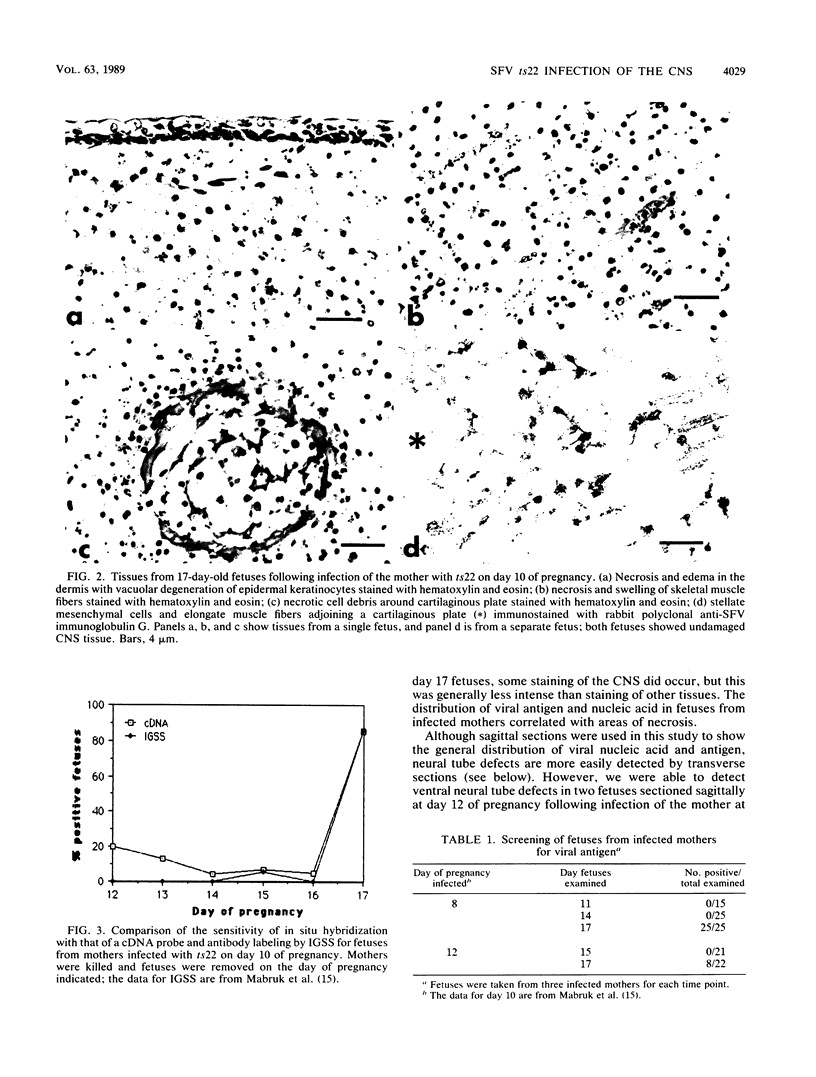
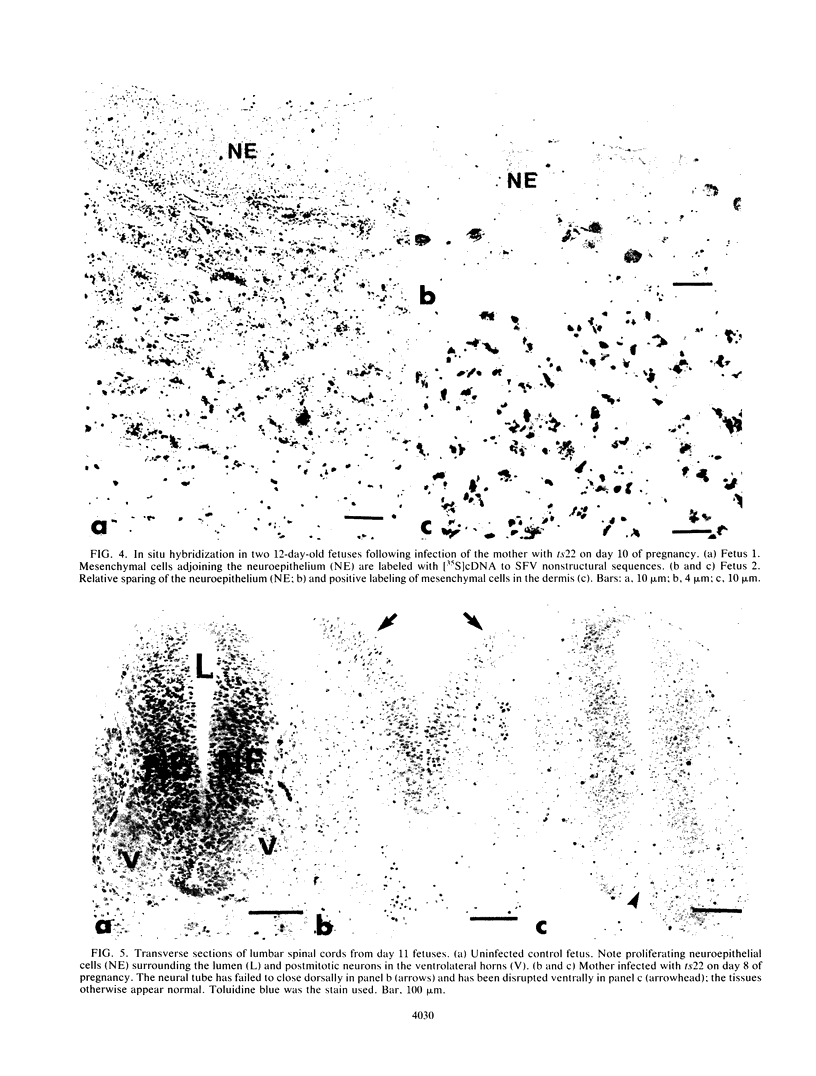
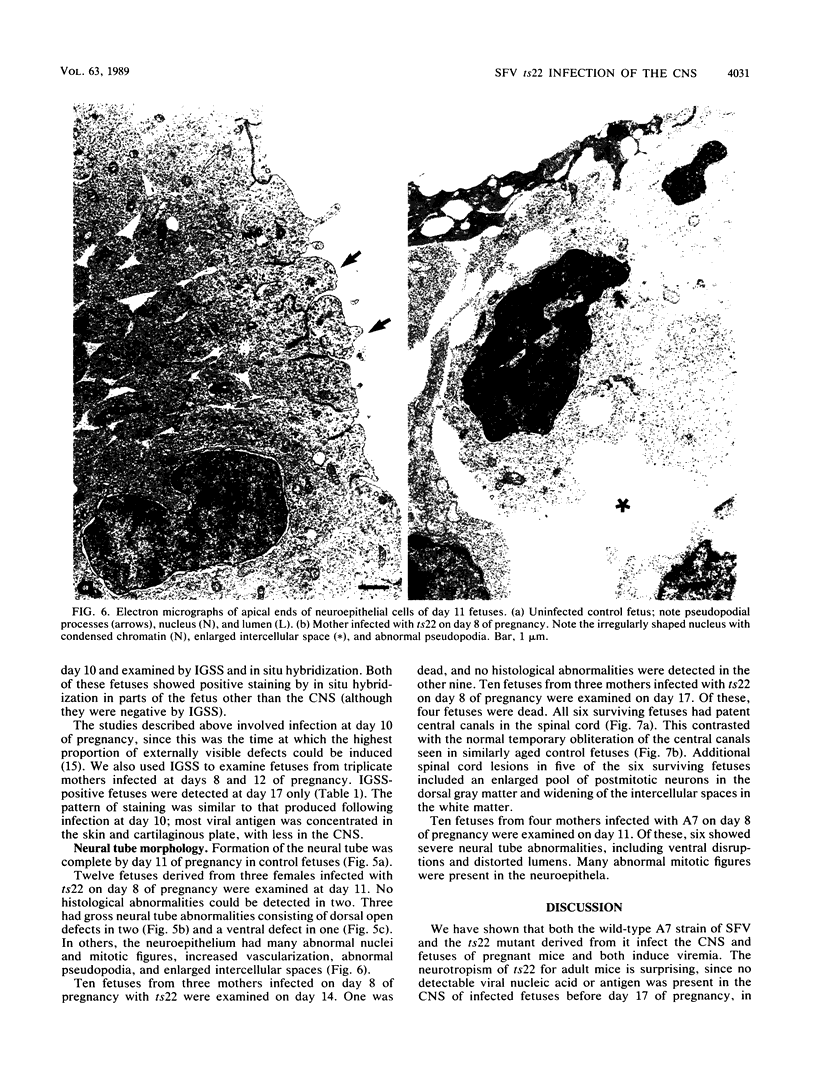
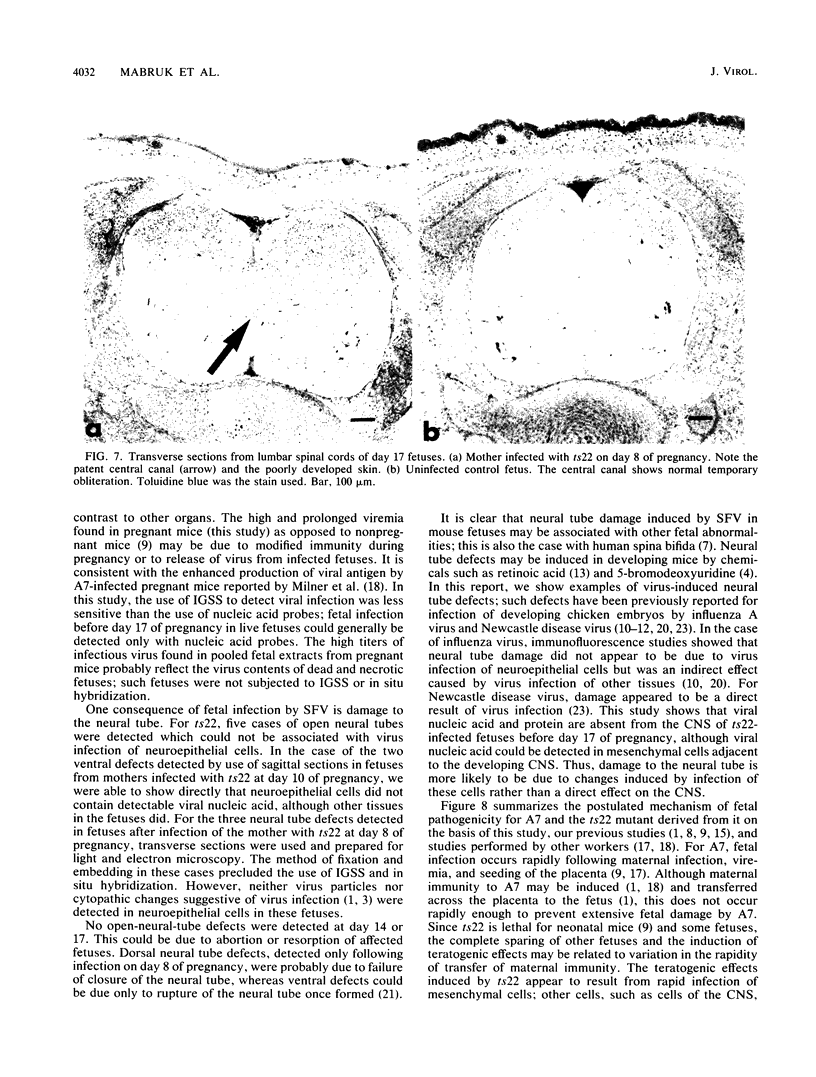
Abstract
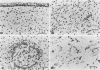
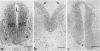
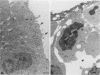
The A7 strain of Semliki Forest virus induces rapid fetal death in pregnant mice, whereas the ts22 mutant derived from it is teratogenic for a proportion of fetuses. Both A7 and ts22 induce viremia and infect the central nervous systems and fetuses of pregnant mice. Using immunogold-silver staining, a cDNA probe for a Semliki Forest virus nonstructural sequence, and a riboprobe derived from the same sequence, we showed that the skin and musculoskeletal systems of fetuses from mothers infected with ts22 were often heavily infected but the central nervous systems were not labeled before day 17 of pregnancy. Damage to the neural tube, including open-neural-tube defects, was detected in fetuses following infection of the mother at days 8 and 10 of pregnancy with both A7 and ts22. For ts22, neural tube damage induced by fetal infection before day 17 of pregnancy appeared to be indirect and caused by virus infection of mesenchymal cells surrounding the developing neural tube.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. J., Carter J., Sheahan B. J. Effect of alphavirus infection on mouse embryos. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1285–1290. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1285-1290.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Samuels J., Kennedy S. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus strain AR339. