Abstract
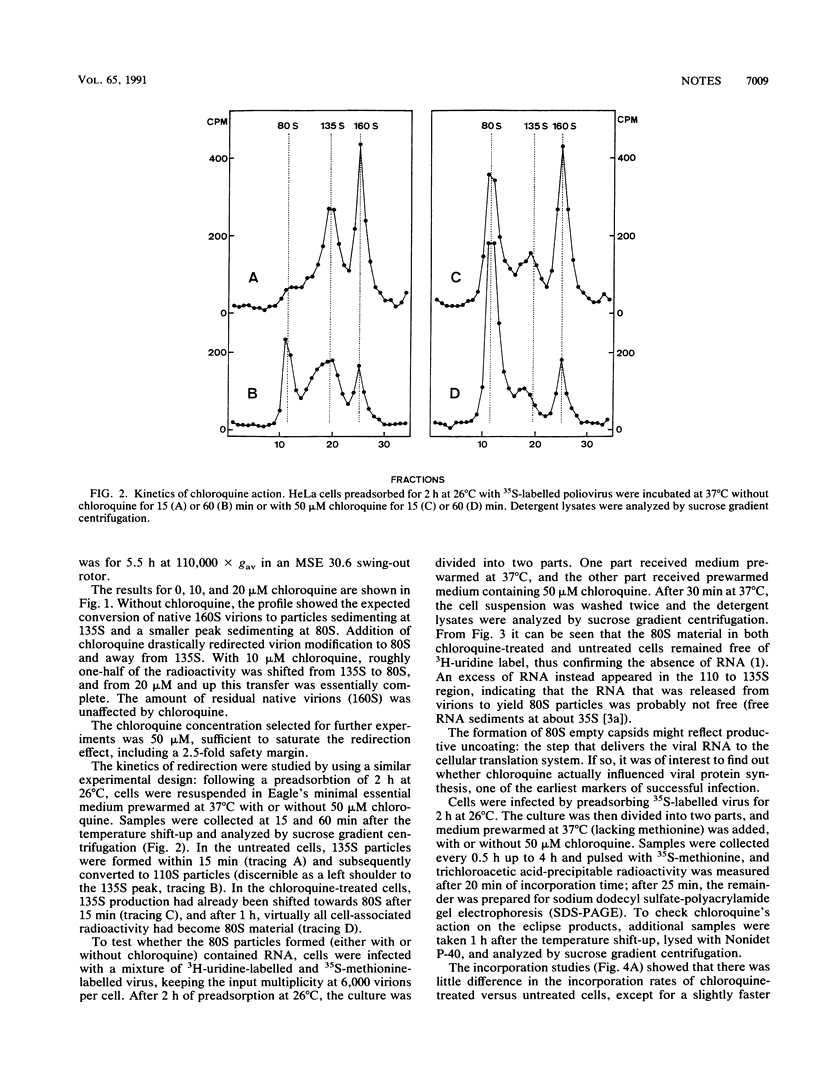
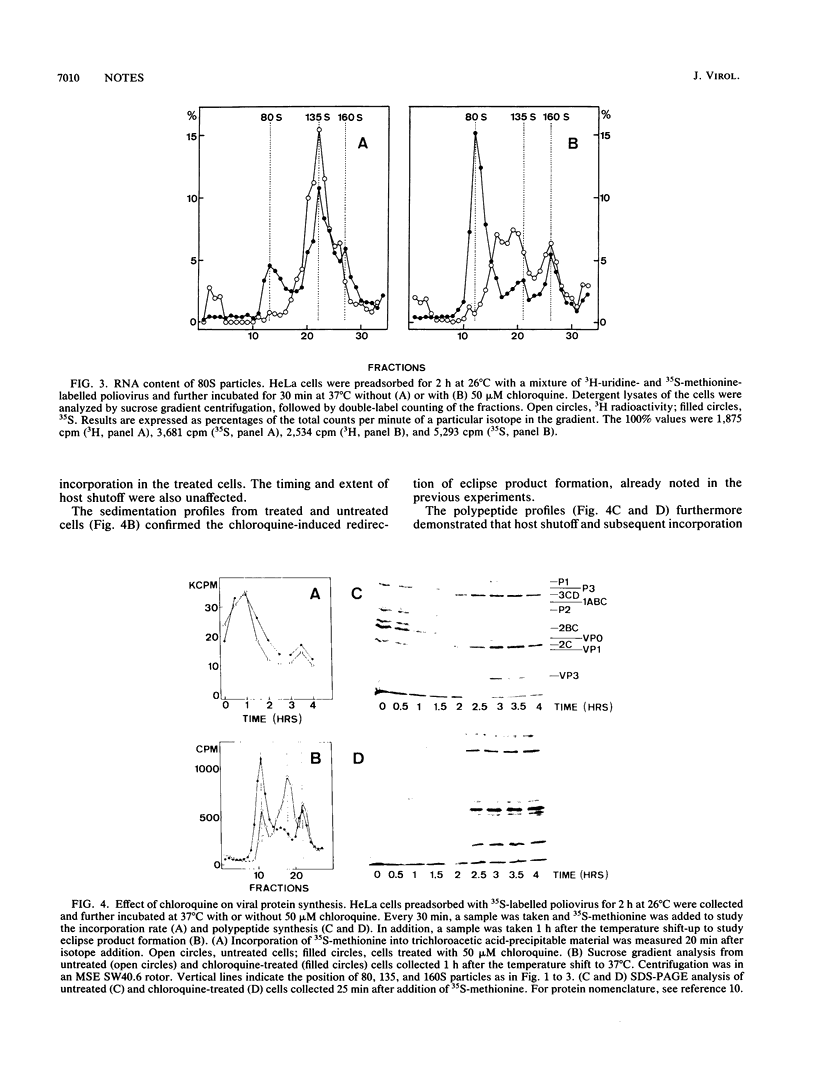
The poliovirus capsid (160S) is modified during eclipse in HeLa cells, which results in at least three types of particles having sedimentation coefficients of 135, 110, and 80S. The lysosomotropic agent chloroquine redirected the production of eclipse products from 135 and 110S particles (containing RNA) to 80S particles (without RNA). The effect started at 5 microM and was fully developed with 20 microM chloroquine. Viral protein synthesis and virion production remained unaffected. The results show that chloroquine can redirect the processing of input virions without interfering with productive uncoating.
