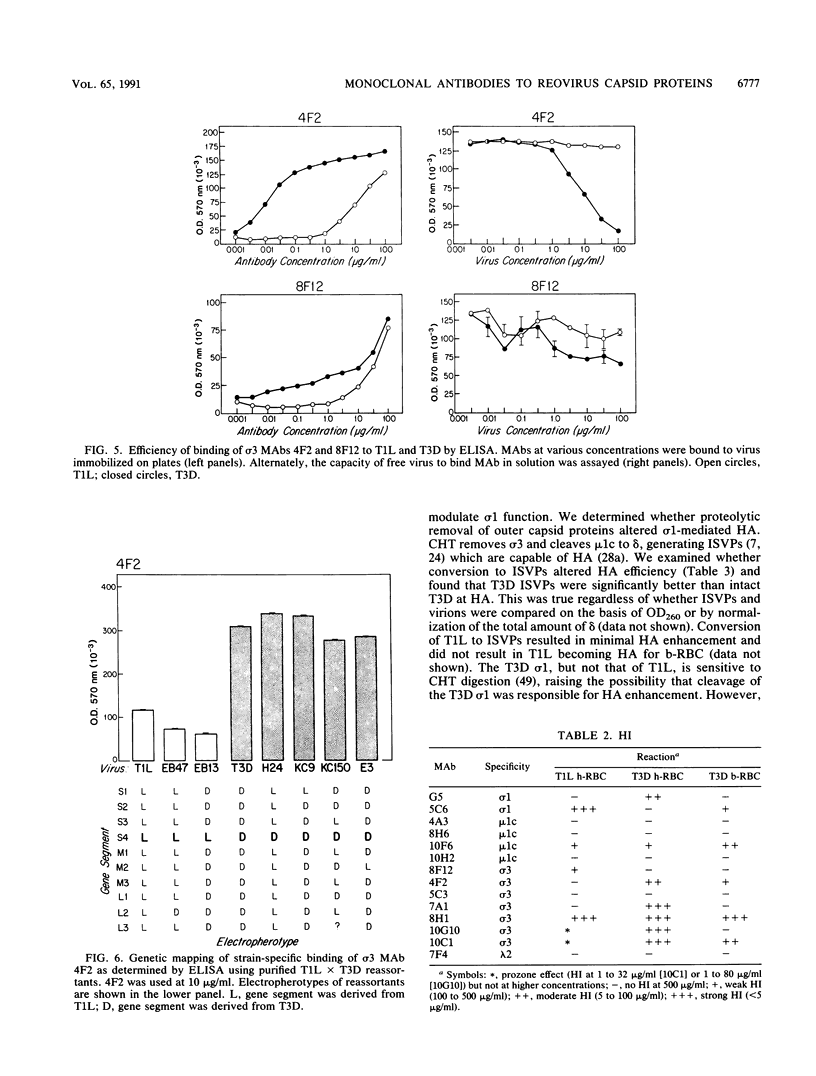
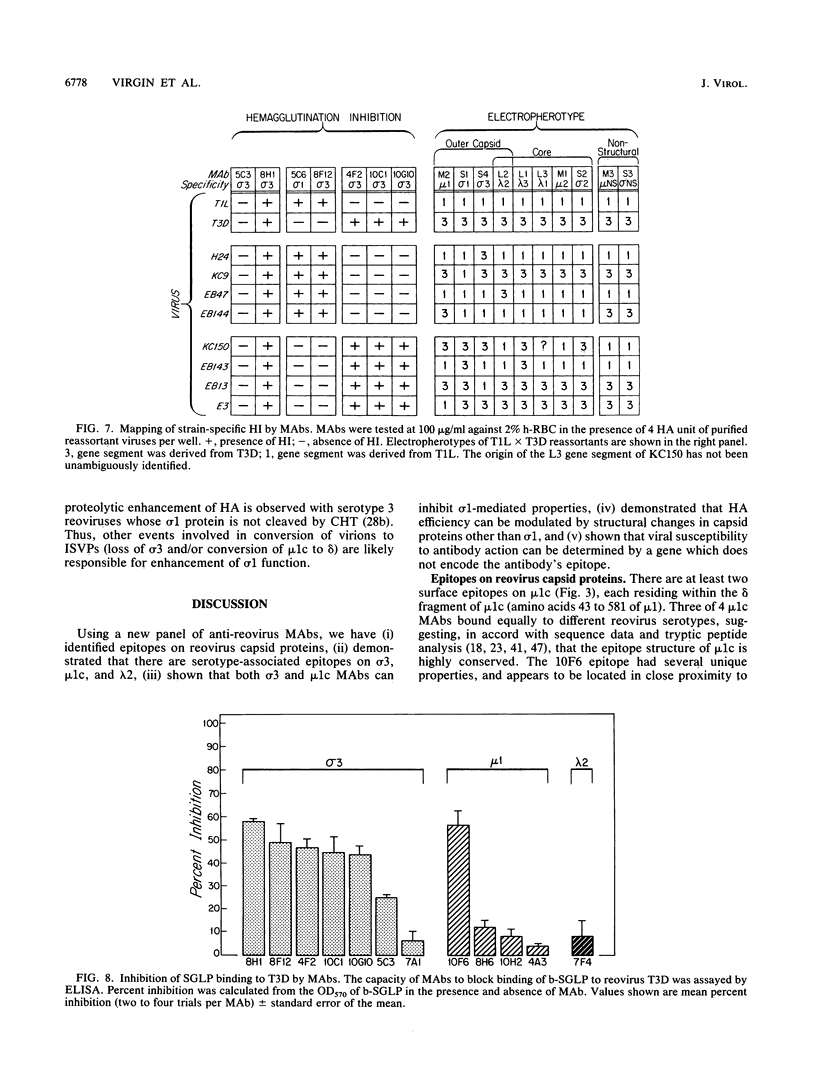
Thirteen newly isolated monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) were used to study relationships between reovirus outer capsid proteins sigma 3, mu 1c, and lambda 2 (core spike) and the cell attachment protein sigma 1. We focused on sigma 1-associated properties of serotype specificity and hemagglutination (HA). Competition between MAbs revealed two surface epitopes on mu 1c that were highly conserved between reovirus serotype 1 Lang (T1L) and serotype 3 Dearing (T3D). There were several differences between T1L and T3D sigma 3 epitope maps. Studies using T1L x T3D reassortants showed that primary sequence differences between T1L and T3D sigma 3 proteins accounted for differences in sigma 3 epitope maps. Four of 12 non-sigma 1 MAbs showed a serotype-associated pattern of binding to 25 reovirus field isolates. Thus, for reovirus field isolates, different sigma 1 proteins are associated with preferred epitopes on other outer capsid proteins. Further evidence for a close structural and functional interrelationship between sigma 3/mu 1c and sigma 1 included (i) inhibition by sigma 3 and mu 1c MAbs of sigma 1-mediated HA, (ii) enhancement of sigma 1-mediated HA by proteolytic cleavage of sigma 3 and mu 1c, and (iii) genetic studies demonstrating that sigma 1 controlled the capacity of sigma 3 MAbs to inhibit HA. These data suggest that (i) epitopes on sigma 3 and mu 1c lie in close proximity to sigma 1 and that MAbs to these epitopes can modulate sigma 1-mediated functions, (ii) these spatial relationships have functional significance, since removal of sigma 3 and/or cleavage of mu 1c to delta can enhance sigma 1 function, (iii) in nature, the sigma 1 protein places selective constraints on the epitope structure of the other capsid proteins, and (iv) viral susceptibility to antibody action can be determined by genes other than that encoding an antibody's epitope.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater J. A., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. Molecular cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence of the reovirus serotype 1 Lang strain s4 mRNA which encodes the major capsid surface polypeptide sigma 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjea A. C., Brechling K. A., Ray C. A., Erikson H., Pickup D. J., Joklik W. K. High-level synthesis of biologically active reovirus protein sigma 1 in a mammalian expression vector system. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):601–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjea A. C., Joklik W. K. Reovirus protein sigma 1 translated in vitro, as well as truncated derivatives of it that lack up to two-thirds of its C-terminal portion, exists as two major tetrameric molecular species that differ in electrophoretic mobility. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):460–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90315-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. M., Bodkin D., Dambrauskas R., Trier J. S., Fields B. N., Wolf J. L. Intraluminal proteolytic activation plays an important role in replication of type 1 reovirus in the intestines of neonatal mice. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1830–1833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1830-1833.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel-Duby R., Jayasuriya A., Chatterjee D., Sonenberg N., Maizel J. V., Jr, Fields B. N. Sequence of reovirus haemagglutinin predicts a coiled-coil structure. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):421–423. doi: 10.1038/315421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodkin D. K., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Proteolytic digestion of reovirus in the intestinal lumens of neonatal mice. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4676–4681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4676-4681.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Copps T. P., Sargent M. D., Long D. G., Chapman J. D. New intermediate subviral particles in the in vitro uncoating of reovirus virions by chymotrypsin. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):552–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.552-564.