Abstract
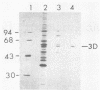
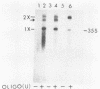
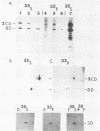
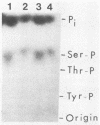
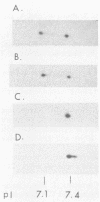
Poliovirus-specific RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (3Dpol) was purified to apparent homogeneity. A single polypeptide of an apparent molecular weight of 63,000 catalyzes the synthesis of dimeric and monomeric RNA products in response to the poliovirion RNA template. Analysis of purified 3Dpol by two-dimensional electrophoresis showed multiple forms of 3Dpol, suggesting posttranslational modification of the protein in virus-infected cells. The two major forms of 3Dpol appear to have approximate pI values of 7.1 and 7.4. Incubation of purified 3Dpol with calf intestinal phosphatase resulted in almost complete disappearance of the pI 7.1 form and a concomitant increase in the intensity of the pI 7.4 form of 3Dpol. Addition of 32P-labeled Pi during infection of HeLa cells with poliovirus resulted in specific labeling of 3Dpol and 3CD, a viral protein which contains the entire 3Dpol sequence. Both 3Dpol and 3CD appear to be phosphorylated at serine residues. Ribosomal salt washes prepared from both mock- and poliovirus-infected cells contain phosphatases capable of dephosphorylating quantitatively the phosphorylated form (pI 7.1) of 3Dpol.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. In vitro copying of viral positive strand RNA by poliovirus replicase. Characterization of the reaction and its products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a host cell protein required for poliovirus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. C., Brown E. G., Takayesu D., Prevec L. Protein kinase activity associated with immunoprecipitates of the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein NS. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A. Purification of host factor required for in vitro transcription of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewalt P. G., Semler B. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of proteinase 3C results in a poliovirus deficient in synthesis of viral RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2162–2170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2162-2170.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Characterization of double-stranded-RNA-activated kinase that phosphorylates alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):832–836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubinski J. M., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Dasgupta A. Mechanism of in vitro synthesis of covalently linked dimeric RNA molecules by the poliovirus replicase. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):459–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.459-467.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubinski J. M., Ransone L. J., Dasgupta A. Primer-dependent synthesis of covalently linked dimeric RNA molecules by poliovirus replicase. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2997–3003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2997-3003.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Stillman B., Gluzman Y. Regulation of SV40 DNA replication by phosphorylation of T antigen. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Gibbons G. F., Dasgupta A. The host protein required for in vitro replication of poliovirus is a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor-2. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Hocko J., Navab M., Dasgupta A. ATP is required for initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis in vitro: demonstration of tyrosine-phosphate linkage between in vitro-synthesized RNA and genome-linked protein. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):515–523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.515-523.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S. Regulation of protein synthesis initiation in eucaryotes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):325–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotch S. J., Palant O., Gluzman Y. Purification and properties of poliovirus RNA polymerase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):216–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.216-225.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Dasgupta A. Activation of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase in HeLa cells after poliovirus infection does not result in increased phosphorylation of eucaryotic initiation factor-2. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1781–1787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1781-1787.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Kitamura N., Rothberg P. G., Wishart W. L., Wimmer E. Poliovirus replication proteins: RNA sequence encoding P3-1b and the sites of proteolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Yang C. F., Takeda N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Analysis of RNA synthesis of type 1 poliovirus by using an in vitro molecular genetic approach. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2816–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2816-2822.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]