Abstract
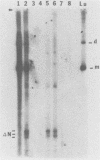
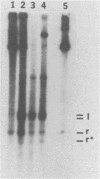
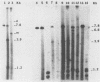
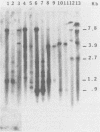
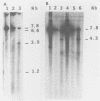
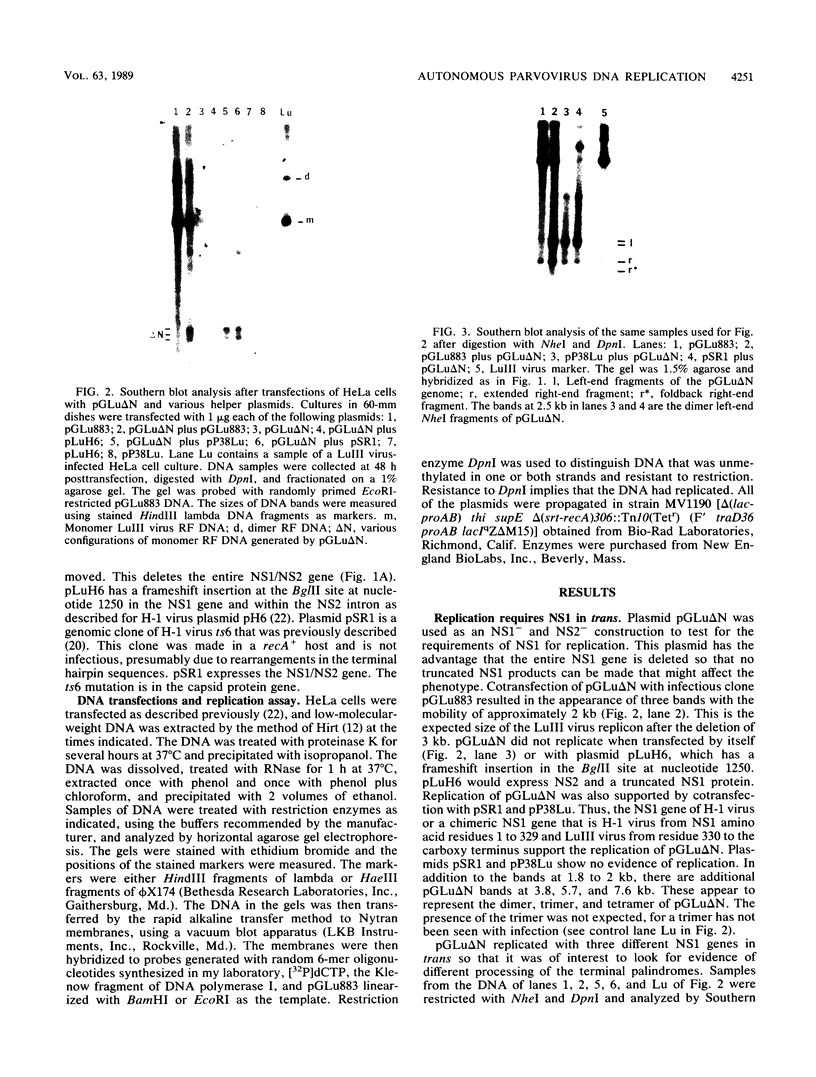
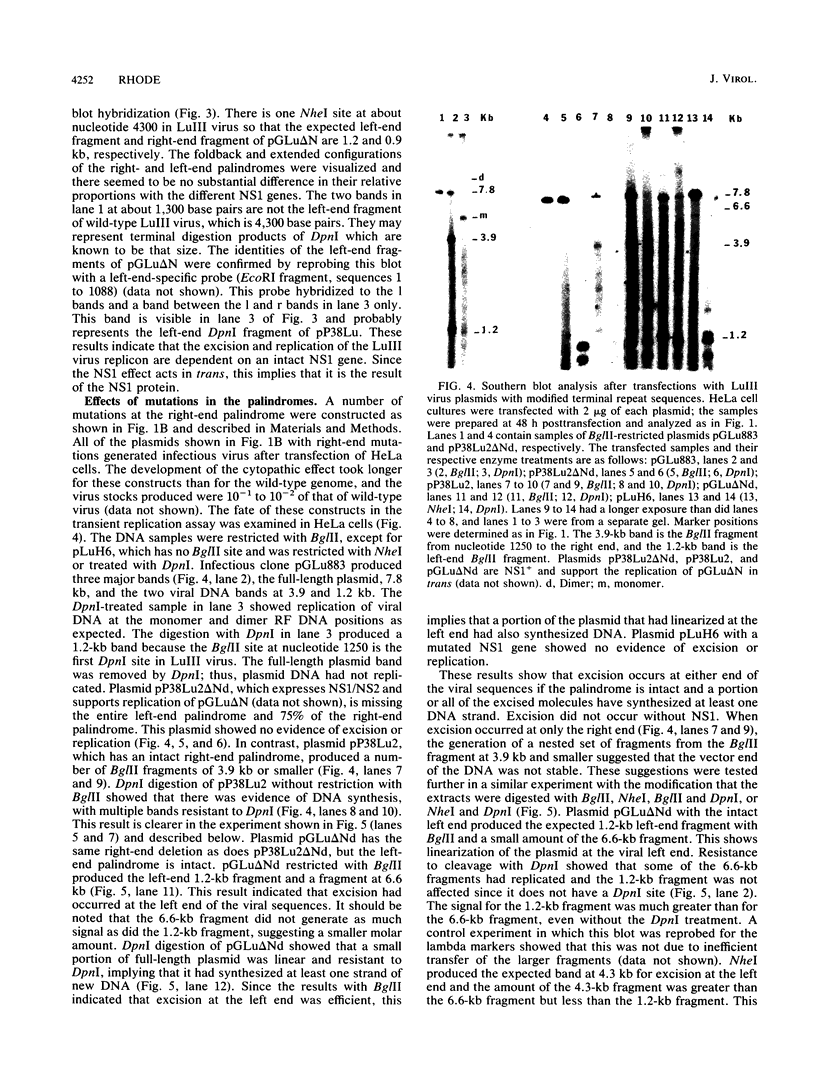
When a bacterial plasmid containing the entire genome of LuIII virus except for the terminal 18 nucleotides from the right end is transfected into HeLa cells, the viral DNA is rescued and replicated, with production of infectious virus. This experimental system was used to examine the viral proteins and cis elements required for the excision and replication of viral DNA. The deletion of the entire NS1 gene provided a viral genome that was excised from the plasmid and replicated only when an NS1 gene was provided in trans. A frameshift mutation in the NS2 intron that truncates NS1 prevented excision and replication. Deletion of the left-end terminal inverted repeat or the right-end inverted repeat prevented excision of viral DNA from that end but not from the wild-type terminus. The viral terminus excised from the plasmid was protected from a processive degradation process, which began on the vector portion of the plasmid. The inhibitor of DNA polymerases alpha and delta, aphidicolin, blocked the excision reaction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton I. A., Lane D. P. Non-structural protein 1 of parvoviruses: homology to purine nucleotide using proteins and early proteins of papovaviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7813–7813. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Mol C. D., Anderson W. F. Structural and functional homology of parvovirus and papovavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):885–893. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Kotin R. M., Labow M. A. Regulation of adeno-associated virus DNA replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 20;951(2-3):425–429. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohenzky R. A., LeFebvre R. B., Berns K. I. Sequence and symmetry requirements within the internal palindromic sequences of the adeno-associated virus terminal repeat. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):316–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The NS-1 polypeptide of minute virus of mice is covalently attached to the 5' termini of duplex replicative-form DNA and progeny single strands. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):851–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.851-860.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffoot N., Shull B. C., Chen K. C., Stout E. R., Lederman M., Bates R. C. Identical ends are not required for the equal encapsidation of plus- and minus-strand parvovirus LuIII DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3180–3184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3180-3184.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Ward D. C. Incomplete genomes of the parvovirus minute virus of mice: selective conservation of genome termini, including the origin for DNA replication. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):276–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.276-292.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J., Muzyczka N. In vitro excision of adeno-associated virus DNA from recombinant plasmids: isolation of an enzyme fraction from HeLa cells that cleaves DNA at poly(G) sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2513–2522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther M., Tattersall P. The terminal protein of minute virus of mice is an 83 kilodalton polypeptide linked to specific forms of double-stranded and single-stranded viral DNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):22–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80977-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Graf L. H., Jr, Berns K. I. Adeno-associated virus gene expression inhibits cellular transformation by heterologous genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Hermonat P. L., Berns K. I. Positive and negative autoregulation of the adeno-associated virus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.251-258.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. B., Riva S., Berns K. I. Conformation takes precedence over sequence in adeno-associated virus DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1416–1419. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Complementation for replicative form DNA replication of a deletion mutant of H-1 by various parvoviruses. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1118-1122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Construction of a genetic switch for inducible trans-activation of gene expression in eucaryotic cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1448–1456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1448-1456.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Defective interfering particles of parvovirus H-1. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):347–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.347-356.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Klaassen B. DNA sequence of the 5' terminus containing the replication origin of parvovirus replicative form DNA. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):990–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.990-999.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Paradiso P. R. Parvovirus genome: nucleotide sequence of H-1 and mapping of its genes by hybrid-arrested translation. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):173–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.173-184.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Replication process of the parvovirus H-1. VI. Characterization of a replication terminus of H-1 replicative-form DNA. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):694–712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.694-712.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Richard S. M. Characterization of the trans-activation-responsive element of the parvovirus H-1 P38 promoter. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2807–2815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2807-2815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd trans-Activation of parvovirus P38 promoter by the 76K noncapsid protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):886–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.886-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEIN H. M., ENDERS J. F. Multiplication and cytopathogenicity of Simian vacuolating virus 40 in cultures of human tissues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Mar;109:495–500. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Chang L. S., Shenk T. A recombinant plasmid from which an infectious adeno-associated virus genome can be excised in vitro and its use to study viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3096–3101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3096-3101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Srivastava A., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P., Tratschin J. D., Carter B. J. Replication of adeno-associated virus DNA. Complementation of naturally occurring rep- mutants by a wild-type genome or an ori- mutant and correction of terminal palindrome deletions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull B. C., Chen K. C., Lederman M., Stout E. R., Bates R. C. Genomic clones of bovine parvovirus: construction and effect of deletions and terminal sequence inversions on infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):417–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.417-426.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Tal J., Carter B. J. Negative and positive regulation in trans of gene expression from adeno-associated virus vectors in mammalian cells by a viral rep gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2884–2894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis G. E., Labieniec-Pintel L., Clemens K. E., Pintel D. Generation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutation in the NS-1 gene of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2736–2744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2736-2744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Sauerbier W. Flanking AT-rich sequences may lower the activation energy of cruciform extrusion in supercoiled DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. The role of palindromic and non-palindromic sequences in arresting DNA synthesis in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):961–986. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker R., Gunther M. Isolation and characterization of thermosensitive mutants from Kilham rat virus, a rodent parvovirus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):163–175. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]