Abstract
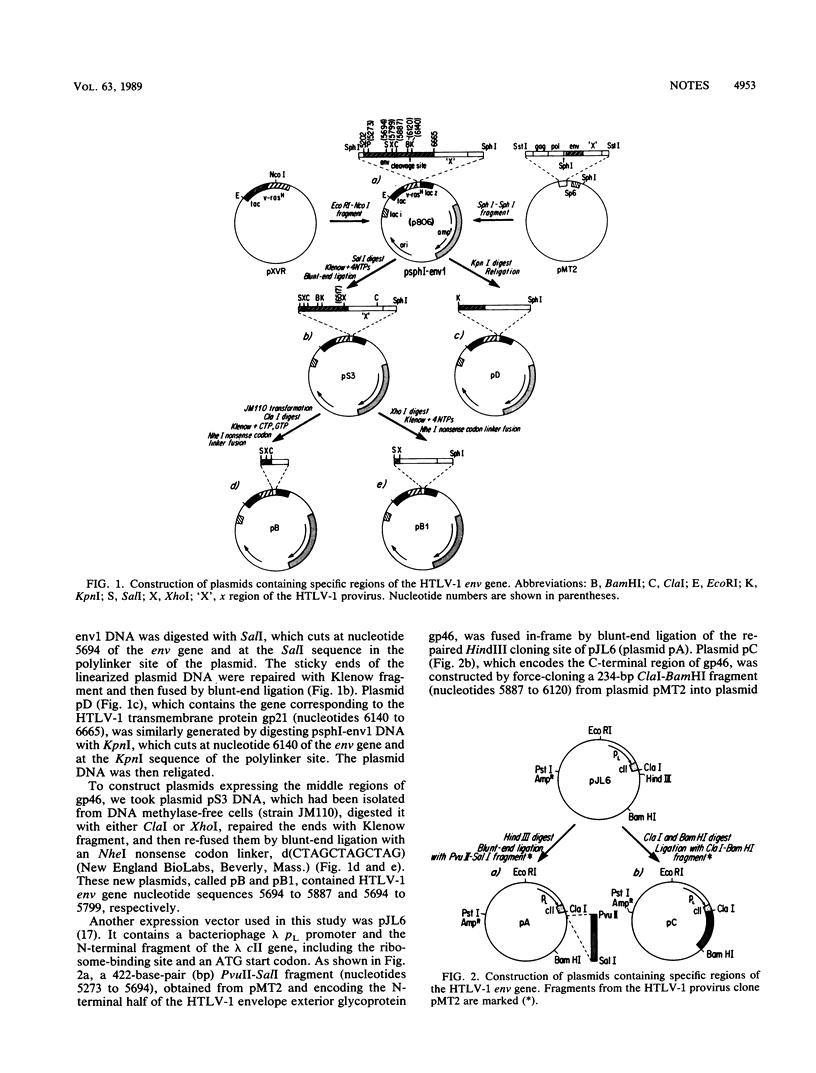
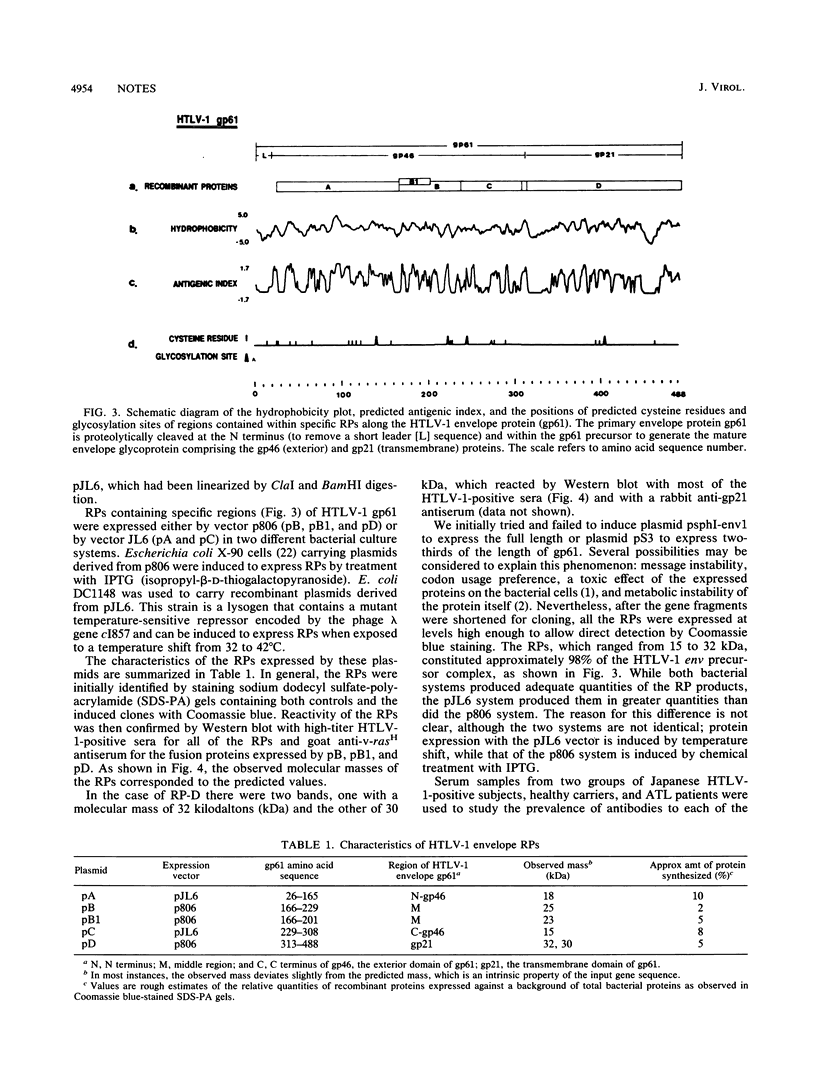
The primary protein product of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) env gene, gp61, is cleaved to produce both the exterior (gp46) and the transmembrane (gp21) portions of the HTLV-1 envelope protein. To compare the reactivity with human antibodies of different regions of this gp61 protein, five plasmids (A, B, B1, C, and D) were constructed to express recombinant proteins (RPs) in Escherichia coli. RP-A, RP-B, RP-B1, and RP-C contain amino acid residues 26 to 165, 166 to 229, 166 to 201, and 229 to 308, respectively, of the exterior envelope protein gp46. Serum samples from HTLV-1-seropositive subjects were assayed for reactivity with these RPs by Western immunoblotting. The percentages of positive reactivity with each of the RPs were as follows: 18.9% (23 of 122) for RP-A, 89.6% (112 of 125) for RP-B, 70.2% (85 of 121) for RP-B1, and 92.9% (117 of 126) for RP-C. These results indicate that the C-terminal half of gp46 (RP-B plus RP-C) can detect 97.6% (123 of 126) of positive samples, while the N-terminal half of gp46 (RP-A) can only detect 18.9% of the HTLV-1-positive sera (P less than 0.005). Furthermore, RP-A, -B, and -C, which together span the entire length of gp46 except the first five amino acids at the N terminus and the last four amino acids at the C- terminus, detected 99.2% (125 of 126) of the HTLV-1-positive subjects. In contrast, RP-D, which contains the HTLV-1 transmembrane envelope protein gp21 minus the first amino acid at the N terminus, had a lower rate of antibody reactivity at 73.7% (84 of 114) (P less than 0.005). The difference in seropositive rates for RP-D between HTLV-1 carriers (55.6%) and adult T-cell leukemia patients (85.5%) is statistically significant (P less than 0.01). This study therefore indicates that the C-terminal half of gp46, especially the amino acid sequence from 200 to 308, contains the most reactive epitopes of the HTLV-1 gp61 envelope glycoprotein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Bröker M., Wurm F. Expression of Herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C antigens in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barin F., M'Boup S., Denis F., Kanki P., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Essex M. Serological evidence for virus related to simian T-lymphotropic retrovirus III in residents of west Africa. Lancet. 