Abstract
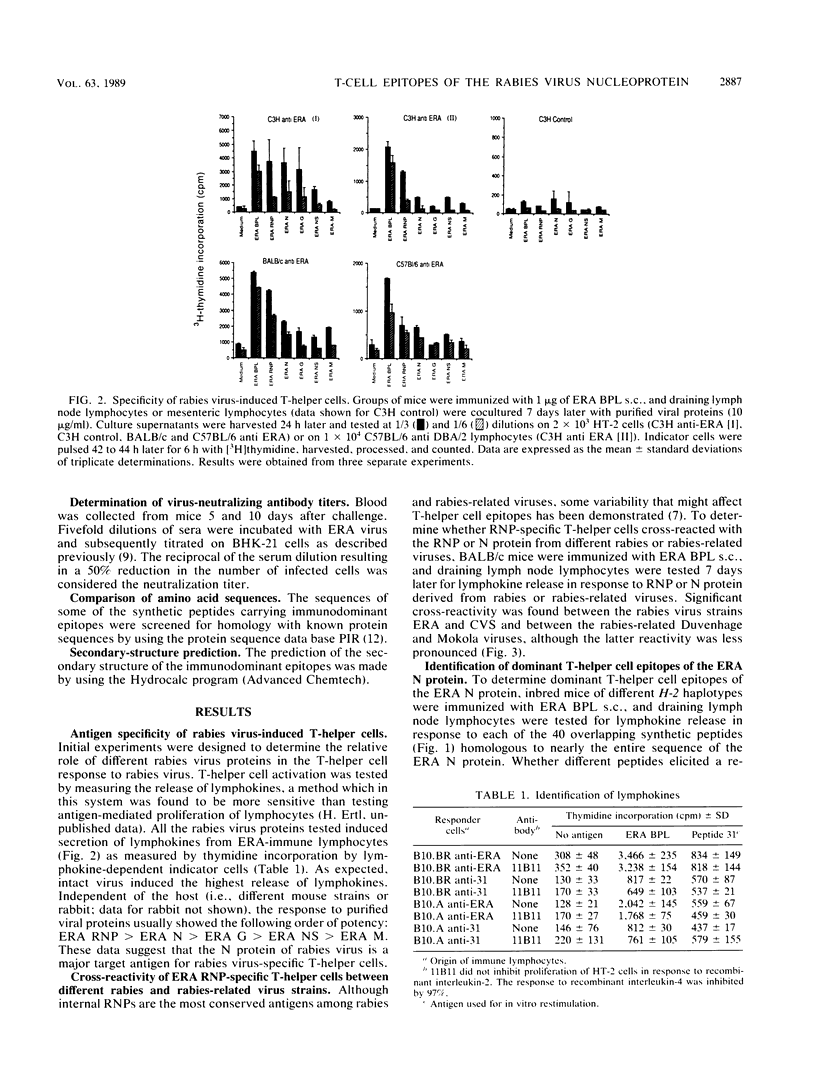
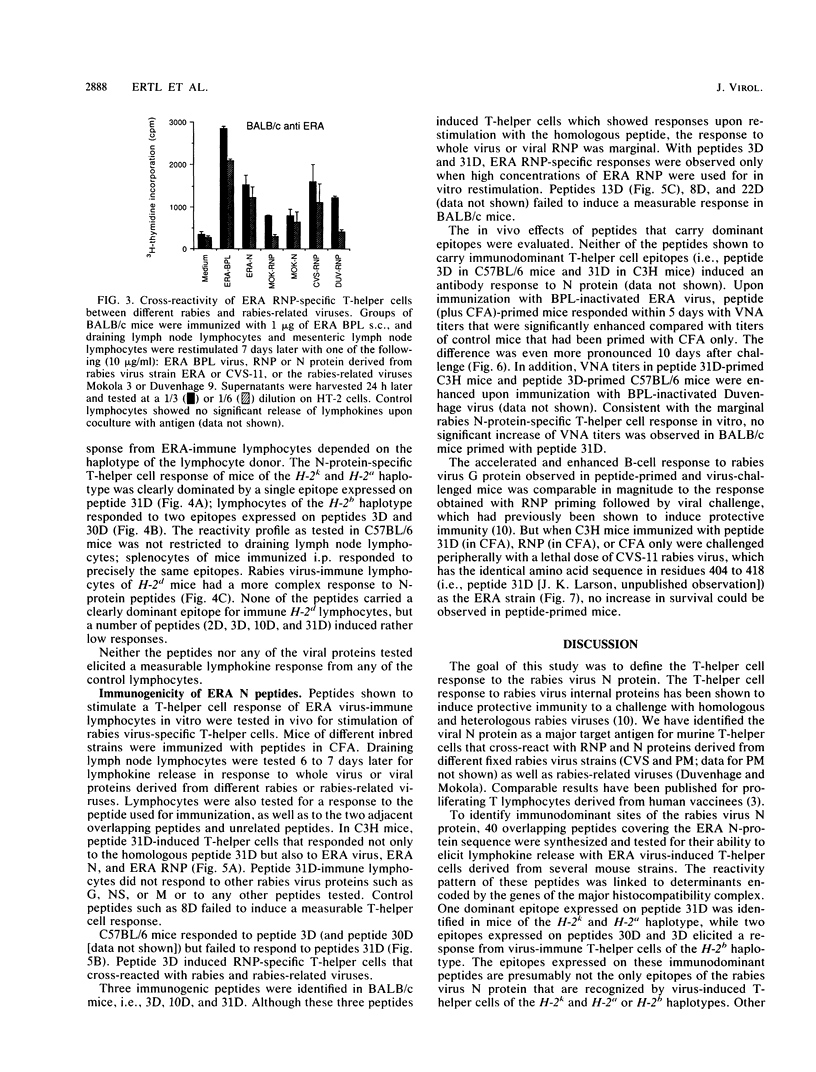
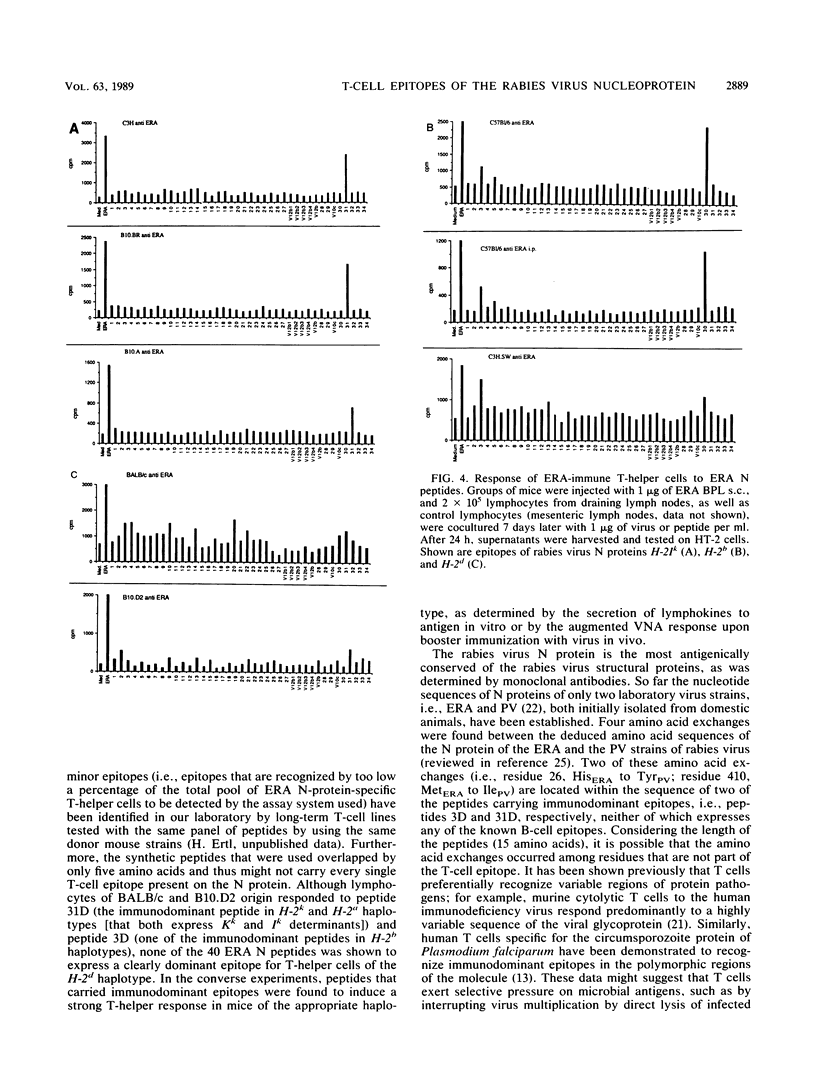
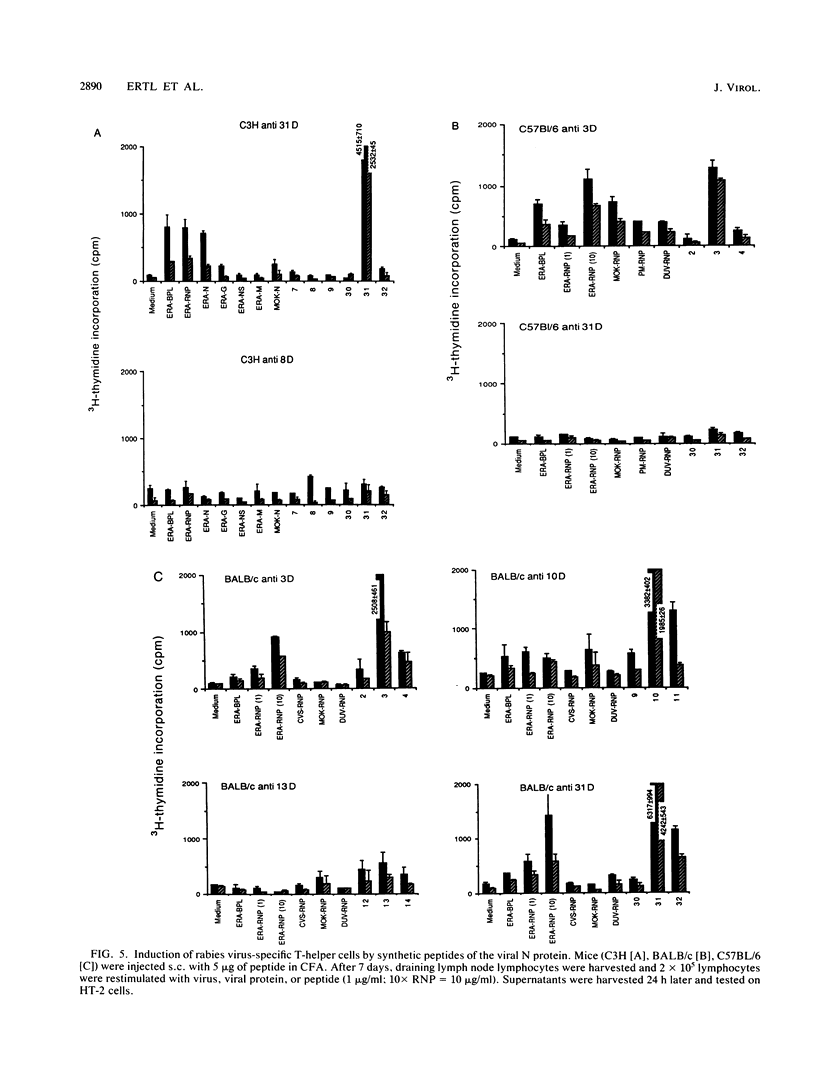
The T-helper cell response to the internal proteins of rabies virus was investigated. The rabies virus nucleoprotein was shown to be a major target antigen for T-helper cells that cross-react between rabies and rabies-related viruses. T-helper cells were assayed in vitro by testing virus-induced lymphocytes for lymphokine secretion in response to antigen. Immunodominant T-helper cell epitopes of the viral nucleoprotein were identified in vitro by using synthetic peptides delineated from the amino acid sequence of the nucleoprotein. The response to synthetic peptides were under Ir gene control. Antigenic peptides were tested in vivo for stimulation of rabies virus-specific T-helper cells. Inoculation of mice with peptides bearing immunodominant T-helper cell epitopes resulted in an accelerated and enhanced neutralizing antibody response upon booster immunization with inactivated rabies virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celis E., Miller R. W., Wiktor T. J., Dietzschold B., Koprowski H. Isolation and characterization of human T cell lines and clones reactive to rabies virus: antigen specificity and production of interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):692–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Dietzschold B., Schneider L. G. Rabies virus glycoprotein. II. Biological and serological characterization. