Abstract
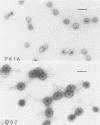
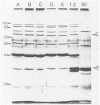
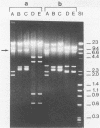
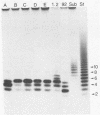
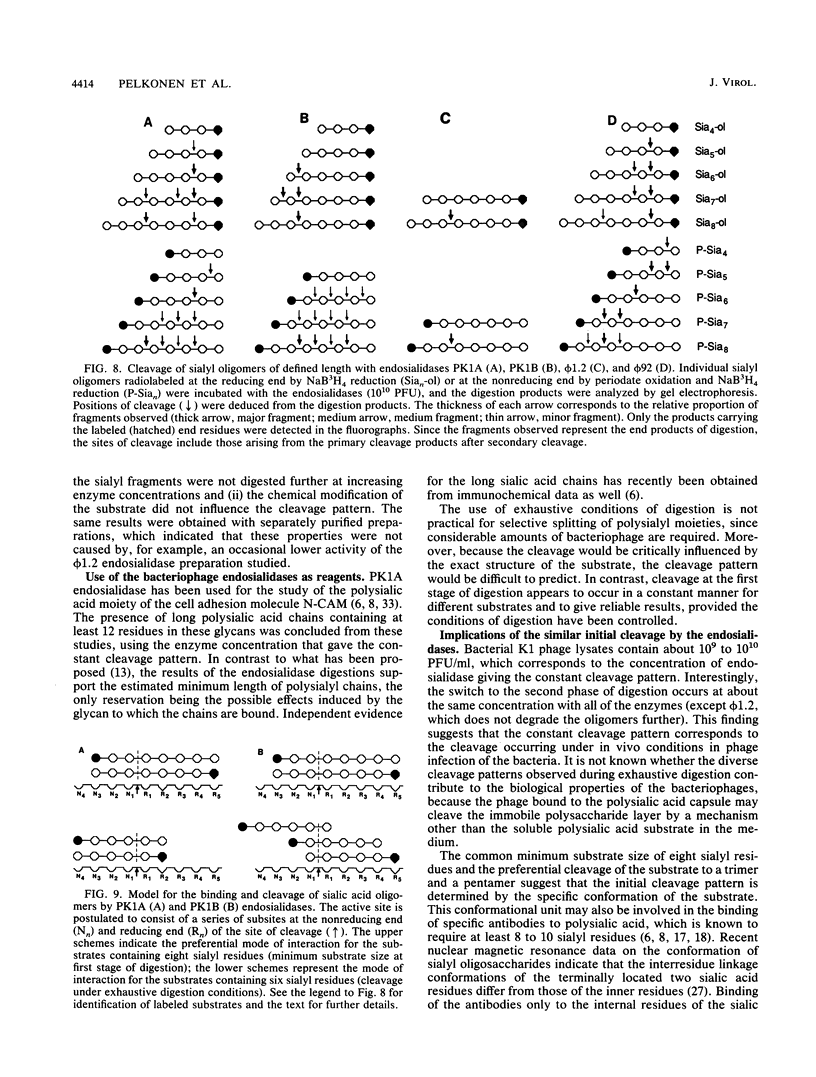
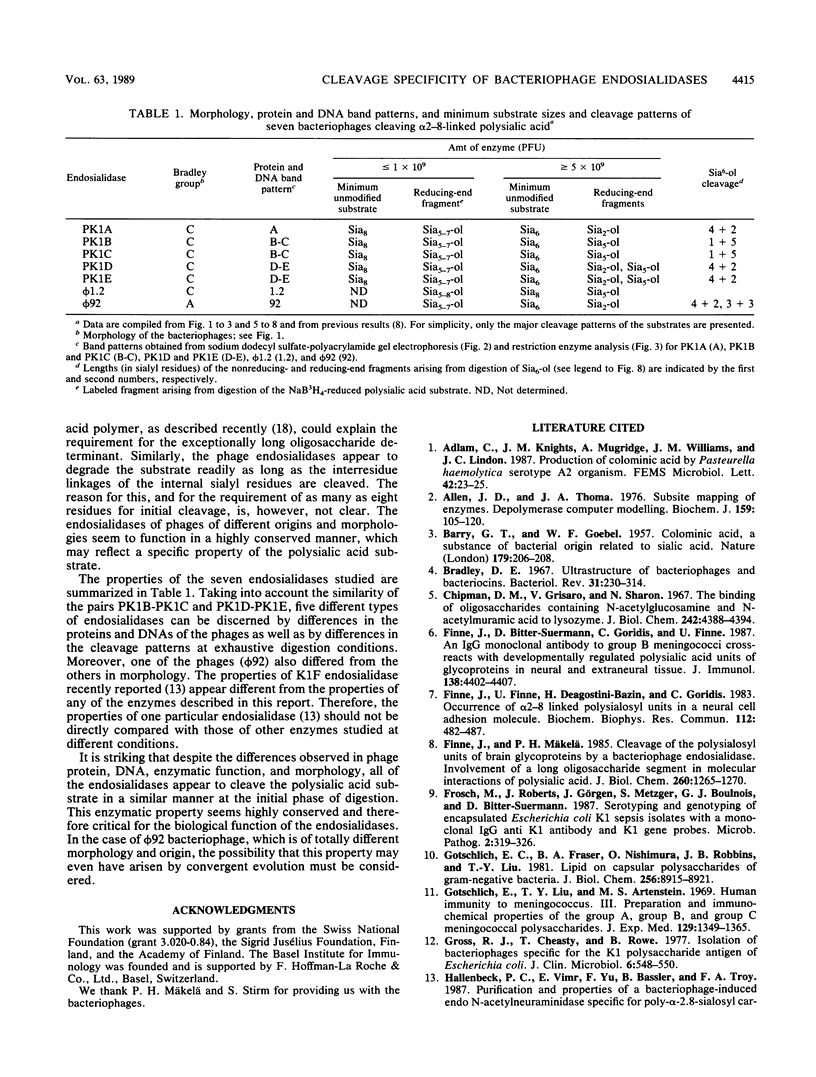
The cleavage specificities of seven bacteriophage endosialidases degrading the alpha 2-8-linked polysialic acid common to bacterial polysaccharides and to the cell adhesion molecule N-CAM were investigated. The bacteriophages studied represented five different phenotypic groups by protein and DNA fragment analysis and two different morphology groups by electron microscopy. Characterization of the fragments arising from the native or chemically modified substrates of different sizes showed that cleavage specificity was influenced by enzyme concentration. At the initial phase of degradation, at concentrations ranging from 20- to 100-fold, the minimum substrate size was an oligomer of eight (in one case, nine) sialic acid units that was preferably cleaved at the same position. Under exhaustive conditions, the oligomers were degraded further, and each enzyme type had its own specificity. The similar initial cleavage of polysialic acid by endosialidases associated with phages of different properties and morphology suggests a conserved mechanism of enzyme-substrate interaction. This mechanism may be conformationally determined and related to the specific properties of polysialic acid in other molecular interactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. D., Thoma J. A. Subsite mapping of enzymes. Depolymerase computer modelling. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 1;159(1):105–120. doi: 10.1042/bj1590105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., GOEBEL W. F. Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature. 1957 Jan 26;179(4552):206–206. doi: 10.1038/179206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipman D. M., Grisaro V., Sharon N. The binding of oligosaccharides containing N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid to lysozyme. The specificity of binding subsites. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4388–4394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Bitter-Suermann D., Goridis C., Finne U. An IgG monoclonal antibody to group B meningococci cross-reacts with developmentally regulated polysialic acid units of glycoproteins in neural and extraneural tissues. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Finne U., Deagostini-Bazin H., Goridis C. Occurrence of alpha 2-8 linked polysialosyl units in a neural cell adhesion molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):482–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Mäkelä P. H. Cleavage of the polysialosyl units of brain glycoproteins by a bacteriophage endosialidase. Involvement of a long oligosaccharide segment in molecular interactions of polysialic acid. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1265–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Roberts I., Görgen I., Metzger S., Boulnois G. J., Bitter-Suermann D. Serotyping and genotyping of encapsulated Escherichia coli K1 sepsis isolates with a monoclonal IgG anti K1 antibody and K1 gene probes. Microb Pathog. 1987 May;2(5):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Fraser B. A., Nishimura O., Robbins J. B., Liu T. Y. Lipid on capsular polysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8915–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Isolation of bacteriophages specific for the K1 polysaccharide antigen of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):548–550. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.548-550.