Full text
PDF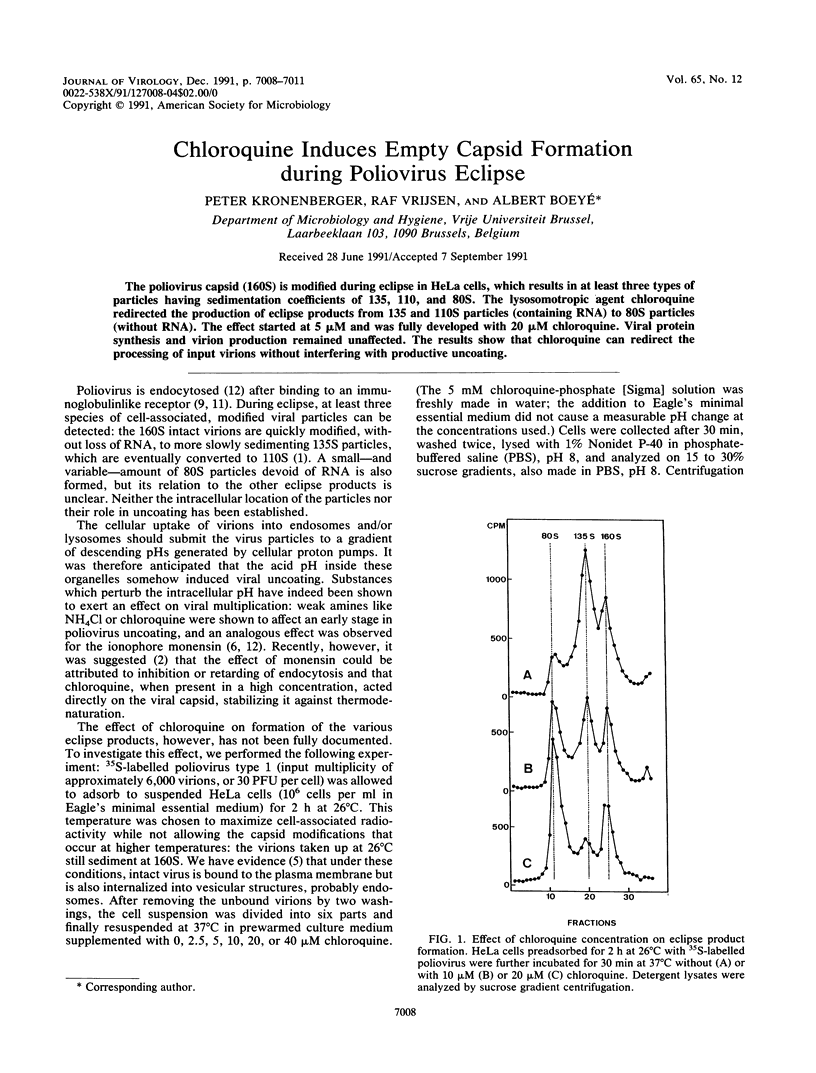

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Everaert L., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. Eclipse products of poliovirus after cold-synchronized infection of HeLa cells. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromeier M., Wetz K. Kinetics of poliovirus uncoating in HeLa cells in a nonacidic environment. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3590–3597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3590-3597.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M., White J. Inhibition of Semliki forest virus penetration by lysosomotropic weak bases. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jan;58(Pt 1):47–61. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooi C., Cervin M., Anderson R. Differentiation of acid-pH-dependent and -nondependent entry pathways for mouse hepatitis virus. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):108–119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90014-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Mechanism of entry into the cytosol of poliovirus type 1: requirement for low pH. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Srikantan V., Bhartiya D. Chloroquine enhances replication of Semliki Forest virus and encephalomyocarditis virus in mice. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):992–995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.992-995.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R. Weak bases and ionophores rapidly and reversibly raise the pH of endocytic vesicles in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):676–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus can enter and infect mammalian cells by way of an intercellular adhesion molecule 1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3598–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichhardt H., Wetz K., Willingmann P., Habermehl K. O. Entry of poliovirus type 1 and Mouse Elberfeld (ME) virus into HEp-2 cells: receptor-mediated endocytosis and endosomal or lysosomal uncoating. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):483–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]