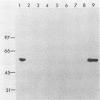
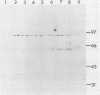
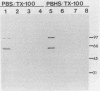
Abstract
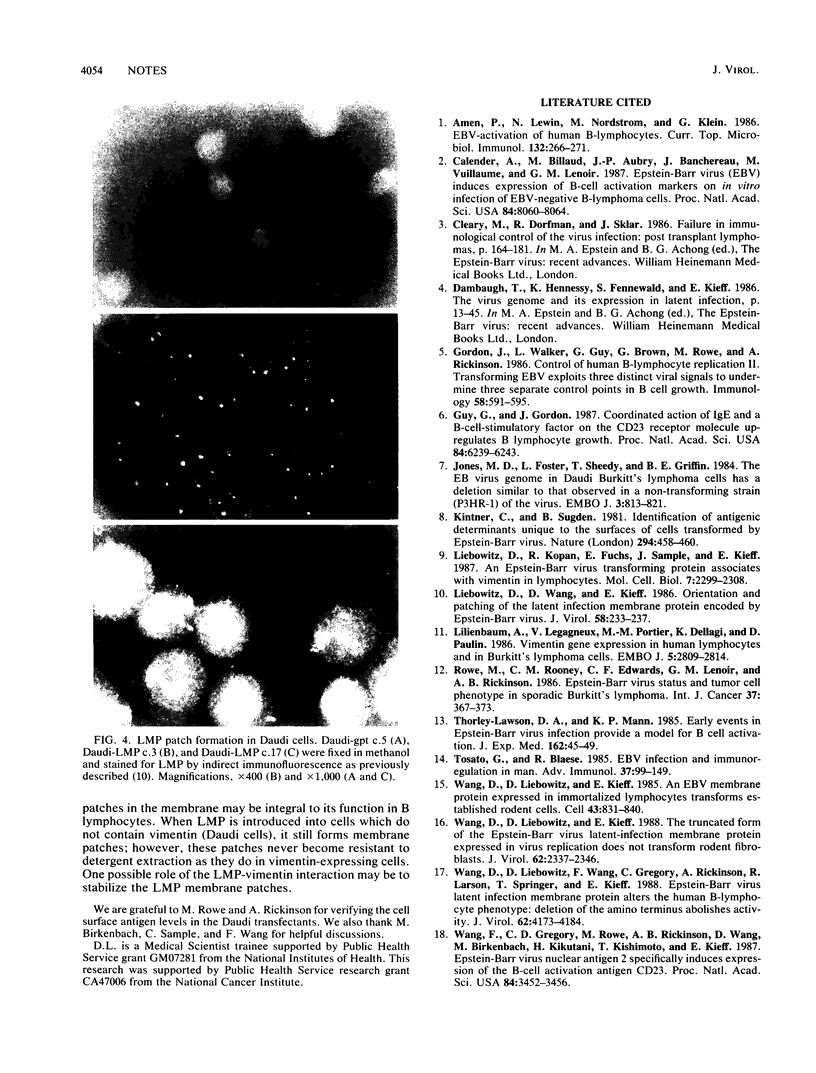
The latent membrane protein (LMP) of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) forms patches associated with the vimentin intermediate filament system in EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines, EBV-infected Burkitt's lymphoma cells, and LMP-transfected, EBV-negative Burkitt's lymphoma cells. By gene transfer, LMP induces the expression of vimentin and B-cell activation antigens in EBV-negative Burkitt's lymphoma cells. We have now expressed LMP in an EBV-positive Burkitt's lymphoma cell line, Daudi, which does not express any LMP or vimentin. In these Daudi transfectants, LMP still formed plasma membrane patches in the absence of vimentin. LMP did not resist nonionic detergent extraction in Daudi cells as it does in vimentin-expressing cells. LMP still retained functional activity as judged by induction of B-cell activation antigens. These data indicate that LMP can form plasma membrane patches and induce B-lymphocyte activation independent of vimentin association.
