Abstract
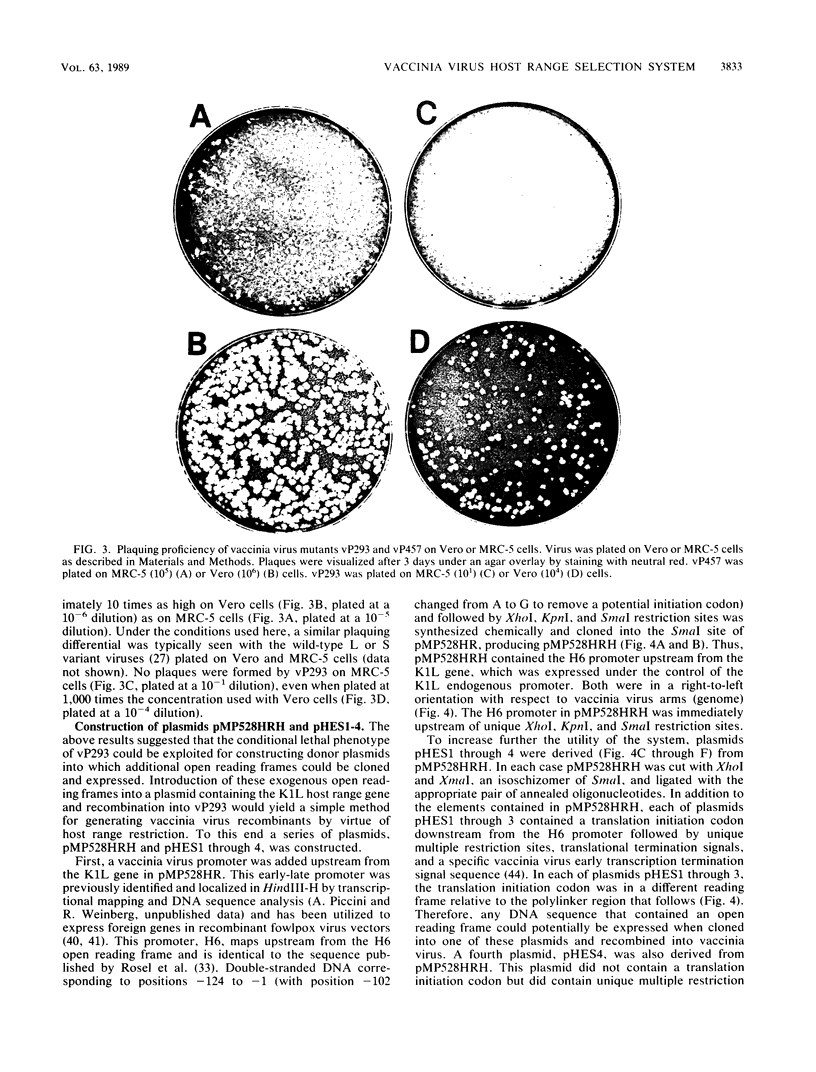
A simple selection system has been developed for the cloning and expression of open reading frames in vaccinia virus. The selection system is based on a conditional lethal (host range) mutant of vaccinia virus. A deletion mutant of the vaccinia virus WR strain was generated by insertion of the neomycin resistance gene from transposon Tn5 and selection with the antibiotic G418. This deletion recombinant, vP293, lacked approximately 21.7 kilobases of DNA beginning 3.8 kilobases from the left end of the genome, vP293, was capable of plaquing on primary chicken embryo fibroblasts and two monkey cell lines (BSC-40 and Vero) but was defective in replication in the human cell line MRC-5. Insertion of the host range gene K1L into vP293 restored the ability to grow on MRC-5 cells. A series of plasmids were constructed which in addition to the K1L gene contained a vaccinia virus early-late promoter, H6, followed by a unique polylinker sequence, translational initiation and termination signals, and an early transcription termination signal. These plasmids, pHES1 through 4, allowed for rapid single-step cloning and expression of any open reading frame when recombined in vivo with vP293 and scored for growth on MRC-5 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle D. B., Coupar B. E. A dominant selectable marker for the construction of recombinant poxviruses. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Koehren F., Kirn A. Host range deletion mutant of vaccinia virus defective in human cells. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Spehner D., Kirn A. Host range restriction of vaccinia virus in Chinese hamster ovary cells: relationship to shutoff of protein synthesis. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.843-850.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Escherichia coli gpt gene provides dominant selection for vaccinia virus open reading frame expression vectors. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1849-1854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Sridhar P., Pacha R. F., Condit R. C. Efficient targeted insertion of an unselected marker into the vaccinia virus genome. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner F., Sambrook J. F. Conditional lethal mutants of rabbitpox virus. II. Mutants (p) that fail to multiply in PK-2a cells. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):600–609. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C. A., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Neomycin resistance as a dominant selectable marker for selection and isolation of vaccinia virus recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1918–1924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEMMELL A., FENNER F. Genetic studies with mammalian poxviruses. III. White (u) mutants of rabbitpox virus. Virology. 1960 May;11:219–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangemi J. D., Sharp D. G. Particle heterogeneity in vaccinia virus populations during passage. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard S., Spehner D., Drillien R., Kirn A. Localization and sequence of a vaccinia virus gene required for multiplication in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5573–5577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard S., Spehner D., Drillien R. Mapping of a vaccinia host range sequence by insertion into the viral thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):316–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.316-318.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of rat cells by DNA of human adenovirus 5. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Lynn D. L., Condit R. C., Kates J. R. Cellular differences in the molecular mechanisms of vaccinia virus host range restriction. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):485–488. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Drillien R., Spehner D., Skory S., Schmitt D., Wiktor T., Koprowski H., Lecocq J. P. Expression of rabies virus glycoprotein from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):163–166. doi: 10.1038/312163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Moss B. Analysis of a large cluster of nonessential genes deleted from a vaccinia virus terminal transposition mutant. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):524–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Cooper P. D. Deletions of the terminal sequences in the genomes of the white pock (u) and host-restricted (p) mutants of rabbitpox virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):135–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLAIN M. E., GREENLAND R. M. RECOMBINATION BETWEEN RABBITPOX VIRUS MUTANTS IN PERMISSIVE AND NONPERMISSIVE CELLS. Virology. 