Abstract
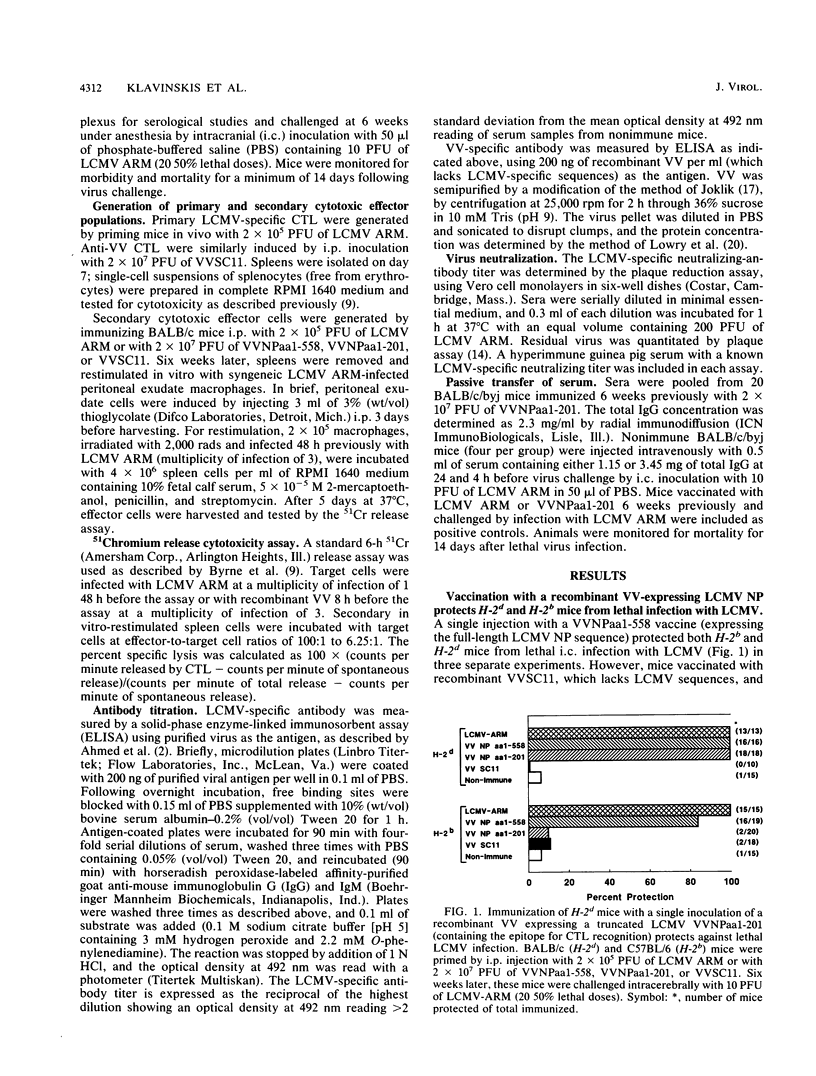
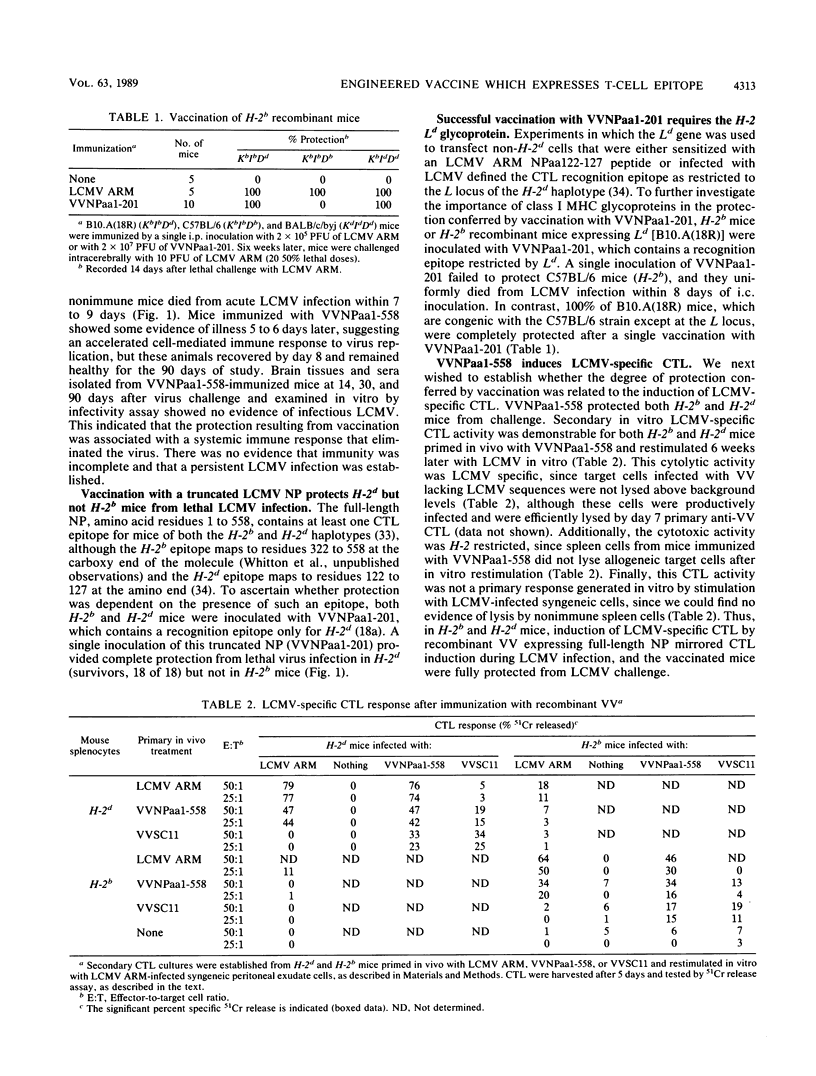
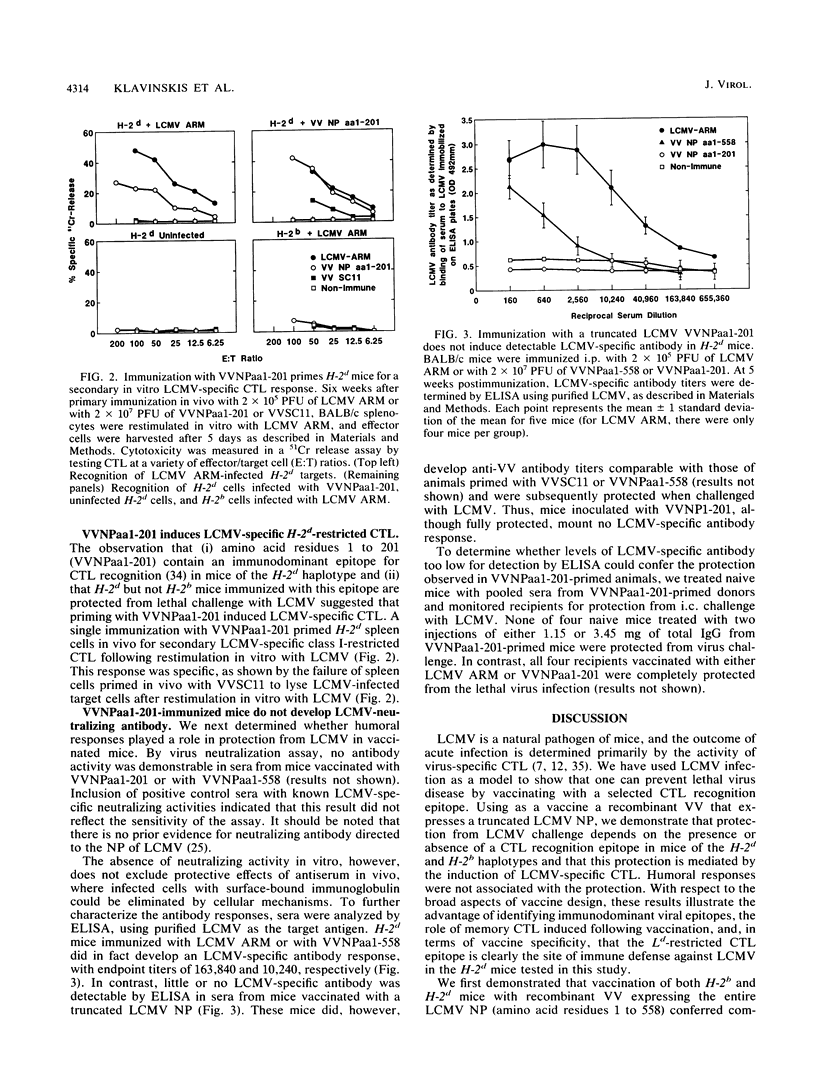
Identification of a single viral T-cell epitope, associated with greater than 95% of the virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity in BALB/c (H-2d) mice (J. L. Whitton, A. Tishon, H. Lewicki, J. Gebhard, T. Cook, M. Salvato, E. Joly, and M. B. A. Oldstone, J. Virol. 63:4303-4310, 1989), permitted us to design a CTL vaccine and test its ability to protect against a lethal virus challenge. Here we show that a single immunization with a recombinant vaccinia virus-lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) vaccine (VVNPaa1-201) expressing the immunodominant epitope completely protected H-2d mice from lethal infection with LCMV but did not protect H-2b mice. Furthermore, we show that the success or failure of immunization was determined entirely by the host class I major histocompatibility glycoproteins. The difference in outcome between mice of these two haplotypes was consistent with the presence or absence in the immunizing sequences of an epitope for CTL recognition and is correlated with the induction of LCMV-specific H-2-restricted CTL in H-2d mice. Protection is not conferred by a humoral immune response, since LCMV-specific antibodies were not detectable in sera from VVNPaa1-201-immunized mice. In addition, passive transfer of sera from vaccinated mice did not confer protection upon naive recipients challenged with LCMV. Hence, the molecular dissection of viral proteins can uncover immunodominant CTL epitope(s) that can be engineered into vaccines that elicit CTL. A single CTL epitope can protect against a lethal virus infection, but the efficacy of the vaccine varies in a major histocompatibility complex-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Byrne J. A., Oldstone M. B. Virus specificity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes generated during acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection: role of the H-2 region in determining cross-reactivity for different lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus strains. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.34-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Salmi A., Butler L. D., Chiller J. M., Oldstone M. B. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):521–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennink J. R., Yewdell J. W., Smith G. L., Moss B. Anti-influenza virus cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize the three viral polymerases and a nonstructural protein: responsiveness to individual viral antigens is major histocompatibility complex controlled. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1098–1102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1098-1102.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braciale T. J., Sweetser M. T., Morrison L. A., Kittlesen D. J., Braciale V. L. Class I major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytolytic T lymphocytes recognize a limited number of sites on the influenza hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):277–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Miles C., Grey H. M. The relation between major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction and the capacity of Ia to bind immunogenic peptides. