Abstract
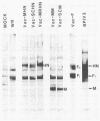
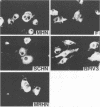
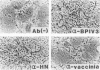
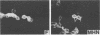
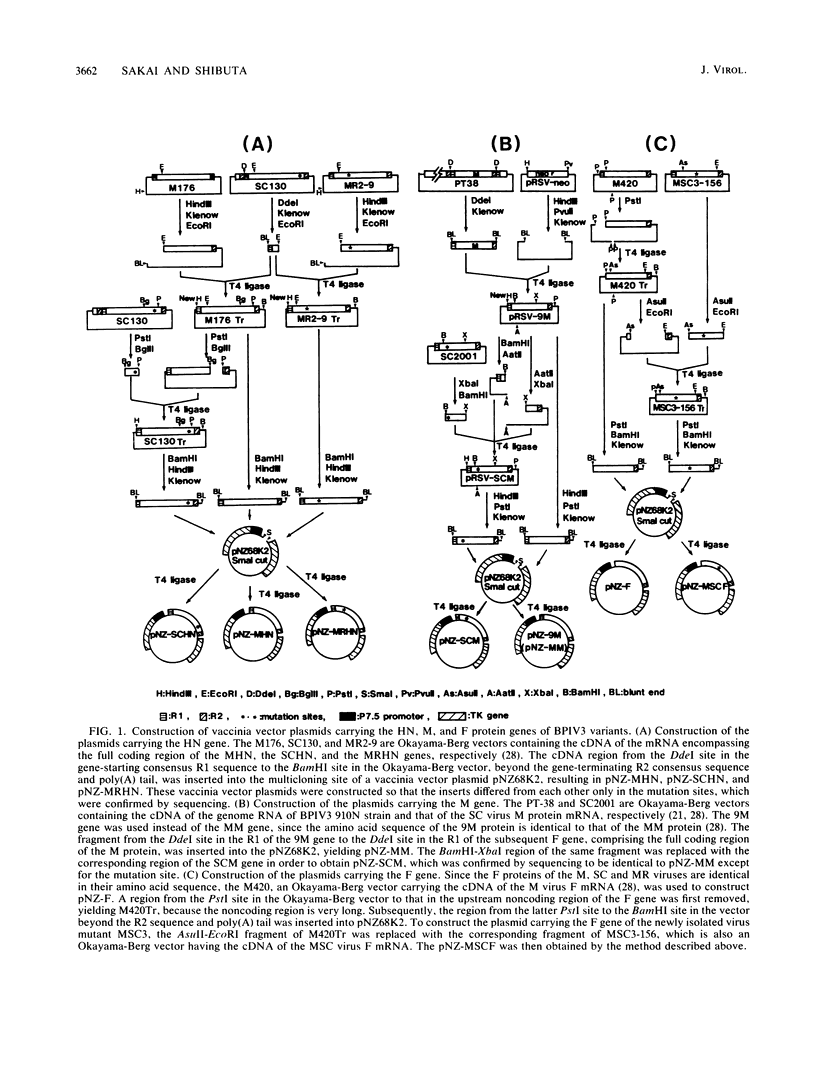
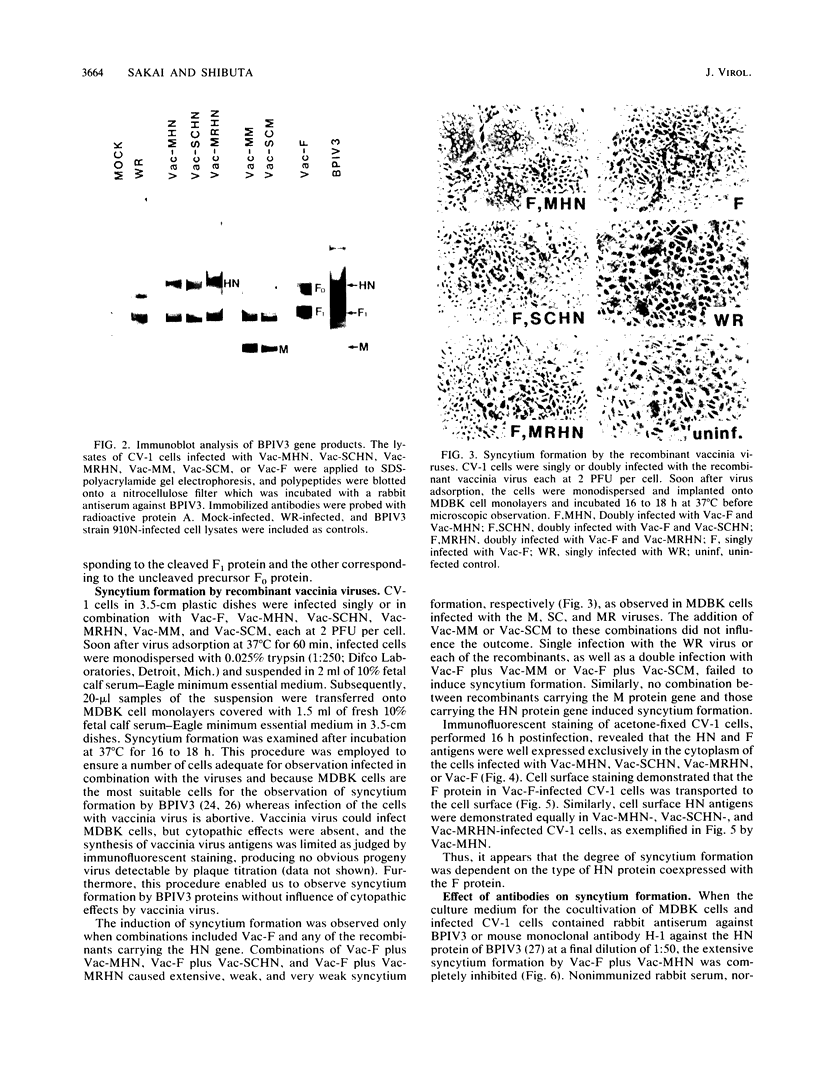
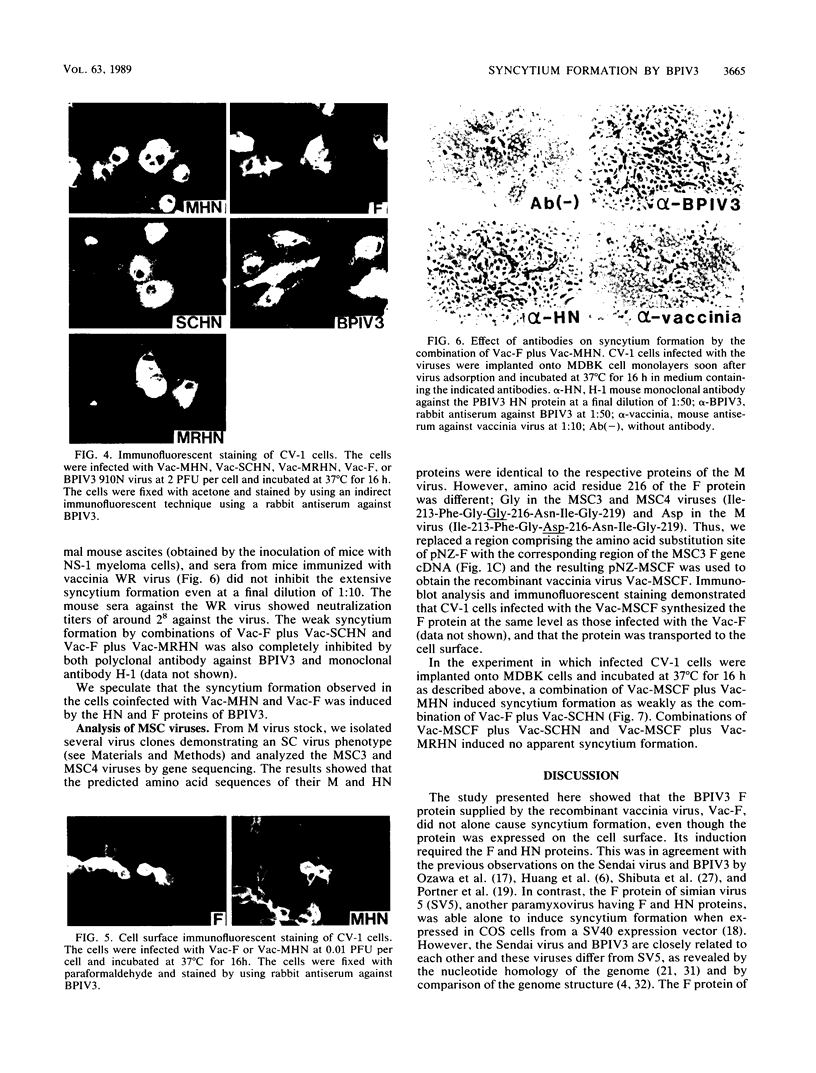
The highly syncytium-inducing M strain and the weakly syncytium-inducing SC strain of bovine parainfluenza 3 virus differ by a single amino acid substitution in each of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) and membrane (M) proteins, while their fusion (F) proteins are identical (T. Shioda, S. Wakao, S. Suzu, and H. Shibuta, Virology 162:388-396, 1988). We constructed recombinant vaccinia viruses which express separately the M virus HN (Vac-MHN), SC virus HN (Vac-SCHN), M virus M (Vac-MM), SC virus M (Vac-SCM), and common F (Vac-F) proteins. CV-1 cells were infected with the recombinants, singly or in combination, and implanted onto indicator MDBK cells for syncytium formation. Combinations of Vac-MHN plus Vac-F and Vac-SCHN plus Vac-F induced extensive and weak syncytium formation, respectively. Vac-F alone did not induce syncytium formation, and both Vac-MM and Vac-SCM had no effect on syncytium formation. These findings indicated that the syncytium formation by bovine parainfluenza 3 virus requires both the F and HN proteins and that the extensive syncytium formation by the M virus is due to the M virus HN protein. MSC, another weakly syncytium-inducing virus variant, newly isolated from the M virus, was identical to the M virus in the primary structure of the HN and M proteins but differed from the M virus by a single amino acid residue in the F protein. The combination of the recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the MSC virus F protein and Vac-MHN resulted in weak syncytium formation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B., Giorgi C., Roux L., Raju R., Dowling P., Chollet A., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus HN gene and its comparison to the influenza virus glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Richardson C. D., Lamb R. A. Cell surface expression and orientation in membranes of the 44-amino-acid SH protein of simian virus 5. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2347–2357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2347-2357.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Reconstitution of membranes with individual paramyxovirus glycoproteins and phospholipid in cholate solution. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):476–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Rott R., Wahn K., Klenk H. D., Kohama T. The function of the neuraminidase in membrane fusion induced by myxoviruses. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen N., Nayak D. P., Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Polarized expression of a chimeric protein in which the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of the influenza virus hemagglutinin have been replaced by those of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9318–9322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Importance of antibodies to the fusion glycoprotein of paramyxoviruses in the prevention of spread of infection. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):275–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Wolinsky J. S. Biochemical features of mumps virus neuraminidases and their relationship with pathogenicity. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):218–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Wolinsky J. S. Conversion of nonfusing mumps virus infections to fusing infections by selective proteolysis of the HN glycoprotein. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa M., Asano A., Okada Y. Biological activities of glycoproteins of HVJ (Sendai virus) studied by reconstitution of hybrid envelope and by concanavalin A-mediated binding: a new function of HANA protein and structural requirement of F protein in hemolysis. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Hiebert S. W., Lamb R. A. Expression at the cell surface of biologically active fusion and hemagglutinin/neuraminidase proteins of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5 from cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Scroggs R. A., Metzger D. W. Distinct functions of antigenic sites of the HN glycoprotein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puddington L., Woodgett C., Rose J. K. Replacement of the cytoplasmic domain alters sorting of a viral glycoprotein in polarized cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2756–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai Y., Suzu S., Shioda T., Shibuta H. Nucleotide sequence of the bovine parainfluenza 3 virus genome: its 3' end and the genes of NP, P, C and M proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2927–2944. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuta H., Adachi A., Kanda T., Matumoto M. Experimental parainfluenzavirus infection in mice: fatal illness with atrophy of thymus and spleen in mice caused by a variant of parainfluenza 3 virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):437–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.437-441.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuta H., Kanda T., Hazama A., Adachi A., Matumoto M. Parainfluenza 3 virus: plaque-type variants lacking neuraminidase activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):262–267. