Abstract
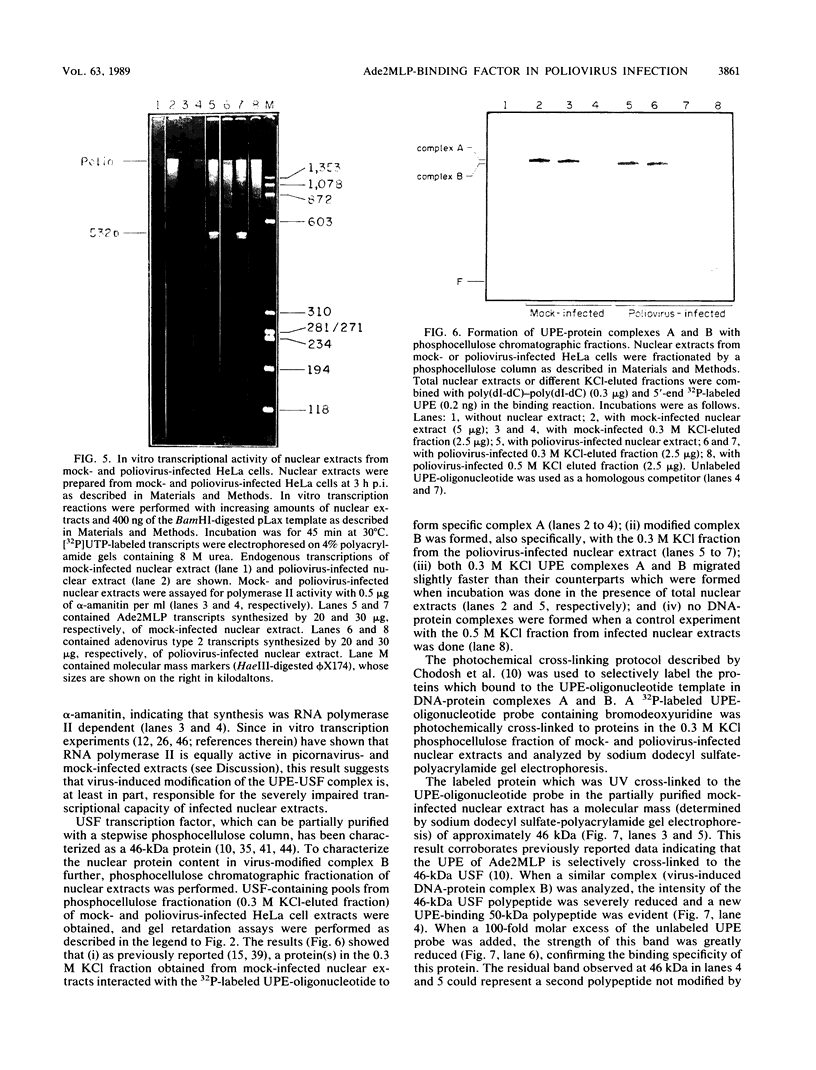
To further characterize the mechanism involved in poliovirus-induced inhibition of HeLa cells mRNA synthesis, in vitro formation of DNA-protein complexes between nuclear upstream stimulatory transcription factor (USF) and the adenovirus type 2 major late promoter upstream promoter element (UPE; located between -45 and -65 base pairs) was studied. Using the gel shift assay, we found differences between the UPE-protein complex formed with partially purified nuclear extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells and that obtained in the presence of mock-infected extracts. Formation of the modified UPE-USF complex coincided with virus-induced inhibition of host cell RNA synthesis in vivo and with a less efficient in vitro transcriptional activity of the nuclear extracts from infected cells. Furthermore, using a cross-linking protocol, we found that the host 46-kilodalton UPE-binding USF factor was severely diminished and that a virus-induced or -modified 50-kilodalton polypeptide appeared to be specifically bound to the UPE template.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Wong J. K., Fitzpatrick V. D., Moyle M., Ingles C. J. The C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Drosophila melanogaster, and mammals: a conserved structure with an essential function. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):321–329. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B., Dahmus M. E., Meares C. F. RNA contacts subunits IIo and IIc in HeLa RNA polymerase II transcription complexes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14226–14231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Halden N. F., Cullen C. R., Corden J. L. Genetic analysis of the repetitive carboxyl-terminal domain of the largest subunit of mouse RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):330–339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Killeen M., Sopta M., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. RAP30/74: a general initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1602–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantero-Aguilar L., Sanchez-Trujillo A., Fernandez-Tomas C. Poliovirion-derived capsid proteins in subviral ribonucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. Inhibition of transcription factor activity by poliovirus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Identification of calf thymus RNA polymerase subunits phosphorylated by two purified protein kinases, correlation with in vivo sites of phosphorylation in HeLa cell RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3332–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Tomás C. The presence of viral-induced proteins in nuclei from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Otero G., Fernández-Tomás C., Gariglio-Vidal P. DNA-bound RNA polymerases during poliovirus infection: reduction in the number of form II enzyme molecules. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradkin L. G., Yoshinaga S. K., Berk A. J., Dasgupta A. Inhibition of host cell RNA polymerase III-mediated transcription by poliovirus: inactivation of specific transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3880–3887. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carranca A., Miguel F., Dahmus M. E., Gariglio P. Structure of monkey kidney cell RNA polymerase II: characterization of RNA polymerase associated with SV40 late transcriptional complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Nov 15;251(1):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockensmith J. W., Kubasek W. L., Vorachek W. R., von Hippel P. H. Laser cross-linking of nucleic acids to proteins. Methodology and first applications to the phage T4 DNA replication system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3512–3518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda Z., Taniguchi T., Shizuta Y. Poly (ADP-Ribose) synthetase. Separation and identification of three proteolytic fragments as the substrate-binding domain, the DNA-binding domain, and the automodification domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4770–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. Y., Dahmus M. E. Immunochemical analysis of mammalian RNA polymerase II subspecies. Stability and relative in vivo concentration. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14219–14225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S., Dasgupta A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor inactivated in poliovirus-infected cells copurifies with transcription factor TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3175–3182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. F., Concino M. F., Weinmann R. Genetic profile of the transcriptional signals from the adenovirus major late promoter. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90657-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard A. C., Egly J. M. The bidirectional upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter binds a single monomeric molecule of the upstream factor. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3027–3034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Riggs A. D. Photochemical attachment of lac repressor to bromodeoxyuridine-substituted lac operator by ultraviolet radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):947–951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Specific interaction between a transcription factor and the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel L. M., Fernandez-Tomas C., Dahmus M. E., Gariglio P. Modification of RNA polymerase IIO subspecies after poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1002–1006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1002-1006.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel L. M., Fernández-Tomas C., Dahmus M. E., Gariglio P. Poliovirus-induced modification of host cell RNA polymerase IIO is prevented by cycloheximide and zinc. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19267–19269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Transcription factor IIS stimulates elongation of RNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3331–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Cohen R. B., Garfinkel S., Thompson J. A. DNA affinity labeling of adenovirus type 2 upstream promoter sequence-binding factors identifies two distinct proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. II. DNA binding properties and transcriptional activity of the purified HeLa USF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11994–12001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lawrence C., Thach R. E., Roeder R. G. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. II. Effect on host RNA synthesis and RNA polymerases. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.611-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X. P., Lee R., Weinmann R. Protein factor(s) binding independently to two different regions of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3729–3744. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R., Wilkinson H., Pfeifer K., Schneider C., Young R., Guarente L. Two or more copies of Drosophila heat shock consensus sequence serve to activate transcription in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8183–8188. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Compilation of transcription regulating proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1879–1902. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Lee J. M., Weeks J. R., Jokerst R. S., Greenleaf A. L. The C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II largest subunit is essential in vivo but is not required for accurate transcription initiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A general transcription factor forms a stable complex with RNA polymerase B (II). Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]