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Evidence for functional domains on the reovirus type 3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):146–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90514-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashdollar L. W., Chmelo R. A., Wiener J. R., Joklik W. K. Sequences of the S1 genes of the three serotypes of reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):24–28. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermody T. S., Nibert M. L., Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N. A sigma 1 region important for hemagglutination by serotype 3 reovirus strains. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5173–5176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5173-5176.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermody T. S., Nibert M. L., Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N. Sequence diversity in S1 genes and S1 translation products of 11 serotype 3 reovirus strains. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4842–4850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4842-4850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Horne D., Cashdollar L. W., Joklik W. K., Lee P. W. Identification of conserved domains in the cell attachment proteins of the three serotypes of reovirus. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. D., Furlong D. B., Trus B. L., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N., Steven A. C. Molecular structure of the cell-attachment protein of reovirus: correlation of computer-processed electron micrographs with sequence-based predictions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2990–3000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2990-3000.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard R. K., Joklik W. K. The antigenic determinants of most of the proteins coded by the three serotypes of reovirus are highly conserved during evolution. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):533–536. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard R. K., Jr, Joklik W. K. Quantitation of the relatedness of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3 at the gene level. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentsch J. R., Fields B. N. Genetic diversity in natural populations of mammalian reoviruses: tryptic peptide analysis of outer capsid polypeptides of murine, bovine, and human type 1 and 3 reovirus strains. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):641–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.641-651.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentsch J. R., Pacitti A. F. Effect of neuraminidase treatment of cells and effect of soluble glycoproteins on type 3 reovirus attachment to murine L cells. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):356–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.356-364.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Seliger L. S., Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus type 3 genome segment S4: nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding a major virion surface protein. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):984–987. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.984-987.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. C., Lee P. W., Miller S. E., Joklik W. K. The interaction of a series of hybridoma IgGs with reovirus particles. Demonstration that the core protein lambda 2 is exposed on the particle surface. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90534-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rosen L., Fields B. N. Polymorphism of the migration of double-stranded RNA genome segments of reovirus isolates from humans, cattle, and mice. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):104–111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.104-111.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasuriya A. K., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the M2 gene segment of reovirus type 3 dearing and analysis of its protein product mu 1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Protein sigma 1 is the reovirus cell attachment protein. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masri S. A., Nagata L., Mah D. C., Lee P. W. Functional expression in Escherichia coli of cloned reovirus S1 gene encoding the viral cell attachment protein sigma 1. Virology. 1986 Feb;149(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhillips T. H., Ramig R. F. Extragenic suppression of temperature-sensitive phenotype in reovirus: mapping suppressor mutations. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):428–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata L., Masri S. A., Pon R. T., Lee P. W. Analysis of functional domains on reovirus cell attachment protein sigma 1 using cloned S1 gene deletion mutants. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibert M. L., Dermody T. S., Fields B. N. Structure of the reovirus cell-attachment protein: a model for the domain organization of sigma 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2976–2989. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2976-2989.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacitti A. F., Gentsch J. R. Inhibition of reovirus type 3 binding to host cells by sialylated glycoproteins is mediated through the viral attachment protein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1407–1415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1407-1415.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R. W., Choi A. H., Lee P. W. The alpha-anomeric form of sialic acid is the minimal receptor determinant recognized by reovirus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):382–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R. W., Lee P. W. Glycophorin is the reovirus receptor on human erythrocytes. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90351-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN L., ABINANTI F. R., HOVIS J. F. Further observations on the natural infection of cattle with reoviruses. Am J Hyg. 1963 Jan;77:38–48. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN L., HOVIS J. F., MASTROTA F. M., BELL J. A., HUEBNER R. J. Observations on a newly recognized virus (Abney) of the reovirus family. Am J Hyg. 1960 Mar;71:258–265. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Fields B. N. Revertants of temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus: evidence for frequent extragenic suppression. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., White R. M., Fields B. N. Suppression of the temperature-sensitive phenotype of a mutant of reovirus type 3. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):406–407. doi: 10.1126/science.831284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturzenbecker L. J., Nibert M., Furlong D., Fields B. N. Intracellular digestion of reovirus particles requires a low pH and is an essential step in the viral infectious cycle. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2351–2361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2351-2361.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarlow O., McCorquodale J. G., McCrae M. A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the gene (M2) encoding the major virion structural protein (mu 1-mu 1C) of serotypes 1 and 3 of mammalian reovirus. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90629-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N., Tyler K. L. Antibody protects against lethal infection with the neurally spreading reovirus type 3 (Dearing). J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4594–4604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4594-4604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Fields B. N. Neutralization of reovirus: the gene responsible for the neutralization antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1305–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. Identification of the gene coding for the hemagglutinin of reovirus. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):581–584. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Joklik W. K. Comparison of the reovirus serotype 1, 2, and 3 S3 genome segments encoding the nonstructural protein sigma NS. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):332–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Joklik W. K. Evolution of reovirus genes: a comparison of serotype 1, 2, and 3 M2 genome segments, which encode the major structural capsid protein mu 1C. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. C., Gill M. J., Alibhai S. S., Shahrabadi M. S., Lee P. W. Purification and characterization of the reovirus cell attachment protein sigma 1. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. C., Lim D., Duncan R., Shahrabadi M. S., Cashdollar L. W., Lee P. W. The cell attachment proteins of type 1 and type 3 reovirus are differentially susceptible to trypsin and chymotrypsin. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


