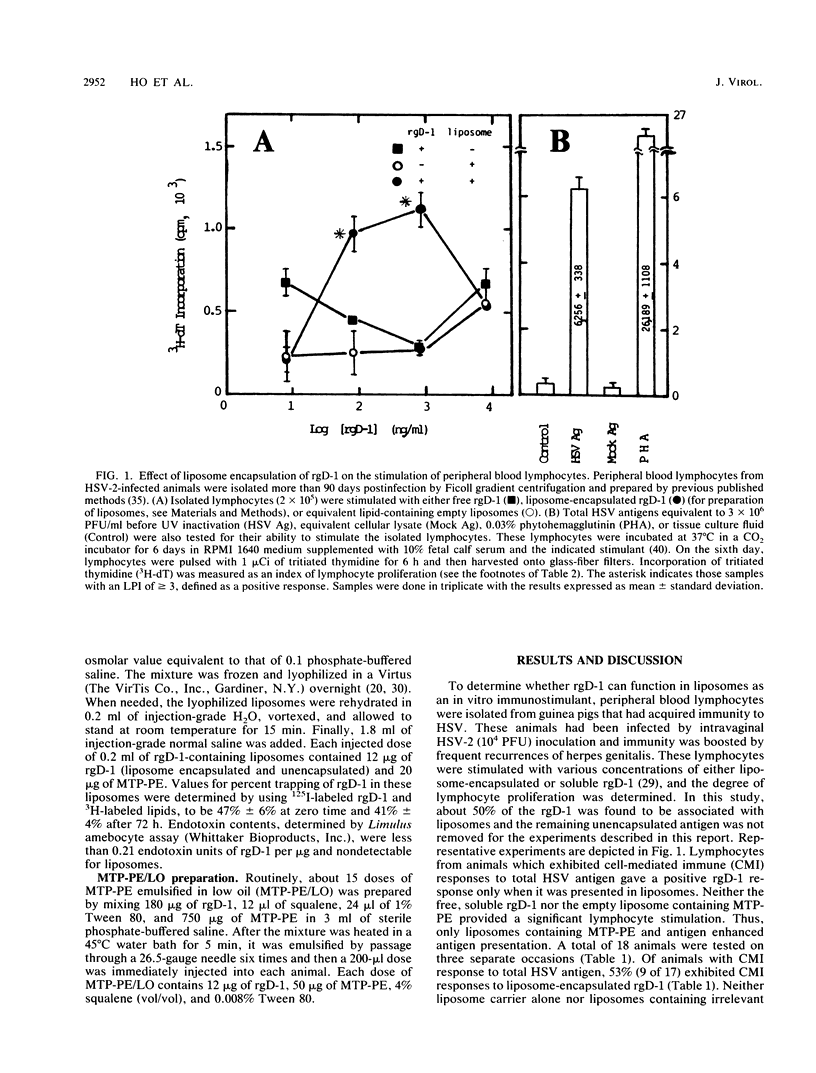
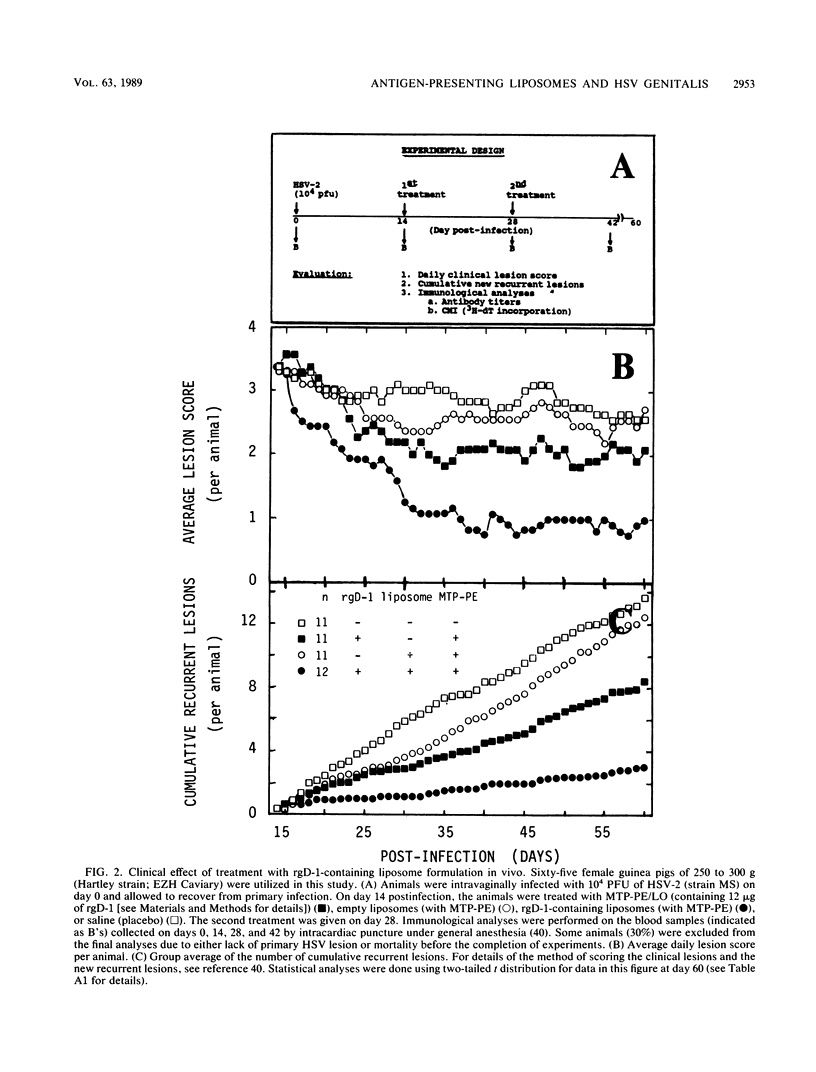
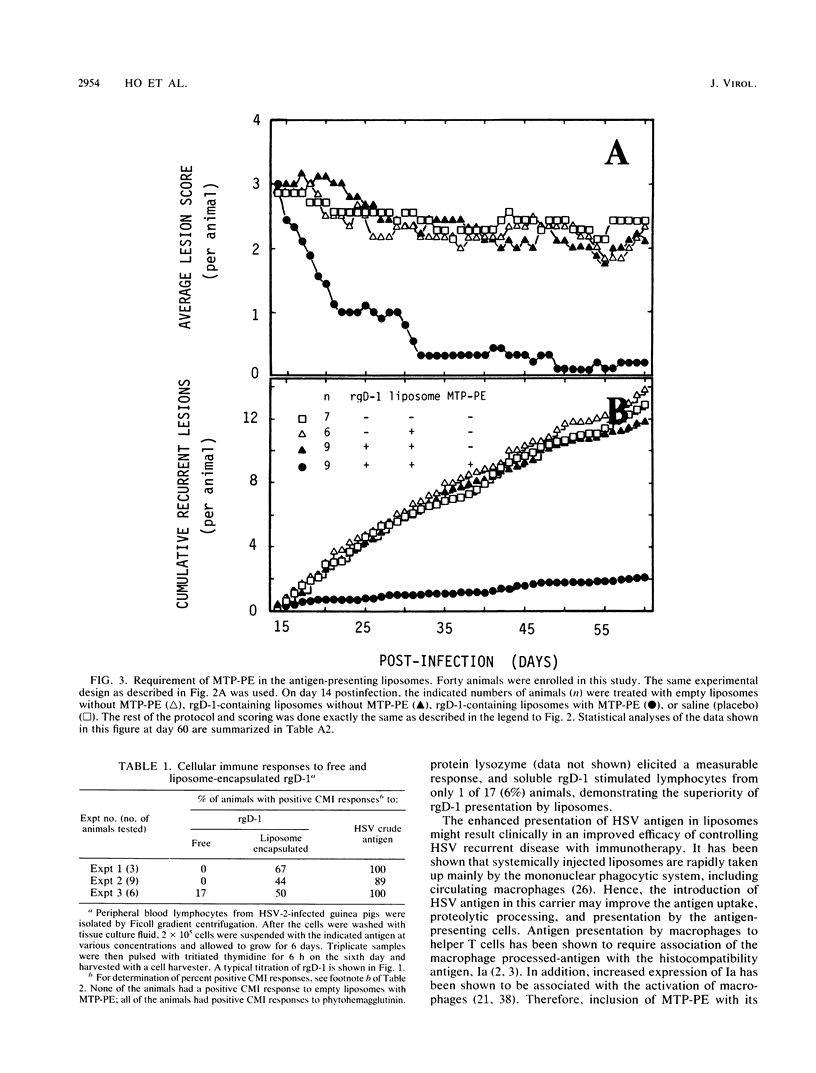
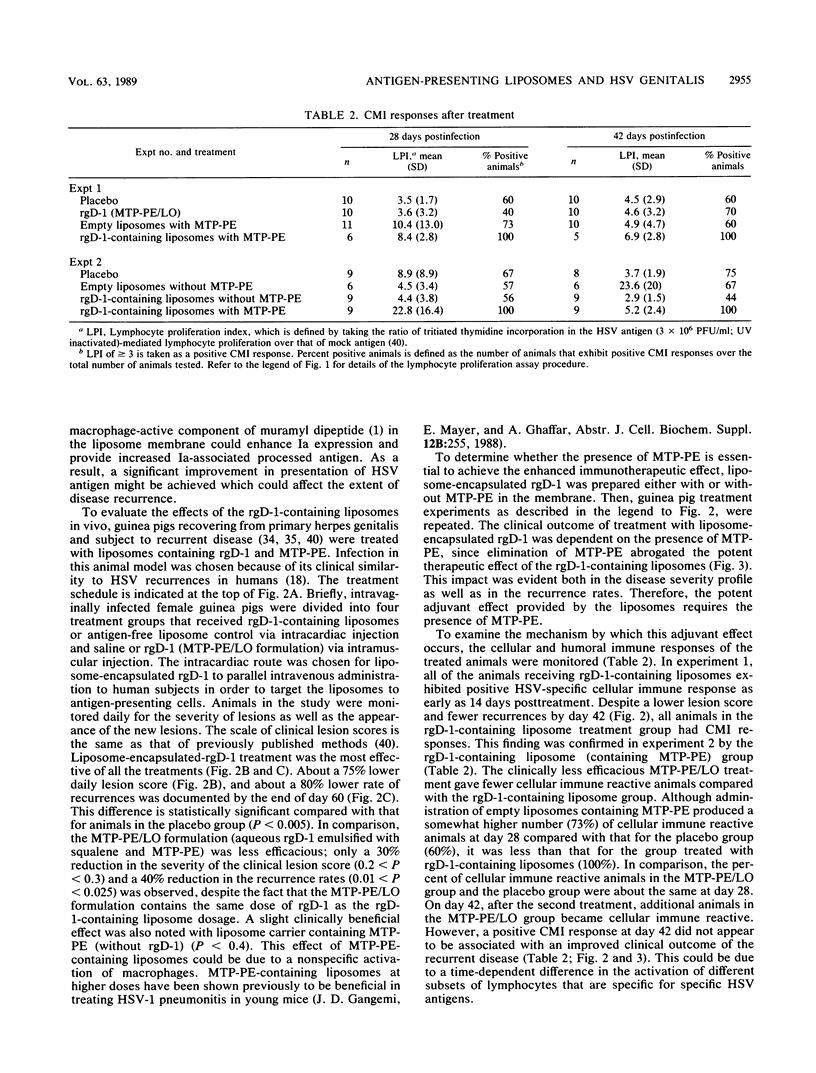
Abstract
The therapeutic and immunologic effects of a liposome preparation containing both a macrophage activator, muramyl-tripeptide-phosphatidylethanolamine, and a recombinant antigen, glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus type 1, have been investigated. This preparation was tested in vitro for the ability to stimulate peripheral blood lymphocytes and in vivo for the control of recurrent herpes genitalis in guinea pigs. Our results show that the liposome-antigen-adjuvant preparation is capable of enhancing antigen-specific lymphocyte stimulation, which may be related to the observed 75% suppression of the frequency and severity of reactivation of recurrent herpes simplex virus type 2 genitalis compared with that of placebo controls.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam A., Petit J. F., Lefrancier P., Lederer E. Muramyl peptides. Chemical structure, biological activity and mechanism of action. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Dec 4;41:27–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00225295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. Antigenic competition at the level of peptide-Ia binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behbehani K., Pan S. C., Unanue E. R. Marked increase in Ia-bearing macrophages during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 May;19(2):190–195. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Gregory T., Crase D., Lasky L. A. Protection from genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infection by vaccination with cloned type 1 glycoprotein D. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1490–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.2983428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Vogt P. E., Gregory T., Lasky L. A., Kern E. R. Efficacy of recombinant glycoprotein D subunit vaccines on the development of primary, recurrent, and latent genital infections with herpes simplex virus type 2 in guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):897–902. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni A., Toffano G., Leon A., Boarato E. Pharmacological effects of phosphatidylserine liposomes. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):331–333. doi: 10.1038/260331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Dillon M., Lovett M., Acuna G., Taylor S., Cherry J. D., Johnson B. L., Wiesmeier E., Growdon W., Creagh-Kirk T. Treatment of first episodes of genital herpes simplex virus infection with oral acyclovir. A randomized double-blind controlled trial in normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 21;308(16):916–921. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304213081602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Spear P. G. Infections with herpes simplex viruses (1). N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. L., Merigan T. C. gamma Interferon production appears to predict time of recurrence of herpes labialis. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2397–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. L., Nelson P. A., Fathman C. G., Merigan T. C. Interferon gamma production by herpes simplex virus antigen-specific T cell clones from patients with recurrent herpes labialis. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):249–258. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Mills J. Acute and latent herpes simplex virus neurological disease in mice immunized with purified virus-specific glycoproteins gB or gD. J Med Virol. 1985 Sep;17(1):9–18. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Drugs five years later: acyclovir. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):859–874. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. M., Critchlow C., Benedetti J., Mertz G. J., Connor J. D., Hintz M. A., Fahnlander A., Remington M., Winter C., Corey L. A double-blind study of oral acyclovir for suppression of recurrences of genital herpes simplex virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1551–1556. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J., Rouse B. T., Huang L. Target-sensitive immunoliposomes as an efficient drug carrier for antiviral activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13973–13978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J., Ting-Beall H. P., Rouse B. T., Huang L. Kinetic and ultrastructural studies of interactions of target-sensitive immunoliposomes with herpes simplex virus. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):500–506. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinghorn G. R., Jeavons M., Rowland M., Abeywickreme I., Barton I. G., Potter C. W., Hickmott E. A. Acyclovir prophylaxis of recurrent genital herpes: randomised placebo controlled crossover study. Genitourin Med. 1985 Dec;61(6):387–390. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.6.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P. New insights into antigen recognition. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2435000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindel A., Faherty A., Carney O., Patou G., Freris M., Williams P. Dosage and safety of long-term suppressive acyclovir therapy for recurrent genital herpes. Lancet. 1988 Apr 23;1(8591):926–928. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91725-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salk J. Prospects for the control of AIDS by immunizing seropositive individuals. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):473–476. doi: 10.1038/327473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador L., Burke R. L., Ott G., Van Nest G. The effect of adjuvants on the efficacy of a recombinant herpes simplex virus glycoprotein vaccine. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1720–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shew R. L., Deamer D. W. A novel method for encapsulation of macromolecules in liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 11;816(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Fidler I. J. Synergistic activation by lymphokines and muramyl dipeptide of tumoricidal properties in rat alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2454–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry L. R., Bernstein D. I., Burke R. L., Pachl C., Myers M. G. Vaccination with recombinant herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: protection against initial and recurrent genital herpes. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):914–920. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry L. R., Burke R., Myers M. G. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein treatment of recurrent genital herpes. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):156–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry L. R., Kern E. R., Richards J. T., Abbott T. M., Overall J. C., Jr Genital herpes in guinea pigs: pathogenesis of the primary infection and description of recurrent disease. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):397–404. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry L. R., Kern E. R., Richards J. T., Overall J. C., Jr Recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infection in guinea pigs. Intervirology. 1985;24(4):226–231. doi: 10.1159/000149647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Takiff H. E., Seidlin M., Bachrach S., Lininger L., DiGiovanna J. J., Western K. A., Smith H. A., Lehrman S. N., Creagh-Kirk T. Suppression of frequently recurring genital herpes. A placebo-controlled double-blind trial of oral acyclovir. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1545–1550. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torseth J. W., Merigan T. C. Significance of local gamma interferon in recurrent herpes simplex infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):979–984. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Regulation of guinea-pig immune functions by interleukin 2: critical role of natural killer activity in acute HSV-2 genital infection. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3310–3317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Rasmussen L., Merigan T. C. Acute genital infection in guinea pigs: effect of recombinant interleukin-2 on herpes simplex virus type 2. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):134–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