Full text
PDF

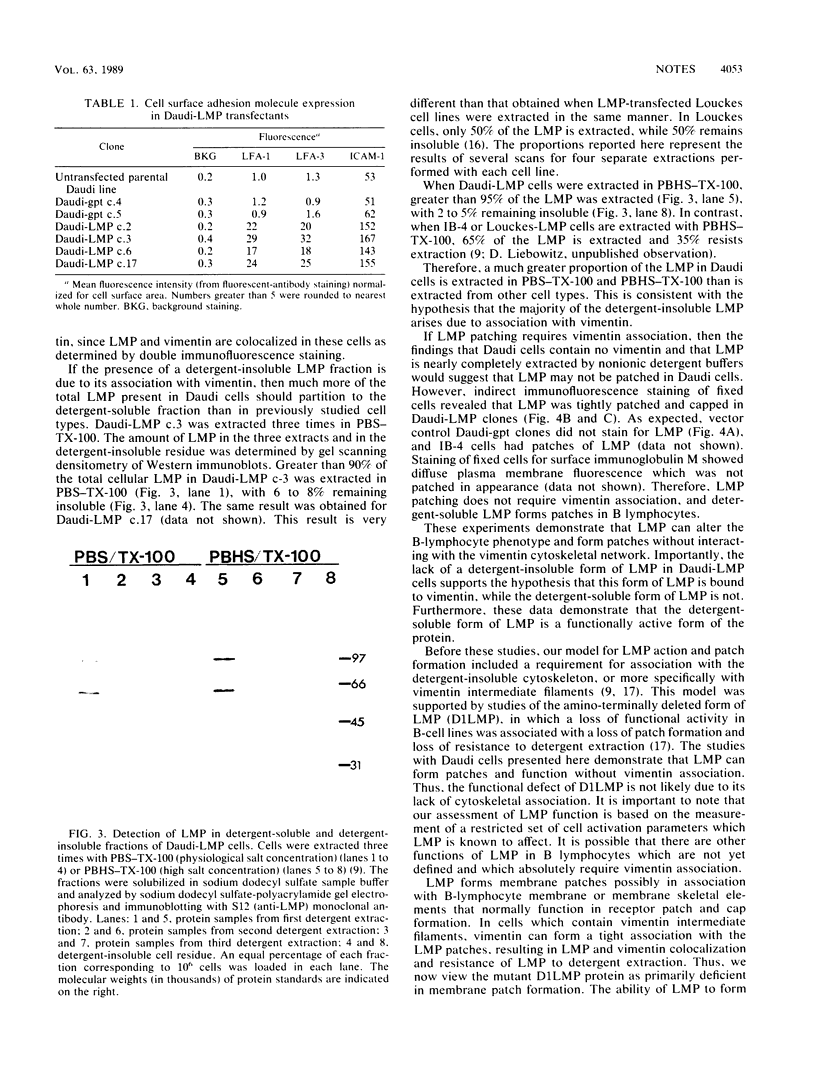
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aman P., Lewin N., Nordström M., Klein G. EBV-activation of human B-lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;132:266–271. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71562-4_40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Walker L., Guy G., Brown G., Rowe M., Rickinson A. Control of human B-lymphocyte replication. II. Transforming Epstein-Barr virus exploits three distinct viral signals to undermine three separate control points in B-cell growth. Immunology. 1986 Aug;58(4):591–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Gordon J. Coordinated action of IgE and a B-cell-stimulatory factor on the CD23 receptor molecule up-regulates B-lymphocyte growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. D., Foster L., Sheedy T., Griffin B. E. The EB virus genome in Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells has a deletion similar to that observed in a non-transforming strain (P3HR-1) of the virus. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):813–821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01890.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C., Sugden B. Identification of antigenic determinants unique to the surfaces of cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):458–460. doi: 10.1038/294458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Kopan R., Fuchs E., Sample J., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein associates with vimentin in lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2299–2308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Wang D., Kieff E. Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilienbaum A., Legagneux V., Portier M. M., Dellagi K., Paulin D. Vimentin gene: expression in human lymphocytes and in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2809–2814. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rooney C. M., Edwards C. F., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus status and tumour cell phenotype in sporadic Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1986 Mar 15;37(3):367–373. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910370307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Mann K. P. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection provide a model for B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):45–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Blaese R. M. Epstein-Barr virus infection and immunoregulation in man. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:99–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. The truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein expressed in virus replication does not transform rodent fibroblasts. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2337-2346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]