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.262-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuta H., Kanda T., Nozawa A., Sato S., Kumanishi T. Experimental parainfluenza virus infection in mice: growth and spread of a highly pathogenic variant of parainfluenza 3 virus in the mouse brain. Arch Virol. 1985;83(1-2):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01310963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuta H., Nozawa A., Shioda T., Kanda T. Neuraminidase activity and syncytial formation in variants of parainfluenza 3 virus. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):780–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.780-788.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuta H., Suzu S., Shioda T. Differences in bovine parainfluenza 3 virus variants studied by monoclonal antibodies against viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):688–696. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Wakao S., Suzu S., Shibuta H. Differences in bovine parainfluenza 3 virus variants studied by sequencing of the genes of viral envelope proteins. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):388–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W., Earl P., Moss B. Surface expression of viral glycoproteins is polarized in epithelial cells infected with recombinant vaccinia viral vectors. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):237–245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Yasuda A., Miki K., Morita M., Suzuki K., Uchida N., Hashizume S. Gene structures of low-neurovirulent vaccinia virus LC16m0, LC16m8, and their Lister original (LO) strains. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(5):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Lamb R. A., Paterson R. G. Two mRNAs that differ by two nontemplated nucleotides encode the amino coterminal proteins P and V of the paramyxovirus SV5. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):891–902. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(88)91285-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda T., Gotoh B., Sakaguchi T., Kida H., Nagai Y. Identification of amino acids relevant to three antigenic determinants on the fusion protein of Newcastle disease virus that are involved in fusion inhibition and neutralization. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4427–4430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4427-4430.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Distinctive nucleotide sequences adjacent to multiple initiation and termination sites of an early vaccinia virus gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Aronowski J. Identification of amino acids involved in the sialidase activity of the mumps virus hemagglutinin-neuraminadase protein. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):226–232. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]