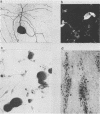
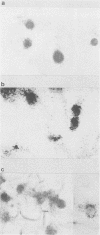
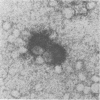
Abstract
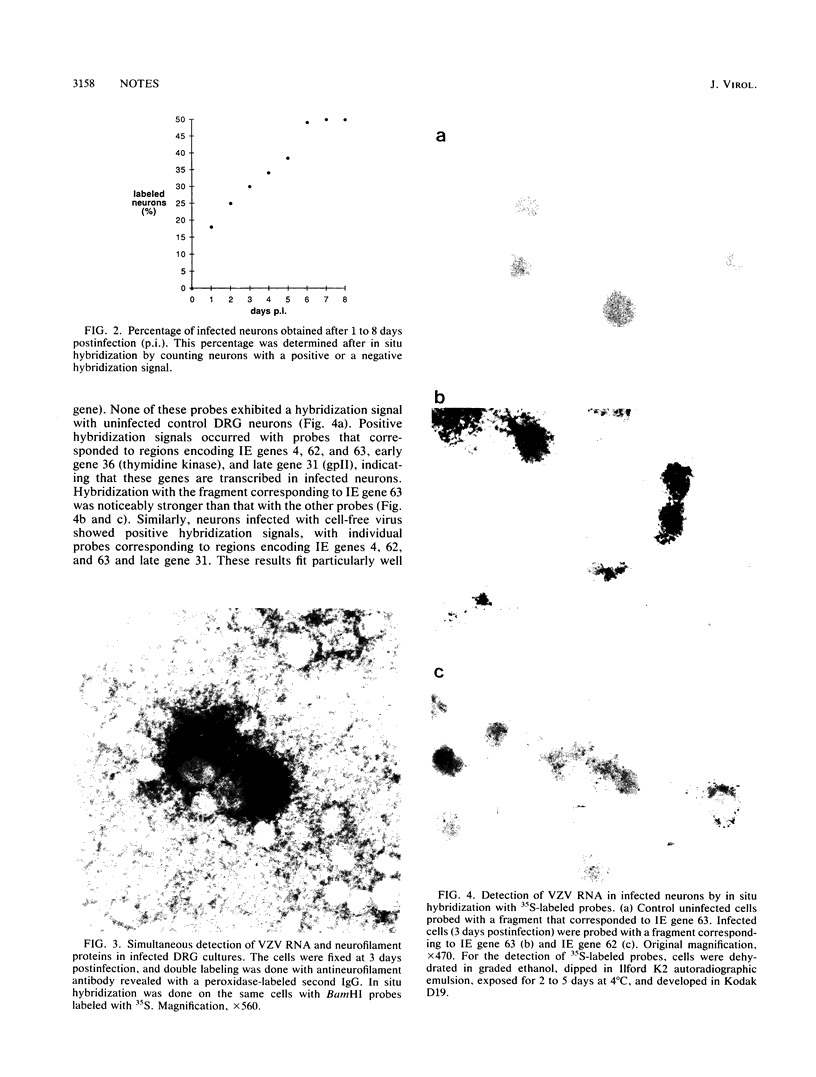
We report here an in vitro model of neuronal infection by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Such a model has been achieved by using dissociated adult rat dorsal root ganglia cells infected by cocultivation with VZV-infected MRC5 cells or with cell-free virus. Indirect VZV immunolabeling, in situ hybridization, and neuron-specific immunolabeling demonstrated that VZV infection occurred selectively in neurons. VZV-specific immunolabeling detected a few neurons 1 or 2 days postinfection but not later. Genome detection using cloned VZV DNA probes revealed a hybridization signal primarily with RNA. Within 1 to 6 days postinfection, a progressive increase of VZV-specific hybridization was observed in up to 50% of the neurons. RNAs corresponding to immediate-early, early, and late genes were found, and transcripts of immediate-early gene 63 were particularly abundant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T., Cash E. Simultaneous in situ detection of viral RNA and antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5445–5448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigati D. J., Myerson D., Leary J. J., Spalholz B., Travis S. Z., Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D., Ward D. C. Detection of viral genomes in cultured cells and paraffin-embedded tissue sections using biotin-labeled hybridization probes. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):32–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Latent herpes simplex virus in human trigeminal ganglia. Detection of an immediate early gene "anti-sense" transcript by in situ hybridization. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 3;317(23):1427–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712033172302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Straus S. E. Patterns of gene expression and sites of latency in human nerve ganglia are different for varicella-zoster and herpes simplex viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9773–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd J., Solter D., Jessell T. M. Monoclonal antibodies against carbohydrate differentiation antigens identify subsets of primary sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):469–472. doi: 10.1038/311469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. R., Hyman R. W. Varicella zoster virus DNA exists as two isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Vafai A., Shtram Y., Becker Y., Devlin M., Wellish M. Varicella-zoster virus DNA in human sensory ganglia. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):478–480. doi: 10.1038/306478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Perrotta D. M., Brunell P. A., Smith G. C. Cell-free varicella-zoster virus in cultured human melanoma cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):15–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPE-SIMPSON R. E. THE NATURE OF HERPES ZOSTER: A LONG-TERM STUDY AND A NEW HYPOTHESIS. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Jan;58:9–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W., Ecker J. R., Tenser R. B. Varicella-zoster virus RNA in human trigeminal ganglia. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):814–816. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90736-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Reinhold W., Fan C. M., Zorn S., Hay J., Straus S. E. Transcription mapping of the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.600-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Notkins A. L. Continued expression of a poly(A)+ transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1700–1703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1700-1703.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Aulakh H. S., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J., Casey T. A., Vande Woude G. F., Owens J., Smith H. A. Structure of varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):516–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.516-525.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Murray R. S., Wellish M., Devlin M., Gilden D. H. Expression of varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex virus in normal human trigeminal ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2362–2366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Rong B. L., Kinney-Thomas E. Varicella-zoster virus infection of human sensory neurons. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):384–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]