Abstract
Using herpes simplex viruses deleted and restored for the latency-associated transcripts (LATs), we have quantitatively assessed the role of the transcripts in establishment and maintenance of latent infection. Determination of the number of neurons latently infected and the copy number of viral genomes per latently infected ganglion indicated that there is no difference between viruses expressing and not expressing the transcripts. In addition, the amount of viral DNA present in ganglia latently infected with the LAT-negative virus KOS 8117 did not differ from the value for LAT+ counterparts over an 11-month period of analysis. From these results we conclude that LATs play no role in establishment or maintenance of a latent infection with herpes simplex virus type 1. If these transcripts play a role in latency, they must function during the reactivation step.
Full text
PDF
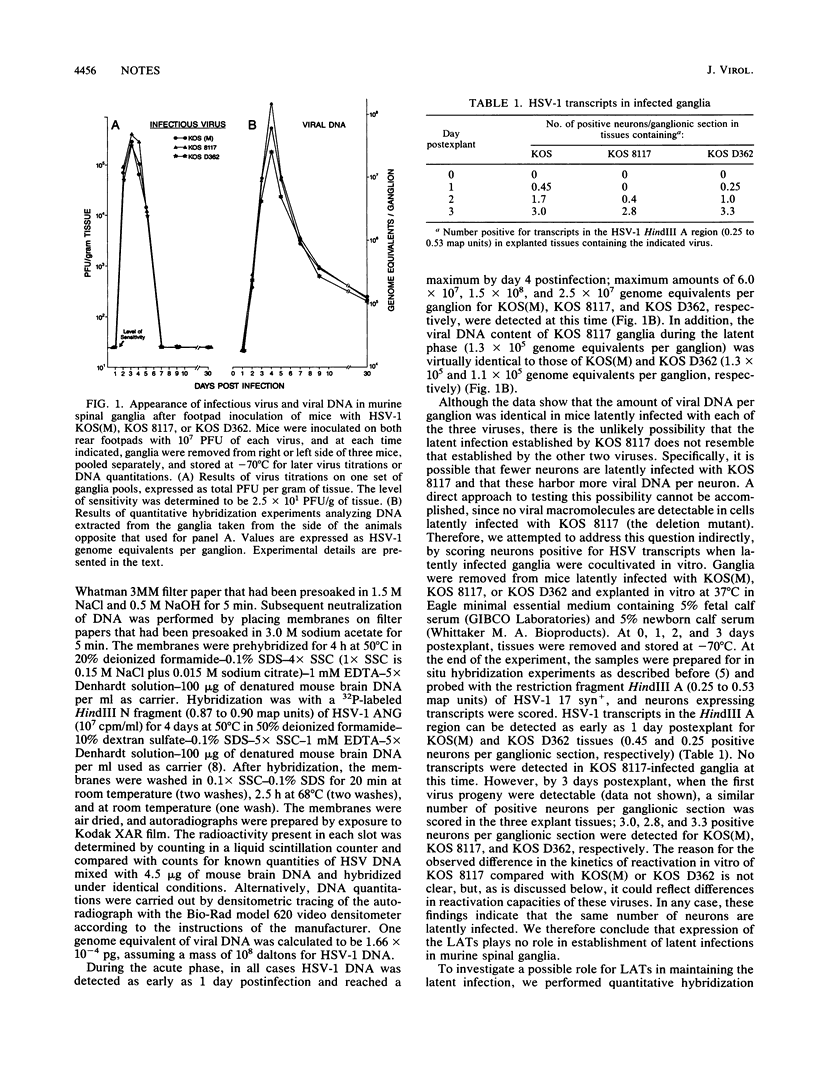

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Latent herpes simplex virus in human trigeminal ganglia. Detection of an immediate early gene "anti-sense" transcript by in situ hybridization. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 3;317(23):1427–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712033172302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatly A. M., Spivack J. G., Lavi E., Fraser N. W. RNA from an immediate early region of the type 1 herpes simplex virus genome is present in the trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Minson A. C., Field H. J., Anderson J. R., Wildy P. Detection of herpes simplex virus-specific DNA sequences in latently infected mice and in humans. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.446-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Johnson B., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T. RNA complementary to herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 gene demonstrated in neurons of human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1832–1835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1832-1835.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javier R. T., Stevens J. G., Dissette V. B., Wagner E. K. A herpes simplex virus transcript abundant in latently infected neurons is dispensable for establishment of the latent state. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):254–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Notkins A. L. Continued expression of a poly(A)+ transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1700–1703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1700-1703.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Nesburn A. B., Ghiasi H., Ong J., Lewis T. L., Lokensgard J. R., Wechsler S. L. Detection of latency-related viral RNAs in trigeminal ganglia of rabbits latently infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3820–3826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3820-3826.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedarati F., Javier R. T., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of a lethal mixed infection in mice with two nonneuroinvasive herpes simplex virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3037–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3037-3039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedarati F., Stevens J. G. Biological basis for virulence of three strains of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2389–2395. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts during latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3841–3847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3841-3847.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Lirette R. P., Brown S. M., MacLean A. R., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Fraser N. W. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts are evidently not essential for latent infection. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):505–511. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Lavi E., Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3493–3496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3493-3496.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Haarr L., Porter D. D., Cook M. L., Wagner E. K. Prominence of the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript in trigeminal ganglia from seropositive humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):117–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Flanagan W. M., Devi-Rao G., Zhang Y. F., Hill J. M., Anderson K. P., Stevens J. G. The herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript is spliced during the latent phase of infection. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4577–4585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4577-4585.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Nesburn A. B., Watson R., Slanina S., Ghiasi H. Fine mapping of the major latency-related RNA of herpes simplex virus type 1 in humans. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):3101–3106. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-3101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