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higa H. H., Varki A. Acetyl-coenzyme A:polysialic acid O-acetyltransferase from K1-positive Escherichia coli. The enzyme responsible for the O-acetyl plus phenotype and for O-acetyl form variation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8872–8878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi K. Interpretation of dependency of rate parameters on the degree of polymerization of substrate in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Evaluation of subsite affinities of exo-enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Kinetics of homophilic binding by embryonic and adult forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5762–5766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Roy R., Michon F. Determinant specificities of the groups B and C polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2651–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Liao J., Osserman E. F., Gamian A., Michon F., Jennings H. J. The epitope associated with the binding of the capsular polysaccharide of the group B meningococcus and of Escherichia coli K1 to a human monoclonal macroglobulin, IgMNOV. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):699–711. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Boschek B., Thiele H., Stirm S. Endo-N-acetylneuraminidase associated with bacteriophage particles. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):697–704. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.697-704.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Boschek B., Thiele H., Stirm S. Substrate specificity of two bacteriophage-associated endo-N-acetylneuraminidases. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):367–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.367-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Stirm S. Polysialic acid depolymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:786–792. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGUIRE E. J., BINKLEY S. B. THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF COLOMINIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:247–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michon F., Brisson J. R., Jennings H. J. Conformational differences between linear alpha (2----8)-linked homosialooligosaccharides and the epitope of the group B meningococcal polysaccharide. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8399–8405. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. W., Florini J. R. A rapid method for desalting small volumes of solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen S., Häyrinen J., Finne J. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the capsular polysaccharides of Escherichia coli K1 and other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2646–2653. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2646-2653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepin C. A., Wood H. G. Polyphosphate glucokinase from Propionibacterium shermanii. Kinetics and demonstration that the mechanism involves both processive and nonprocessive type reactions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4476–4480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Taatjes D. J., Bitter-Suermann D., Finne J. Polysialic acid units are spatially and temporally expressed in developing postnatal rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1969–1973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Watanabe M., Silver J., Troy F. A., Vimr E. R. Specific alteration of NCAM-mediated cell adhesion by an endoneuraminidase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1842–1849. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul R., Hirn M., Deagostini-Bazin H., Rougon G., Goridis C. Adult and embryonic mouse neural cell adhesion molecules have different binding properties. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):347–349. doi: 10.1038/304347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. Successful treatment of experimental Escherichia coli infections in mice using phage: its general superiority over antibiotics. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Feb;128(2):307–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson S., Taylor P. W. Neuraminidase associated with coliphage E that specifically depolymerizes the Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):374–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.374-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., McCoy R. D., Vollger H. F., Wilkison N. C., Troy F. A. Use of prokaryotic-derived probes to identify poly(sialic acid) in neonatal neuronal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]