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):371–380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Sheahan B. J., Dimmock N. J. Semliki Forest virus infection of mice: a model for genetic and molecular analysis of viral pathogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):395–408. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannigan J. G. The effects of 5-bromodeoxyuridine on fusion of the cranial neural folds in the mouse embryo. Teratology. 1985 Oct;32(2):229–239. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420320211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. N., Sheahan B. J., Atkins G. J. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Semliki Forest virus mutants with altered virulence. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):141–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates M. C., Sheahan B. J., O'Sullivan M. A., Atkins G. J. The pathogenicity of the A7, M9 and L10 strains of Semliki Forest virus for weanling mice and primary mouse brain cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2365–2373. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. N., Jones K. L., Rorke L. B., Chernoff G. F., James H. E. Central nervous system anomalies associated with meningomyelocele, hydrocephalus, and the Arnold-Chiari malformation: reappraisal of theories regarding the pathogenesis of posterior neural tube closure defects. Neurosurgery. 1986 May;18(5):559–564. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198605000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne A. M., O'Sullivan M. A., Atkins G. J. Infection of cultured early mouse embryos with Semliki Forest and rubella viruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1091–1098. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne A. M., O'Sullivan M. A., Atkins G. J. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Semliki Forest virus mutants with altered pathogenicity for mouse embryos. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):107–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. P., Klasnja R., Johnson R. T. Neural tube defects of chick embryos: an indirect result of influenza A virus infection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):68–74. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197101000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T. Effects of viral infection on the developing nervous system. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 21;287(12):599–604. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209212871208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapron-Brás C. M., Trasler D. G. Gene-teratogen interaction and its morphological basis in retinoic acid-induced mouse spina bifida. Teratology. 1984 Aug;30(1):143–150. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420300118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Keränen S., Pettersson R. F., Käriäinen L. 18S defective interfering RNA of Semliki Forest virus contains a triplicated linear repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabruk M. J., Flack A. M., Glasgow G. M., Smyth J. M., Folan J. C., Bannigan J. G., O'Sullivan M. A., Sheahan B. J., Atkins G. J. Teratogenicity of the Semliki Forest virus mutant ts22 for the foetal mouse: induction of skeletal and skin defects. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2755–2762. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. R., Marshall I. D., Mullbacher A. Effect of pregnancy on stimulation of alphavirus immunity in mice. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):73–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.73-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. R., Marshall I. D. Pathogenesis of in utero infections with abortogenic and non-abortogenic alphaviruses in mice. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.66-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai R., Gould E. A., Smith H. Infection patterns in mice of an avirulent and virulent strain of Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Dec;52(6):669–677. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON G. G., WILLIAMSON A. P., BLATTNER R. J. Origin of myeloschisis in chick embryos infected with influenza-A virus. Yale J Biol Med. 1960 Jun;32:449–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheahan B. J., Gates M. C., Caffrey J. F., Atkins G. J. Oligodendrocyte infection and demyelination produced in mice by the M9 mutant of Semliki Forest virus. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(3-4):257–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00691874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. P., Blattner R. J., Robertson G. G. The relationship of viral antigen to virus-induced defects in chick embryos. Newcastle disease virus. Dev Biol. 1965 Dec;12(3):498–519. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]