Abstract
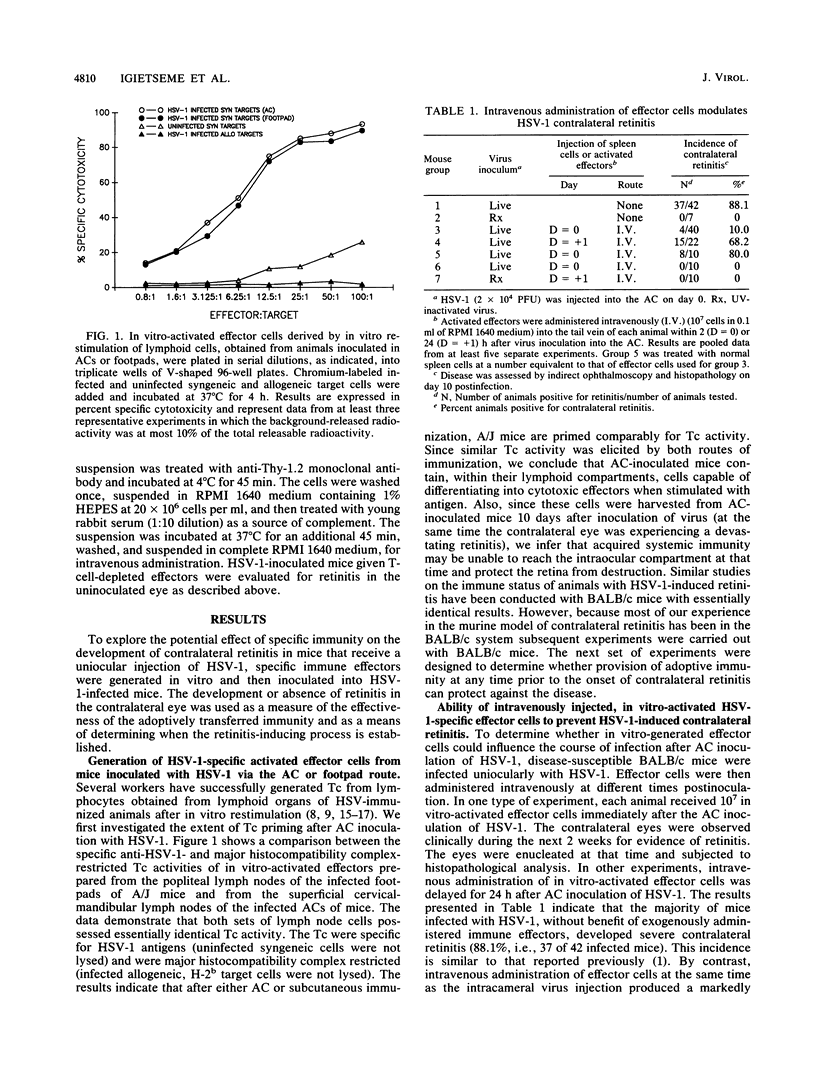
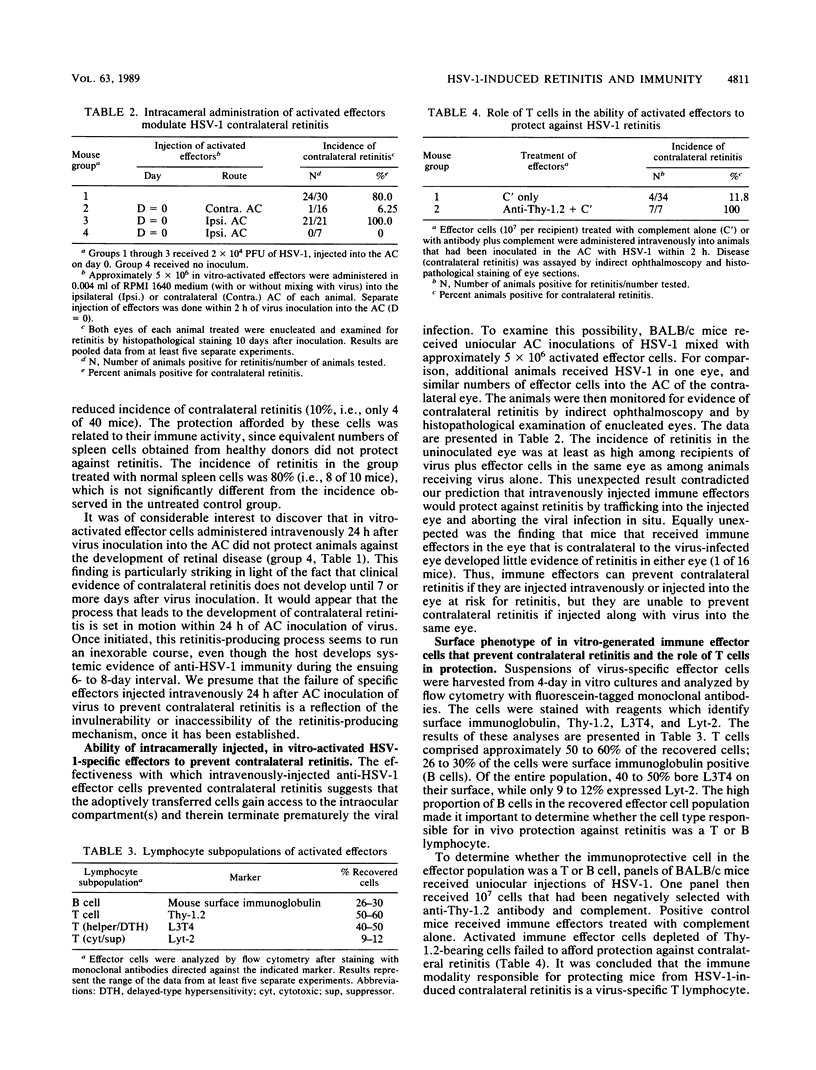
A form of acute retinal necrosis occurred in the contralateral eyes of susceptible mice 1 week after each received a uniocular injection of live herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) in the anterior chamber. Although these mice did not develop systemic delayed hypersensitivity to virus antigens, their sera contained virus-specific antibodies at the time contralateral retinitis occurred. These findings suggest that systemic immunity might not be able to protect against contralateral retinitis. To explore this possibility further, we examined lymph nodes and spleens of intraocularly infected mice to determine whether their lymphoid tissues contained primed HSV-1-specific cytotoxic T cells. Virus-specific cytotoxic T cells were readily identified in these mice. We wondered why successful immune priming did not confer protection against HSV-1 retinitis. We examined this issue by evaluating the capacity of in vitro-generated, HSV-1-specific effector T cells to prevent retinitis by infusing these cells by various routes and at various times into mice that received an intracameral injection of HSV-1. The results revealed that virus-specific effector cells could prevent contralateral retinitis if injected intravenously or into the anterior chamber of the contralateral eye at the same time that virus was injected into one eye. However, the effector cells failed to prevent retinitis if they were injected into the same eye that received HSV-1 or if their intravenous administration was delayed until 24 h after the HSV-1 injection into the eye. We concluded that immune T cells can protect against contralateral retinal necrosis caused by uniocular injection of HSV-1 into the anterior chamber but only if they are administered during the first 24 h after virus infection. We propose that a retinitis-inducing process is set in motion during this early time interval postinfection. Once the process has been initiated and established, it is no longer susceptible to immune intervention. It would appear that mice that are susceptible to contralateral retinitis fail to mobilize a protective response quickly enough to ward off the establishment of the retinitis-inducing process and its disastrous eventuality.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton S. S., Streilein J. W. Two waves of virus following anterior chamber inoculation of HSV-1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Mar;28(3):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau R. H., Jennings S. R. Modulation of acute and latent herpes simplex virus infection in C57BL/6 mice by adoptive transfer of immune lymphocytes with cytolytic activity. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1480–1484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1480-1484.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., Mauel J., Cerottini J. C., Chapuis B. Quantitative assay of the lytic action of immune lymphoid cells on 51-Cr-labelled allogeneic target cells in vitro; inhibition by isoantibody and by drugs. Immunology. 1968 Feb;14(2):181–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins S. W., Gonzalez A., Atherton S. S. Herpes simplex retinitis in the mouse. Clinicopathologic correlations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Jul;30(7):1485–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt B. M., Hill J. M. T lymphocytes in the trigeminal ganglia of rabbits during corneal HSV infection. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Nov;29(11):1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Taylor W., Mitchison N. A., Simpson E. MHC matching shows that at least two T-cell subsets determine resistance to HSV. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):66–68. doi: 10.1038/277067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty D., Cousins S. W., Atherton S. S. HSV-1 retinitis and delayed hypersensitivity in DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Dec;28(12):1994–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen H. S., Russell R. G., Rouse B. T. Recovery from lethal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection is mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):197–204. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.197-204.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen S. C., Andersen H. K. Recovery of mice from herpes simplex virus type 2 hepatitis: adoptive transfer of recovery with immune spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):743–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.743-749.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi S., Hayashida I., Higa K., Wada T., Mori R. Role of Lyt-1 positive immune T cells in recovery from herpes simplex virus infection in mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(4):359–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Ashford N. P. Split T-cell tolerance in herpes simplex virus-infected mice and its implication for anti-viral immunity. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):761–767. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Phelan J., Wildy P. Cell-mediated immunity in herpes simplex virus-infected mice: H-2 mapping of the delayed-type hypersensitivity response and the antiviral T cell response. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1260–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E. Role for cell-mediated immunity in the resistance of mice to subcutaneous herpes simplex virus infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.166-172.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Jung H., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. The role of T cells in anti-herpes simplex virus immunity. I. Induction of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Horohov D. W. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes in herpesvirus infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;6(1-2):35–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid D. S., Rouse B. T. Cellular interactions in the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to herpes simplex virus antigens: differential antigen activation requirements for the helper T lymphocyte and cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Omata Y., Schneweis K. E. Protection of mice from fatal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by adoptive transfer of cloned virus-specific and H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum J. A., McCulley J. P., Niederkorn J. Y., Streilein J. W. Ocular disease induced in mice by anterior chamber inoculation of herpes simplex virus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984 Sep;25(9):1065–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum J. A., Niederkorn J. Y., McCulley J. P., Streilein J. W. Intracameral inoculation of herpes simplex virus type I induces anterior chamber associated immune deviation. Curr Eye Res. 1982;2(10):691–697. doi: 10.3109/02713688209019998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


