Abstract
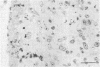
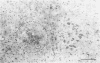
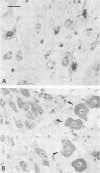
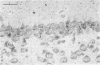
The spread of herpes simplex virus (HSV) was studied in the mouse central nervous system (CNS) after ocular inoculation. Sites of active viral replication in the CNS were identified by autoradiographic localization of neuronal uptake of tritiated thymidine. Labeled neurons were first noted in the CNS at 4 days postinoculation in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus, ipsilateral spinal trigeminal nucleus, pars caudalis, pars interpolaris, and ipsilateral dorsal horn of the rostral cervical spinal cord. By 5 days postinoculation, additional sites of labeling included the seventh nerve nucleus, nucleus locus coeruleus, and the nuclei raphe magnus and raphe pallidus. None of these sites are contiguous to nuclei infected at 4 days, but all are synaptically related to these nuclei. By 7 days postinoculation, no new foci of labeled cells were noted in the brain stem, but labeled neurons were noted in the amygdala, hippocampus, and somatosensory cortex. Neurons in both the amygdala and hippocampus receive axonal projections from the locus coeruleus. On the basis of these findings, we conclude that the spread of HSV in the CNS after intracameral inoculation is not diffuse but is restricted to a small number of noncontiguous foci in the brain stem and cortex which become infected in a sequential fashion. Since these regions are synaptically related, the principal route of the spread of HSV in the CNS after ocular infection appears to be along axons, presumably via axonal transport rather than by local spread.
Full text
PDF
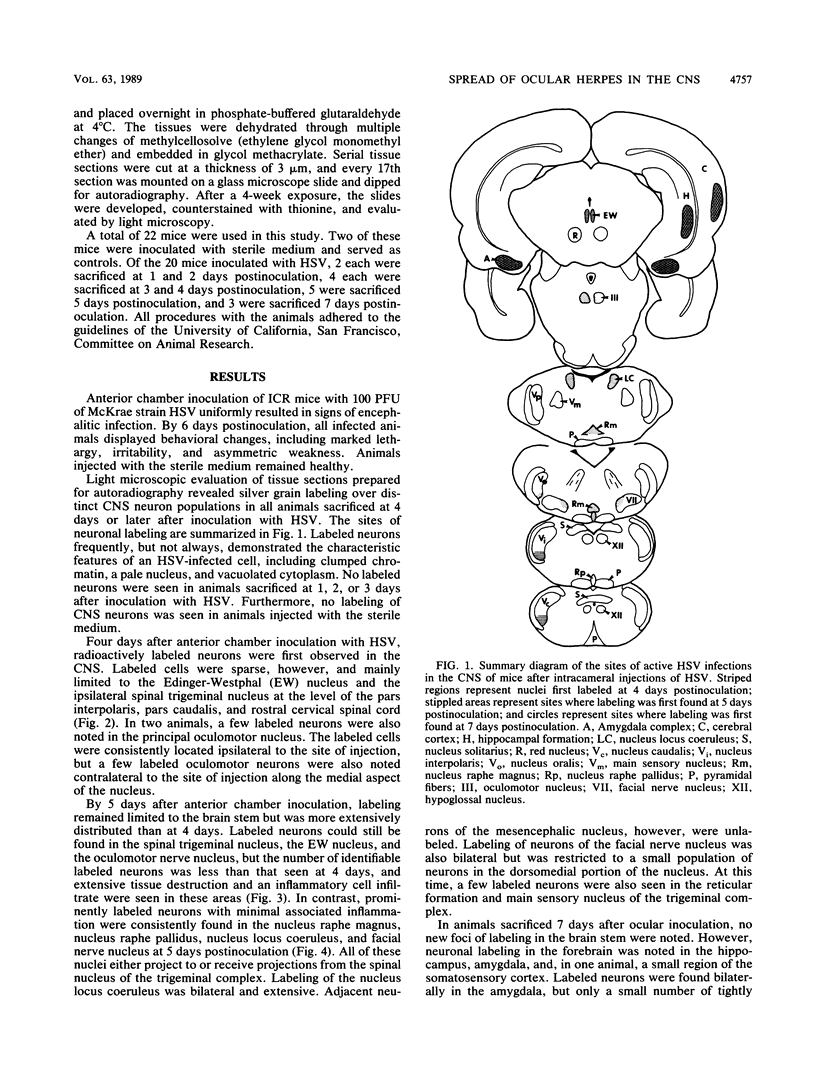
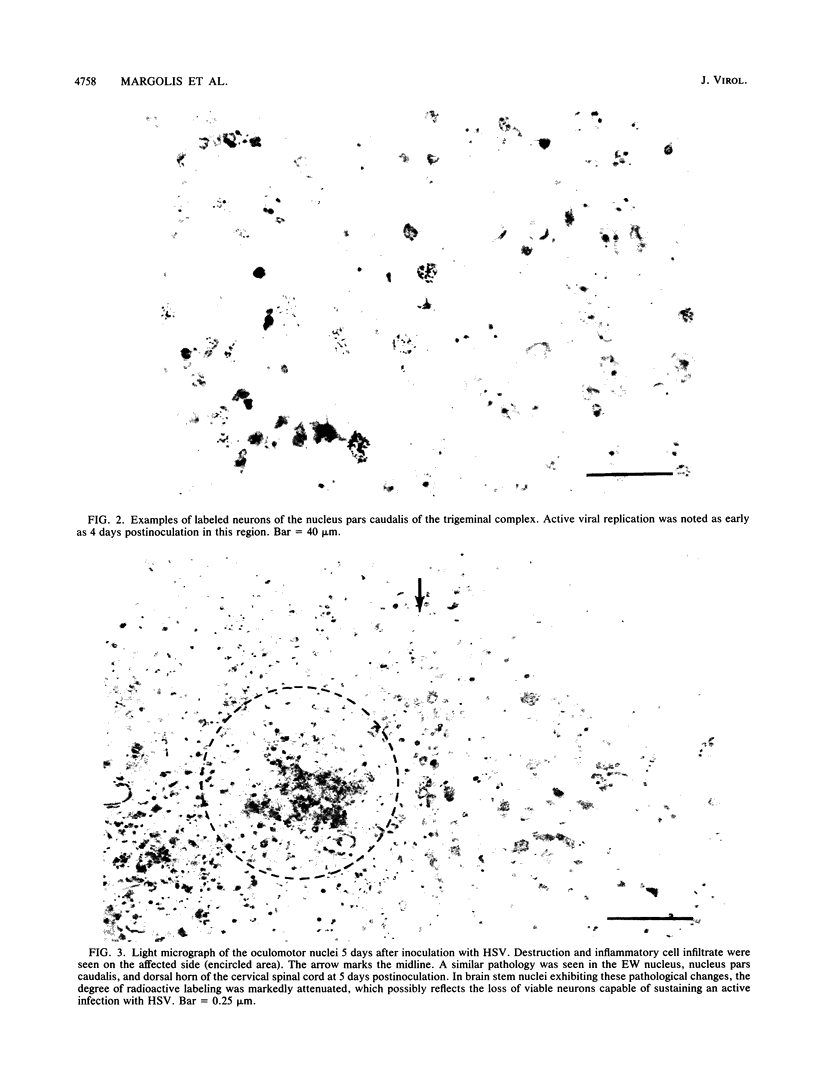



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baringer J. R., Griffith J. F. Experimental herpes simplex encephalitis: early neuropathologic changes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Jan;29(1):89–104. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197001000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basbaum A. I., Clanton C. H., Fields H. L. Three bulbospinal pathways from the rostral medulla of the cat: an autoradiographic study of pain modulating systems. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 15;178(2):209–224. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleator G. M., Klapper P. E., Sharma H., Longson M. A rat model of herpes encephalitis with special reference to its potential for the development of diagnostic brain imaging. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Jun;79(1-2):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatly A. M., Spivack J. G., Lavi E., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts in peripheral and central nervous system tissues of mice map to similar regions of the viral genome. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):749–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.749-756.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockfield S., Gobel S. An anatomical demonstration of projections to the medullary dorsal horn (trigeminal nucleus caudalis) from rostral trigeminal nuclei and the contralateral caudal medulla. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 9;252(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger R. J., Benevento L. A. A horseradish peroxidase study of the innervation of the internal structures of the eye. Evidence for a direct pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980 Jun;19(6):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. E., Halaris A. E., McIlhany M., Moore R. Y. Ascending projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. I. Axonal transport in central noradrenaline neurons. Brain Res. 1977 May 20;127(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. E., Moore R. Y. Ascending projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. II. Autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1977 May 20;127(1):25–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. E., Yang T. Z. The efferent projections from the reticular formation and the locus coeruleus studied by anterograde and retrograde axonal transport in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Dec 1;242(1):56–92. doi: 10.1002/cne.902420105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knotts F. B., Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic encephalitis in mice after ophthalmic inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):16–27. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Nennesmo L., Persson L., Lycke E. Neuron to neuron transmission of herpes simplex virus. Transport of virus from skin to brainstem nuclei. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Apr;54(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera P., Dolivo M., Coulon P., Flamand A. Pathways of the early propagation of virulent and avirulent rabies strains from the eye to the brain. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):158–162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.158-162.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marfurt C. F., Del Toro D. R. Corneal sensory pathway in the rat: a horseradish peroxidase tracing study. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jul 15;261(3):450–459. doi: 10.1002/cne.902610309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis T., Togni B., LaVail J., Dawson C. R. Identifying HSV infected neurons after ocular inoculation. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Jan;6(1):119–126. doi: 10.3109/02713688709020078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin X., Dolivo M. Neuronal and transneuronal tracing in the trigeminal system of the rat using the herpes virus suis. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 29;273(2):253–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90850-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Openshaw H., Ellis W. G. Herpes simplex virus infection of motor neurons: hypoglossal model. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):409–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.409-413.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parelman J. J., Fay M. T., Burde R. M. Confirmatory evidence for a direct parasympathetic pathway to internal eye structures. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1984;82:371–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Rubenstein R., Price R. W., Fox J. J., Watanabe K. A. Diagnostic imaging of herpes simplex virus encephalitis using a radiolabeled antiviral drug: autoradiographic assessment in an animal model. Ann Neurol. 1984 Jun;15(6):548–558. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamovits T. L., Miller N. R., Burde R. M. Intracranial oculomotor nerve paresis with anisocoria and pupillary parasympathetic hypersensitivity. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987 Oct 15;104(4):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(87)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. T., Apkarian A. V., Hodge C. J., Jr Sources of the catecholaminergic innervation of the trigeminal nucleus caudalis in cat. Exp Neurol. 1985 Oct;90(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(85)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroop W. G., Rock D. L., Fraser N. W. Localization of herpes simplex virus in the trigeminal and olfactory systems of the mouse central nervous system during acute and latent infections by in situ hybridization. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):27–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A. H., Esiri M. M. Herpes simplex encephalitis. Immunohistological demonstration of spread of virus via olfactory pathways in mice. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Aug-Sep;60(3):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini G., Kuypers H. G., Simmons A. Retrograde transneuronal transfer of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV 1) from motoneurones. Brain Res. 1987 Oct 6;422(2):242–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90931-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini G., Kuypers H. G., Strick P. L. Transneuronal transfer of herpes virus from peripheral nerves to cortex and brainstem. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):89–91. doi: 10.1126/science.2536188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westheimer G., Blair S. M. The parasympathetic pathways to internal eye muscles. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973 Mar;12(3):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]