1985 Dec 21;2(8469-70):1387–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P., Nagy K., Weiss R. A. Pseudotypes of human T-cell leukemia virus types 1 and 2: neutralization by patients' sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Gelmann E. P., Reitz M. S., Jr Homology of human T-cell leukaemia virus envelope gene with class I HLA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):60–62. doi: 10.1038/305060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland T. D., Tsai W. P., Kim Y. D., Oroszlan S. Envelope proteins of human T cell leukemia virus type I: characterization by antisera to synthetic peptides and identification of a natural epitope. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2945–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden M., Newman M., Fisher A. G., Mann D. L., Howley P. M., Reitz M. S. Type 1 human T-cell leukemia virus small envelope protein expressed in mouse cells by using a bovine papilloma virus-derived shuttle vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3320–3324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Nagata K., Hanaoka M., Nakai M., Matsumoto T., Kinoshita K. I., Shirakawa S., Miyoshi I. Adult T-cell leukemia: antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki J., Okayama A., Tachibana N., Yokota T., Shishime E., Tsuda K., Mueller N. Comparative diagnostic assay results for detecting antibody to HTLV-I in Japanese blood donor samples: higher positivity rates by particle agglutination assay [corrected]. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(4):340–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Raine C. S., Mingioli E. S., McFarlin D. E. Isolation of an HTLV-1-like retrovirus from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):540–543. doi: 10.1038/331540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Yoshikura H., Hattori S., Seiki M., Yoshida M. Envelope proteins of human T-cell leukemia virus: expression in Escherichia coli and its application to studies of env gene functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6202–6206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Z., Chou M. J., Matsuda M., Huang J. H., Chen Y. M., Redfield R., Mayer K., Essex M., Lee T. H. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 has an additional coding sequence in the central region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi I., Kubonishi I., Yoshimoto S., Akagi T., Ohtsuki Y., Shiraishi Y., Nagata K., Hinuma Y. Type C virus particles in a cord T-cell line derived by co-cultivating normal human cord leukocytes and human leukaemic T cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):770–771. doi: 10.1038/294770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Usuku K., Izumo S., Ijichi N., Amitani H., Igata A., Matsumoto M., Tara M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986 May 3;1(8488):1031–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Schley C., Mahoney M., Harlow E., Schaffhausen B. S., Roberts T. M. Polyomavirus small t antigen: overproduction in bacteria, purification, and utilization for monoclonal and polyclonal antibody production. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1075–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1075-1084.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarin P. S., Robert-Gurroff M., Kalyanaraman V. S., Mann D., Minowada J., Gallo R. C. Isolation and transmission of human retrovirus (human t-cell leukemia virus). Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):856–859. doi: 10.1126/science.6600519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel K. P., Lautenberger J. A., Jorcyk C. L., Josephs S., Wong-Staal F., Papas T. S. Diagnostic potential for human malignancies of bacterially produced HTLV-I envelope protein. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1094–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.6208612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Lapis P., Vande Woude G. F., Papas T. High-level expression vectors to synthesize unfused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;42(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H., Tochikura T., Sato T., Konno T., Hirayoshi K., Seki M., Ito Y., Hatanaka M., Hinuma Y., Sugimoto M. Effect of the recombinant vaccinia viruses that express HTLV-I envelope gene on HTLV-I infection. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3379–3384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Lawton T., Knall C., Karr R. W., Berman P., Gregory T., Reinherz E. L. Analysis of host-virus interactions in AIDS with anti-gp120 T cell clones: effect of HIV sequence variation and a mechanism for CD4+ cell depletion. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Seiki M., Yamaguchi K., Takatsuki K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2534–2537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