1965 Apr;25:516–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLAIN M. E. THE HOST RANGE AND PLAQUE MORPHOLOGY OF RABBITPOX VIRUS (RPU+) AND ITS U MUTANTS ON CHICK FIBROBLAST, PK-2A, AND L929 CELLS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Feb;43:31–44. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Arrand J. R. Recombinant vaccinia virus induces neutralising antibodies in rabbits against Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen gp340. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3229–3234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04070.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus: a selectable eukaryotic cloning and expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Rothe C. T. The white pock mutants of rabbit poxvirus. I. Spontaneous host range mutants contain deletions. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano E., Panicali D., Paoletti E. Molecular genetics of vaccinia virus: demonstration of marker rescue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1593–1596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Davis S. W., Mercer S. R., Paoletti E. Two major DNA variants present in serially propagated stocks of the WR strain of vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1000–1010. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1000-1010.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Grzelecki A., Huang C. Vaccinia virus vectors utilizing the beta-galactosidase assay for rapid selection of recombinant viruses and measurement of gene expression. Gene. 1986;47(2-3):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Paoletti E. Construction of poxviruses as cloning vectors: insertion of the thymidine kinase gene from herpes simplex virus into the DNA of infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkus M. E., Panicali D., Mercer S., Paoletti E. Insertion and deletion mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkus M. E., Piccini A., Lipinskas B. R., Paoletti E. Recombinant vaccinia virus: immunization against multiple pathogens. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):981–984. doi: 10.1126/science.2992092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccini A., Perkus M. E., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus as an expression vector. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:545–563. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosel J. L., Earl P. L., Weir J. P., Moss B. Conserved TAAATG sequence at the transcriptional and translational initiation sites of vaccinia virus late genes deduced by structural and functional analysis of the HindIII H genome fragment. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):436–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.436-449.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. F., Padgett B. L., Tomkins J. K. Conditional lethal mutants of rabbitpox virus. I. Isolation of host cell-dependent and temperature-dependent mutants. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):592–599. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spehner D., Gillard S., Drillien R., Kirn A. A cowpox virus gene required for multiplication in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1297–1304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1297-1304.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAGAYA I., KITAMURA T., SANO Y. A new mutant of dermovaccinia virus. Nature. 1961 Oct 28;192:381–382. doi: 10.1038/192381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Weinberg R., Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G., Paoletti E. Protective immunity against avian influenza induced by a fowlpox virus recombinant. Vaccine. 1988 Dec;6(6):504–508. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Weinberg R., Languet B., Desmettre P., Paoletti E. Recombinant fowlpox virus inducing protective immunity in non-avian species. Vaccine. 1988 Dec;6(6):497–503. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsman M., Aurelian L., Smith C. C., Lipinskas B. R., Perkus M. E., Paoletti E. Protection of guinea pigs from primary and recurrent herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2 cutaneous disease with vaccinia virus recombinants expressing HSV glycoprotein D. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1188–1197. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. M., Hodges W. M., Hruby D. E. Construction of recombinant vaccinia virus strains using single-stranded DNA insertion vectors. Gene. 1986;49(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen L., Moss B. Oligonucleotide sequence signaling transcriptional termination of vaccinia virus early genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6417–6421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]