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1353–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.2435001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Ahmed R., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. I. Generation and recognition of virus strains and H-2b mutants. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: clearance of virus in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M. J., Stott E. J., Taylor G., Askonas B. A. Clearance of persistent respiratory syncytial virus infections in immunodeficient mice following transfer of primed T cells. Immunology. 1987 Sep;62(1):133–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., Huegin A. W., Sutter S., Bazin H., Hengartner H. H., Zinkernagel R. M. Immunity to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in B cell-depleted mice: evidence for B cell and antibody-independent protection by memory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):913–917. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Val M., Volkmer H., Rothbard J. B., Jonjić S., Messerle M., Schickedanz J., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Molecular basis for cytolytic T-lymphocyte recognition of the murine cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein pp89. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3965–3972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3965-3972.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. Genomic and biological variation among commonly used lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus strains. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1689–1698. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon G., Shastri N., Cogswell J., Wilbur S., Sadegh-Nasseri S., Krzych U., Miller A., Sercarz E. The choice of T-cell epitopes utilized on a protein antigen depends on multiple factors distant from, as well as at the determinant site. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:53–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotch F., Rothbard J., Howland K., Townsend A., McMichael A. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize a fragment of influenza virus matrix protein in association with HLA-A2. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):881–882. doi: 10.1038/326881a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The purification fo four strains of poxvirus. Virology. 1962 Sep;18:9–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., del Val M., Keil G. M., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. A nonstructural viral protein expressed by a recombinant vaccinia virus protects against lethal cytomegalovirus infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1653–1658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1653-1658.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Biological properties of an influenza A virus-specific killer T cell clone. Inhibition of virus replication in vivo and induction of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):225–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J. In vivo effector function of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is highly specific. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):814–826. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. W., Carbone F. R., Bevan M. J. Introduction of soluble protein into the class I pathway of antigen processing and presentation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):777–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon D. F., Townsend A. R., Elvin J. G., Rizza C. R., Gallwey J., McMichael A. J. HIV-1 gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes defined with recombinant vaccinia virus and synthetic peptides. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):484–487. doi: 10.1038/336484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Whitton J. L., Lewicki H., Tishon A. Fine dissection of a nine amino acid glycoprotein epitope, a major determinant recognized by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific class I-restricted H-2Db cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh B. S., Buchmeier M. J. Proteins of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: antigenic topography of the viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):168–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Autran B., Martins L. P., Wain-Hobson S., Raphaël M., Mayaud C., Denis M., Guillon J. M., Debré P. AIDS virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lung disorders. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):348–351. doi: 10.1038/328348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Mutter W., Münch K., Bühring H. J., Koszinowski U. H. CD8-positive T lymphocytes specific for murine cytomegalovirus immediate-early antigens mediate protective immunity. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3102–3108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3102-3108.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Cohen J., Hosmalin A., Cease K. B., Houghten R., Cornette J. L., DeLisi C., Moss B., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. An immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp160 recognized by class I major histocompatibility complex molecule-restricted murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3105–3109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Davey J., Howland K., Rothbard J. B., Askonas B. A. Class I MHC molecules rather than other mouse genes dictate influenza epitope recognition by cytotoxic T cells. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(4-5):267–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00346521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Flexner C., Paradis T. J., Fuller T. C., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Moss B. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is a target for cytotoxic T lymphocytes in infected individuals. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2451288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Gebhard J. R., Lewicki H., Tishon A., Oldstone M. B. Molecular definition of a major cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope in the glycoprotein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):687–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.687-695.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Southern P. J., Oldstone M. B. Analyses of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to glycoprotein and nucleoprotein components of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Tishon A., Lewicki H., Gebhard J., Cook T., Salvato M., Joly E., Oldstone M. B. Molecular analyses of a five-amino-acid cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) epitope: an immunodominant region which induces nonreciprocal CTL cross-reactivity. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4303–4310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4303-4310.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