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):754–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.754-759.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Rupprecht C. E., Tollis M., Lafon M., Mattei J., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H. Antigenic diversity of the glycoprotein and nucleocapsid proteins of rabies and rabies-related viruses: implications for epidemiology and control of rabies. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Nov-Dec;10 (Suppl 4):S785–S798. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_4.s785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Tollis M., Lafon M., Wunner W. H., Koprowski H. Mechanisms of rabies virus neutralization by glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wang H. H., Rupprecht C. E., Celis E., Tollis M., Ertl H., Heber-Katz E., Koprowski H. Induction of protective immunity against rabies by immunization with rabies virus ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9165–9169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wiktor T. J., Wunner W. H., Varrichio A. Chemical and immunological analysis of the rabies soluble glycoprotein. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):330–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbaud S., Vialat P., Pardigon N., Wychowski C., Girard M., Bouloy M. The S segment of the Germiston virus RNA genome can code for three proteins. Virus Res. 1987 Jul;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Pombo D., Quakyi I. A., Riley E. M., Houghten R. A., Menon A., Alling D. W., Berzofsky J. A., Miller L. H. Human T-cell recognition of the circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium falciparum: immunodominant T-cell domains map to the polymorphic regions of the molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1199–1203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P. Immunogenicity of a synthetic HBsAg peptide: enhancement by conjugation to a fatty acid carrier. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jan;21(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otvos L., Jr, Dietzschold B., Kisfaludy L. Solid-phase peptide synthesis using tert.-butyloxycarbonylamino acid pentafluorophenyl esters. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1987 Oct;30(4):511–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1987.tb03359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Fischman H. R., Nathanson N. Recovery from experimental rabies by adoptive transfer of immune cells. J Gen Virol. 1981 Sep;56(Pt 1):25–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser J. E., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Generation of cytolytic T lymphocytes in vitro. IX. induction of secondary CTL responses in primary long-term MLC by supernatants from secondary MLC. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. G., Dietzschold B., Dierks R. E., Matthaeus W., Enzmann P. J., Strohmaier K. Rabies group-specific ribonucleoprotein antigen and a test system for grouping and typing of rhabdoviruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.748-755.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spouge J. L., Guy H. R., Cornette J. L., Margalit H., Cease K., Berzofsky J. A., DeLisi C. Strong conformational propensities enhance T cell antigenicity. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):204–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Cohen J., Hosmalin A., Cease K. B., Houghten R., Cornette J. L., DeLisi C., Moss B., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. An immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp160 recognized by class I major histocompatibility complex molecule-restricted murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3105–3109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordo N., Poch O., Ermine A., Keith G. Primary structure of leader RNA and nucleoprotein genes of the rabies genome: segmented homology with VSV. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2671–2683. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Dietzschold B., Leamnson R. N., Koprowski H. Induction and biological properties of defective interfering particles of rabies virus. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):626–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.626-635.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Dietzschold B., Smith C. L., Lafon M., Golub E. Antigenic variants of CVS rabies virus with altered glycosylation sites. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Larson J. K., Dietzschold B., Smith C. L. The molecular biology of rabies viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Nov-Dec;10 (Suppl 4):S771–S784. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_4.s771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


